Abstract
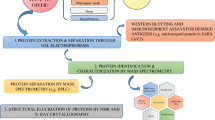
RNA viruses that undergo continuous evolution can cause infectious diseases, leading to considerable harm to public health, individual well-being, and economic growth. The virus transmission can be through human-to-human, animals to humans and insects or vectors. The viruses involved are Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, human immunodeficiency virus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Crimean Congo virus, flaviviruses such as zika and dengue Virus. The viral protein involves with host organism proteins plays a significant part in pathogenesis and infection by avoiding the host defense mechanisms. As proteins have a huge range of functions, proteomics approaches can offer significant prudence in analyzing disease pathogenesis, etiology and discovery of potential antiretroviral pharmaceutical drug target sites and improving diagnostics. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, liquid chromatography, Isotope-coded affinity tag labeling-based protein profiling and Mass spectrometry are utilized for defining the structural arrangement of viral pathogens, virus and host protein interactions, conduct sensitive, high-throughput analyses of them enormously and the development of therapy strategies and improving the diagnostics. This approach also made considerable contributions to the finding of signaling cascades, the information of disease mechanisms regarding proteome changes and posttranslational modifications at some point in infection, the unfolding of viral–host protein interactions and its novel mechanisms against viral proteins. This chapter is centered on describing the usefulness of proteomics techniques that provides large set of information regarding protein interaction and new drug target could be developed for infectious disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson NG, Anderson NL (1996) Twenty years of two-dimensional electrophoresis: past, present and future. Electrophoresis 17(3):443–453
Appelberg S, Gupta S, Svensson Akusjärvi S, Ambikan AT, Mikaeloff F, Saccon E, Neogi U (2020) Dysregulation in Akt/mTOR/HIF-1 signaling identified by proteo-transcriptomics of SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Emerg Microbes Infect 9(1):1748–1760
Biron DG, Moura H, Marche L, Hughes AL, Thomas F (2005) Towards a new conceptual approach to ‘parasitoproteomics.’ Trends Parasitol 21(4):162–168
Bischoff R, Luider TM (2004) Methodological advances in the discovery of protein and peptide disease markers. J Chromatogr B 803(1):27–40
Canton J, Fehr AR, Fernandez-Delgado R, Gutierrez-Alvarez FJ, Sanchez-Aparicio MT, García-Sastre A, Sola I (2018) MERS-CoV 4b protein interferes with the NF-κB-dependent innate immune response during infection. PLoS Pathog 14(1):e1006838
Cifani P, Kentsis A (2017) High sensitivity quantitative proteomics using automated multidimensional nano-flow chromatography and accumulated ion monitoring on quadrupole-Orbitrap-linear ion trap mass spectrometer. Mol Cell Proteomics 16(11):2006–2016
Cloeckaert A, Kuchler K (2020) Grand challenges in infectious diseases: are we prepared for worst-case scenarios? Front Microbiol 11:613383
Cohen J, Powderly WG, Opal SM (2016) Infectious diseases E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences
Coombs KM (2020) Update on Proteomic approaches to uncovering virus-induced protein alterations and virus–host protein interactions during the progression of viral infection. Expert Rev Proteomics 17(7–8):513–532
Evangelou A, Gortzak-Uzan L, Jurisica I, Kislinger T (2007) Mass spectrometry, proteomics, data mining strategies and their applications in infectious disease research. Anti-Infect Agents Med Chem (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Anti-Infective Agents) 6(2):89–105
Excler JL, Saville M, Berkley S, Kim JH (2021) Vaccine development for emerging infectious diseases. Nat Med 27(4):591–600
Farr Zuend C, Tobin NH, Vera T, Kotyrba L, Noël-Romas L, Birse K, Burgener AD (2020) Pregnancy associates with alterations to the host and microbial proteome in vaginal mucosa. Am J Reprod Immunol 83(6):e13235
Figeys D (2004) Combining different ‘omics’ technologies to map and validate protein—protein interactions in humans. Brief Funct Genomics 2(4):357–365
Fraisier C, Rodrigues R, Hai VV, Belghazi M, Bourdon S, Paranhos-Baccala G, Peyrefitte CN (2014) Hepatocyte pathway alterations in response to in vitro Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus infection. Virus Res 179:187–203
Gordon DE, Jang GM, Bouhaddou M, Xu J, Obernier K, White KM, Krogan NJ (2020) A SARS–CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 583(7816):459–468
Greco TM, Cristea IM (2017) Proteomics tracing the footsteps of infectious disease. Mol Cell Proteomics 16(4):S5–S14
Hafirassou ML, Meertens L, Umaña-Diaz C, Labeau A, Dejarnac O, Bonnet-Madin L, Amara A (2017) A global interactome map of the dengue virus NS1 identifies virus restriction and dependency host factors. Cell Rep 21(13):3900–3913
Han L, Ao X, Lin S, Guan S, Zheng L, Han X, Ye H (2019) Quantitative comparative proteomics reveal biomarkers for dengue disease severity. Front Microbiol 10:2836
He Z, Yang C, Yang C, Qi RZ, Po-Ming Tam J, Yu W (2010) Optimization-based peptide mass fingerprinting for protein mixture identification. J Comput Biol 17(3):221–235
Holbrook MR (2017) Historical perspectives on flavivirus research. Viruses 9(5):97
Jia HP, Look DC, Shi L, Hickey M, Pewe L, Netland J, McCray Jr, PB (2005) ACE2 receptor expression and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection depend on differentiation of human airway epithelia. J Virol 79(23):14614–146z21
Kaddour H, Lyu Y, Welch JL, Paromov V, Mandape SN, Sakhare SS, Okeoma CM (2020) Proteomics profiling of autologous blood and semen exosomes from HIV-infected and uninfected individuals reveals compositional and functional variabilities. Mol Cell Proteomics 19(1):78–100
Karr TL (2008) Application of proteomics to ecology and population biology. Heredity 100(2):200–206
Klepac P, Funk S, Hollingsworth TD, Metcalf CJE, Hampson K (2015) Six challenges in the eradication of infectious diseases. Epidemics 10:97–101
Krokhin O, Li Y, Andonov A, Feldmann H, Flick R, Jones S, Standing KG (2003) Mass spectrometric characterization of proteins from the SARS Virus: a preliminary report* S. Mol Cell Proteomics 2(5):346–356
Landi C, Santinelli L, Bianchi L, Shaba E, Ceccarelli G, Cavallari EN, d’Ettorre G (2020) Cognitive impairment and CSF proteome modification after oral bacteriotherapy in HIV patients. J Neurovirol 26:95–106
Lauber WM, Carroll JA, Dufield DR, Kiesel JR, Radabaugh MR, Malone JP (2001) Mass spectrometry compatibility of two-dimensional gel protein stains. Electrophoresis 22(5):906–918
Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V (2020) Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS–CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol 5(4):562–569
Li J, Guo M, Tian X, Wang X, Yang X, Wu P, Liang Q (2021) Virus-host interactome and proteomic survey reveal potential virulence factors influencing SARS–CoV-2 pathogenesis. Med 2(1):99–112
Li W, Moore MJ, Vasilieva N, Sui J, Wong SK, Berne MA, Farzan M (2003) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 426(6965):450–454
Lum KK, Cristea IM (2016) Proteomic approaches to uncovering virus–host protein interactions during the progression of viral infection. Expert Rev Proteomics 13(3):325–340
Luo C, Luo H, Zheng S, Gui C, Yue L, Yu C, Jiang H (2004) Nucleocapsid protein of SARS coronavirus tightly binds to human cyclophilin A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321(3):557–565
Malone, R. W., Homan, J., Callahan, M. V., Glasspool-Malone, J., Damodaran, L., Schneider, A. D. B., … & Zika Response Working Group (2016) Zika virus: medical countermeasure development challenges. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10(3):e0004530
Meyerholz DK, Lambertz AM, McCray PB Jr (2016) Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 distribution in the human respiratory tract: implications for the Middle East respiratory syndrome. Am J Pathol 186(1):78–86
Monteil V, Kwon H, Prado P, Hagelkrüys A, Wimmer RA, Stahl M, Penninger JM (2020) Inhibition of SARS–CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2. Cell 181(4):905–913
Morens DM, Fauci AS (2012) Emerging infectious diseases in 2012: 20 years after the institute of medicine report. Mbio 3(6):e00494-e512
Ndao M (2012) Biomarker discovery in serum/plasma using surface enhanced laser desorption ionization time of flight (SELDI–TOF) Mass Spectrometry. SELDI-TOF Mass Spectrom: Methods Protoc 67–79
Neuman BW, Joseph JS, Saikatendu KS, Serrano P, Chatterjee A, Johnson MA, Kuhn P (2008) Proteomics analysis unravels the functional repertoire of coronavirus nonstructural protein 3. J Virol 82(11):5279–5294
Nhi DM, Huy NT, Ohyama K, Kimura D, Lan NTP, Uchida L, Hirayama K (2016) A proteomic approach identifies candidate early biomarkers to predict severe dengue in children. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10(2):e0004435
Nilsson CL, Larsson T, Gustafsson E, Karlsson KA, Davidsson P (2000) Identification of protein vaccine candidates from helicobacter p ylori using a preparative two-dimensional electrophoretic procedure and mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 72(9):2148–2153
Petriz BA, Franco OL (2014) Application of cutting-edge proteomics technologies for elucidating host–bacteria interactions. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 95:1–24
Pfefferle S, Schöpf J, Kögl M, Friedel CC, Müller MA, Carbajo-Lozoya J, von Brunn A (2011) The SARS-coronavirus-host interactome: identification of cyclophilins as target for pan-coronavirus inhibitors. PLoS Pathog 7(10):e1002331
Pierson TC, Diamond MS (2020) The continued threat of emerging flaviviruses. Nat Microbiol 5(6):796–812
Porta M (ed) (2008) A dictionary of epidemiology. Oxford University Press
Rabelo K, Trugilho MR, Costa SM, Pereira BA, Moreira OC, Ferreira AT, Alves AM (2017) The effect of the dengue non-structural 1 protein expression over the HepG2 cell proteins in a proteomic approach. J Proteomics 152:339–354
Raj VS, Mou H, Smits SL, Dekkers DH, Müller MA, Dijkman R, Haagmans BL (2013) Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 495(7440):251–254
Rieder F, Steininger C (2014) Cytomegalovirus vaccine: phase II clinical trial results. Clin Microbiol Infect 20:95–102
Rose RM, Besdine RW (1982) Infectious disease. Health and disease in old age. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 345–368
Saraswathy N, Ramalingam P (2011) Concepts and techniques in genomics and proteomics. Elsevier
Shajahan A, Supekar NT, Gleinich AS, Azadi P (2020) Deducing the N-and O-glycosylation profile of the spike protein of novel coronavirus SARS–CoV-2. Glycobiology 30(12):981–988
Smith SA, Blake TA, Ifa DR, Cooks RG, Ouyang Z (2007) Dual-source mass spectrometer with MALDI-LIT-ESI configuration. J Proteome Res 6(2):837–845
Spengler JR, Bente DA, Bray M, Burt F, Hewson R, Korukluoglu G, Papa A (2018) Second international conference on Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. Antiviral Res 150:137–147
Sperk M, Van Domselaar R, Rodriguez JE, Mikaeloff F, Sá Vinhas B, Saccon E, Neogi U (2020) Utility of proteomics in emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases caused by RNA viruses. J Proteome Res 19(11):4259–4274
Stebbins CE, Galán JE (2001) Structural mimicry in bacterial virulence. Nature 412(6848):701–705
Trinh HV, Grossmann J, Gehrig P, Roschitzki B, Schlapbach R, Greber UF, Hemmi S (2013) iTRAQ-based and label-free proteomics approaches for studies of human adenovirus infections. Int J Proteomics
Viswanathan K, Früh K (2007) Viral proteomics: global evaluation of viruses and their interaction with the host. Expert Rev Proteomics 4(6):815–829
WHO HIV dashboard, 2021 [online database]. https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/strategic-information/hiv-data-and-statistics. Accessed 27 Jan 2023
Wee S, Alli-Shaik A, Kek R, Swa HL, Tien WP, Lim VW, Gunaratne J (2019) Multiplex targeted mass spectrometry assay for one-shot flavivirus diagnosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(14):6754–6759
Wolfe ND, Dunavan CP, Diamond J (2007) Origins of major human infectious diseases. Nature 447(7142):279–283
World Health Organization (2005) Combating emerging infectious diseases in the South-East Asia region (No. SEA-CD-139). WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia
World Health Organization (2023) COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update, edition 125
**ao X, Feng Y, Zhu Z, Dimitrov DS (2011) Identification of a putative Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus entry factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 411(2):253–258
Zicari S, Sessa L, Cotugno N, Ruggiero A, Morrocchi E, Concato C, Palma P (2019) Immune activation, inflammation, and non-AIDS co-morbidities in HIV-infected patients under long-term ART. Viruses 11(3):200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Talele, D., Talele, C. (2023). Proteomics Novel Prospects in Target Therapy for Infectious Diseases. In: Kulkarni, S., Haghi, A.K., Manwatkar, S. (eds) Novel Technologies in Biosystems, Biomedical & Drug Delivery. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-5281-6_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-5281-6_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-5280-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-5281-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)