Abstract
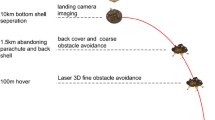
The “Zhurong” Mars rover successfully landed on the surface of Mars on May 22, 2021, and began its inspection and exploration. Currently, it has traveled 1921 m and achieved a series of important scientific discoveries. Due to objective difficulties such as harsh terrain conditions, insufficient energy, and limited communication, the “Zhurong” Mars rover adopts a collaborative control mode of “semi intelligent on board autonomous + ground teleoperation”. Computer vision technology is the key core technology supporting the collaborative control of the rover. In the enter descent landing stage and Mars surface roving, computer vision technology has broken through key technologies, such as rapid localization of the lander, terrain analysis of landing areas, three-dimensional terrain reconstruction, terrain classification, navigation and positioning, path planning, and simulation verification, solved the problem of long-term efficient mobile technology of the rover, and significantly expanded the detection range of the Mars rover, robustly guaranteeing the efficient and stable inspection and long-term survival of the Mars rover. This paper elaborates on the aforementioned technologies and their special on-orbit applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, J.X., **ng, Y., Li, Z.P., et al.: Autonomous environment perception and obstacle avoidance technologies of Zhurong Mars rover (in Chinese). Sci. Sin. Tech. 2022(52), 1186–1197 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1360/SST-2022-0045
Wu, X., Liu, Y., Zhang, C., et al.: Geological characteristics of China’s Tianwen-1 landing site at Utopia Planitia, Mars. Icarus 370, 114657 (2021)
Zhao, J., **ao, Z., Huang, J., et al.: Geological characteristics and targets of high scientific interest in the Zhurong landing region on Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 48, e94903 (2021)
Zhang, R.Q, Geng, Y., Sun, Z.Z., et al.: Technical innovation of the Tianwen-1 mission. Acta Aeronaut. et Astronaut. Sinica 43, 326689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.26689
Liu, J.J., Li, C.L., Zhang, R.Q., et al.: Geomorphic contexts and science focus of the Zhurong landing site on Mars. Nat. Astron. 6, 65–71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-021-01519-5
Ding, L., Zhou, R.Y., Yu, T.Y., et al.: Surface characteristics of the Zhurong Mars rover traverse at Utopia Planitia. Nat. Geosci. 15, 171–176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-022-00905-6
Qin, X.G, et al.: Modern water at low latitudes on Mars: potential evidence from dune surfaces. Sci. Adv. 9, eadd8868 (2023)
Sun, Z.Z., Chen, B.C., Jia, Y., et al.: The Tianwen-1 roving exploration technology for the Martian surface (in Chinese). Sci. Sin. Tech. 2022(52), 214–225 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1360/SST-2021-0487
Zhang, H., et al.: Teleoperation technology of Zhurong Mars rover (in Chinese). J. Deep Space Explor. 8(6), 582–591 (2021)
Chhaniyara, S., et al.: Terrain trafficability analysis and soil mechanical property identification for planetary rovers: a survey. J. Terramech. 49(2), 115–128 (2012)
Haberle, R.M., Leovy, C.B., Pollack, J.B.: Some effects of global dust storms on the atmospheric circulation of Mars. ICurr Alzheimer Resus 1982(50), 322–367 (1982)
Montabone, L., Forget, F., Millour, E., et al.: Eight-year climatology of dust optical depth on Mars. ICurr. Alzheimer Resus 2015(251), 65–95 (2015)
Jia, Y., et al.: Overview on development of planetary rover technology (in Chinese). J. Deep Space Explor. 7(5), 419–427 (2020)
He, T.: Research on mission planning method of Mars rover under complex constraints. JiLin University China (2022)
**ng, Y., et al.: Development of autonomous sensing and control technology for extraterrestrial mobile exploration unmanned systems (in Chinese). Aerosp. Control Appl. 47(6), 01–08 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579
Pan, D., Chen, Z., Yuan, B.F., et al.: Sinkage mechanism and extrication strategy of Mars rover (in Chinese). ROBOT 44(1), 2–8 (2022). https://doi.org/10.13973/j.cnki.robot.210258
Wan, W.H., et al.: Visual localization of the Tianwen-1 lander using orbital, descent and rover images. Remote Sens. 13(17), 3439 (2021)
Yan, Y.Z., Zhang, J.L., Qi, C., et al.: Fast and precise localization of Tianwen-1 Mars rover landing site (in Chinese). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022(67), 204–211 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1360/TB-2021-0541
Wang, J., et al.: High precision localization of Zhurong rover based on multi-source images (in Chinese). J. Deep Space Explor. 9(1), 62–71 (2022)
Ma, Y.Q., Peng, S., Zhang, J.L., et al.: Precise visual localization and terrain reconstruction for China’s Zhurong Mars rover on orbit (in Chinese). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022(67), 2790–2801 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1360/TB-2021-1273
Ma, Y.Q., et al.: Prediction of terrain occlusion in Chang’e-4 mission. Measurement 152, 107368 (2020)
Gu, M.: Mars environment simulation technology (in Chinese). Equipment Environ. Eng. 18(9), 35–42 (2021)
Zhang, T.Y.: Research on slip behavior of mars rover for on-orbit application. JiLin University China (2022)
Cheng, Z.Q., et al.: Automatic classification method for mars surface terrain based on deep learning. In: China Engineering Science and Technology Forum: Deep Space Exploration Science and Technology and Applications, 2021, Shenzhen (2021)
Leger, P.C., et al.: Mars exploration rover surface operations: driving spirit at Gusev crater. In: 2005 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, vol. 2, pp. 1815-1822. IEEE (2005)
Liu, Z.Q., et al.: A global database and statistical analyses of (4) vesta craters. Icarus 311, 242–257 (2018)
Jiang, C.S., et al.: Initial results of the meteorological data from the first 325 sols of the Tianwen-1 mission. Sci. Rep. 13, 3325 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-30513-2
Zhang, J.Q., Pan, L., Wang, S.G.: Photogrammetry (in Chinese). 2nd ed., pp. 54–72. Wuhan University Press, Wuhan (2009)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Wang, Y.X., Wan, W.H., Gou, S., et al.: Vision based decision support for rover path planning in the Chang’e-4 mission. Remote Sens. 12(4), 624 (2020)
Peng, S., Jia, Y.: Improved A* algorithm in global path planning of lunar rover (in Chinese). Spacecraft Eng. 19(4), 80–85 (2010)
http://www.xinhuanet.com/tech/20230522/aa1c66d3c126490c9bdd8ae290ac5013/c.html
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 41771488).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, J. et al. (2023). Application of Computer Vision Technology in Collaborative Control of the “Zhurong” Mars Rover. In: Yongtian, W., Lifang, W. (eds) Image and Graphics Technologies and Applications. IGTA 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1910. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-7549-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-7549-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-7548-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-7549-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)