Abstract
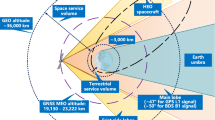
Global Navigation Satellite system (GNSS) is initially designed to provide services to objects on the earth surfaces, or in the earth-orbits with altitude below 3000 km. However, previous researches show that GNSS receivers mounted on GEO satellites can receive GNSS signals and generate positioning and navigation results as well. Considering that in some harsh situations, such as bad observation geometry, weak signal acquisition, etc., the on-board GNSS receivers can only transfer pseudo-range data to GEO satellites, this paper proposed an autonomous navigation method in which the information from GNSS receiver, optical attitude sensors, and inter-satellite links are fused together: at first, the extended state equation and measurement equation of a GEO satellite with optical sensor’s errors are deduced; then, an extended Kalman filter is designed to evaluate and compensate optical sensor’s errors via constructed earth-centered vector bias; later, a sequential correction is carried out using inter-satellite link measurements; finally, the performance of proposed method is analyzed through Monte-Carlo simulation. It shows that the average distance and velocity evaluation errors of proposed method are around 0.2 km and 0.05 m/s individually; the performance can meet the requirements of survivability of a class of high-orbit, long-life and high-value satellites.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jun, X., **, W.: Development and contribution of Beidou navigation satellite attitude and control technologies. Aerosp. Control Appl. 47(5) (2021)
Wei, W., Chaoyang, X., Wenshuai, F.: State of the art and perspecitves of autonomous navigation technology. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica 42(11) (2021)
Jiansong, C.: Research on attitude sensor based satellite autonomous navigation and error calibration methods. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree in Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 10. (Ch) (2019)
Dayi, W., Bowen, H., Jiongqi, W. etc.: State estimation method for spacecraft autonomous navigation: review. Acta Aeronautica ET Astronautica Sinica 42(4) (2021)
Jianhua, Z., Bo, X.: Constellation Precise Orbit Determination and Autonomous Orbit Determination: Theory and Method. Science Press, Bei**g (2015), 6
Kewen, L., **nlong, W., Liangliang, S.: Availability analysis of GNSS signal in high orbit. Aero Weaponry 28(1) (2021)
Meng, W., Tao, S., Dun, W.: Development of GNSS technology for high earth orbit spacecraft. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica 49(9), P1158-1167 (2020)
Jiaxin, C., **nlong, W., Nengjie, Y.: etc. modeling and intensity analysis of GNSS signal link for high orbit spacecraft. J. Bei**g Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 44(7) (2018)
Weisong, J., Lianlian, Z., Luming, L. etc.: Design of Beidou-3 satellite avionics system. Astronaut. Syst. Eng. Technol. 4(6) (2020)
Shancheng, T.: Satellite Attitude Dynamics and Control. China Aerospace Press, Bei**g (2005)
Simon, D.: Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches. Wiley (2006)
Yang, G., Meng, W., Lei, L. etc.: GNSS receiver techniques based on high earth orbit spacecraft. Chinese Space Sci. Technol. 37(3), 101–109 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Aerospace Information Research Institute
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, L., Chang, J., Guo, J. (2024). A Multi-source Data Fusion Navigation Method of Spacecraft with Limited GNSS Signals. In: Yang, C., **e, J. (eds) China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC 2024) Proceedings. CSNC 2024. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1092. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6928-9_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6928-9_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-6927-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-6928-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)