Abstract
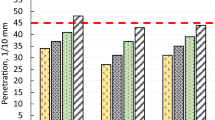
Bituminous binders encounter different distress during the life cycle of flexible pavement construction. Fatigue cracking and rut resistance are the most important characteristics of the binder. Addition of environmental-friendly modifiers/additives into the binder improves the rheological properties of bituminous binders. In this study, the effect of waste engine oil (WEO) on rheological characteristics of plain bitumen (VG30) as an additive was assessed through laboratory investigations. Also rutting and fatigue performance characteristics of the modified bitumen were investigated using Dynamic Shear Rheometer. From the Multiple Stress Creep Recovery test, the percentage recovery and Non-recovery creep compliance at different dosages of additive were evaluated. Linear Amplitude Sweep to determine \({\text{G}}\, * \,/{\text{sin}}\delta\) and \({\text{G}}\, * \,{\text{sin}}\delta\) indices for the bio-additive modified bitumen containing different percentages of WEO. The chemical properties of waste engine oil were identified by conducting Fourier Transform Infra-Red Spectroscopy. Overall it was found that WEO can be used as a softening agent to the aged bituminous binder.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu S, Meng H, Xu Y, Zhou S (2018) Evaluation of rheological characteristics of asphalt modified with waste engine oil (WEO). Pet Sci Technol 36(6):475–480
Jia X, Huang B, Bowers BF, Zhao S (2018) Infrared spectra and rheological properties of asphalt cement containing waste engine oil residues. Constr Build Mater 50:683–691
Hesp SA, Shurvell HF (2010) X-ray fluorescence detection of waste engine oil residue in asphalt and its effect on cracking in service. Int J Pavement Eng 11(6):541–553
Abu ER, Ossmaz ME, Farouq R, Abd-Elfatah M (2015) Used motor oil treatment: turning waste oil into valuable products. Int J Chem Biochem Sci (7):57–67
Abro R, Chen X, Harijan K, Dhakan ZA, Ammar M (2013) A comparative study of recycling of used engine oil using extraction by composite solvent, single solvent, and acid, Hindawi Limited. ISRN Chem Eng ID 952589, (7):1–5
Li H, Dong B, Wang W, Zhao G, Guo P, Ma Q (2019) Effect of waste engine oil and waste cooking oil on performance improvement of aged asphalt, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute. Appl Sci 9:1767
ASTM D 4402 (2006) Standard Test Method for Viscosity Determination of Asphalt at Elevated Temperatures Using a Rotational Viscometer, U.S. Department of Defence, ASTM International
AASHTO TP101 (2014) Standard Method of Test for Estimating Fatigue Resistance of Asphalt Binders Using the Linear Amplitude Sweep (LAS), American Association of State Highways and Transportation Officials
Fu H, **e L, Dou D, Li L, Yu M, Yao S (2007) Storage stability and compatibility of asphalt binder modified by SBS graft copolymer. Constr Build Mater 21:1528–1533
Patel K, Prasad S (2020) Characterization of waste engine oil (WEO) pyrolytic oil and diesel blended oil: fuel properties and compositional analysis. Mater Today: Proc 33(8):4933–4936
AASTHO T315 (2012) Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR), American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials
AASHTO T350–14 (2014) Standard Method of Testing for Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test of Asphalt Binder Using Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR), American Association of State Highways and Transportation Officials
Bureau of Indian Standards: Methods for Testing Tar and Bituminous materials. Standard IS-1201-1978 to IS-1220-1978. New Delhi
Wang H, Derewecki K (2013) Rheological properties of asphalt binder partially substituted with wood lignin. In: Proceedings of the 2013 airfield and highway pavement conference. Los Angeles, CA, USA, pp 977–986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Srikanth, T., Amal, R., Sivakumar, M. (2024). Rheological Characteristics of Waste Engine Oil-Modified Bituminous Binder. In: Singh, D., Maji, A., Karmarkar, O., Gupta, M., Velaga, N.R., Debbarma, S. (eds) Transportation Research. TPMDC 2022. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 434. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6090-3_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6090-3_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-6089-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-6090-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)