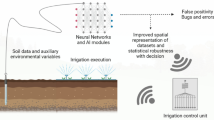
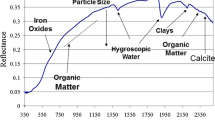
Abstract
Soil management is important for sustainable agriculture, playing a vital role in food production and maintaining ecological functions in the agroecosystem. Effective soil management depends on highly accurate soil property estimation. Machine learning (ML) is an effective tool for data mining, selection of key soil properties, modeling the non-linear relationship between different soil properties. Through coupling with spectral imaging, ML algorithms have been extensively used to estimate physical, chemical, and biological properties quickly and accurately for more effective soil management. Most of the soil properties are estimated by either near infrared (NIR), Vis-NIR, or mid-infrared (MIR) in combination with different ML algorithms. Spectroscopy is widely used in estimation of chemical properties of soil samples. Spectral imaging from both UAV and satellite platforms should be taken to improve the spatial resolution of different soil properties. Spectral image super-resolution should be taken to generate spectral images in high spatial, spectral, and temporal resolutions; more advanced algorithms, especially deep learning (DL) should be taken for soil properties’ estimation based on the generated ‘super’ images. Using hyperspectral modeling, soil water content, soil organic matter, total N, total K, total P, clay and sand were found to be successfully predicted. Generally, MIR produced better predictions than Vis-NIR, but Vis-NIR outperformed MIR for a number of properties. An advantage of Vis-NIR is instrument portability although a new range of MIR portable devices is becoming available. In-field predictions for water, total organic C, extractable phosphorus, and total N appear similar to laboratory methods, but there are issues regarding, for example, sample heterogeneity, moisture content, and surface roughness. More precise and detailed soil property estimation will facilitate future soil management.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi H, Williams LJ (2010) Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Stat 2:433–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/wics.101
Abdi H, Williams LJ (2013) Partial least squares methods: partial least squares correlation and partial least square regression. In: Reisfeld B, Mayeno AN (eds) Computational toxicology: volume II, methods in molecular biology. Springer, pp 549–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-059-5_23
Adeline KRM, Gomez C, Gorretta N et al (2017) Predictive ability of soil properties to spectral degradation from laboratory Vis-NIR spectroscopy data. Geoderma 288:143–153
Aldana-Jague E, Heckrath G, Macdonald A et al (2016) UAS-based soil carbon map** using Vis-NIR (480-1000 nm) multi-spectral imaging: potential and limitations. Geoderma 275:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.04.012
Amin I, Fikrat F, Mammadov E et al (2020) Soil organic carbon prediction by Vis-NIR spectroscopy: case study the Kur-Aras plain, Azerbaijan. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 51:726–734. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2020.1729367
Amundson R, Berhe AA, Hopmans JW et al (2015) Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 348:6235. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1261071
Ba Y, Liu J, Han J et al (2020) Application of Vis-NIR spectroscopy for determination the content of organic matter in saline-alkali soils. Spectrochim Acta Part A 229:117863
Bai L, Wang C, Zang S et al (2018) Map** soil alkalinity and salinity in northern Songnen plain, China with the HJ-1 hyperspectral imager data and partial least squares regression. Sensors 18:3855
Bai Z, **e M, Hu B et al (2022) Estimation of soil organic carbon using Vis-NIR spectral data and spectral feature bands selection in southern **njiang. China Sensors 22:6124
Bao YD, He Y, Fang H et al (2007) Spectral characterization and N content prediction of soil with different particle size and moisture content. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 27:62–65
Batey T (2009) Soil compaction and soil management - a review. Soil Use Manag 25:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1475-2743.2009.00236.X
Biau G, Scornet E (2016) A random forest guided tour. TEST 25:197–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11749-016-0481-7
Blanchet G, Libohova Z, Joost S et al (2017) Spatial variability of potassium in agricultural soils of the canton of Fribourg, Switzerland. Geoderma 290:107–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.12.002
Blanco-Canqui H, Ruis SJ (2018) No-tillage and soil physical environment. Geoderma 326:164–200
Bogrekci I, Lee WS (2005a) Spectral phosphorus map** using diffuse reflectance of soils and grass. Biosyst Eng 91:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.04.015
Bogrekci I, Lee WS (2005b) Spectral soil signatures and sensing phosphorus. Biosyst Eng 92:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.09.001
Bormann H, Klaassen K (2008) Seasonal and land use dependent variability of soil hydraulic and soil hydrological properties of two Northern German soils. Geoderma 145:295–302
Boser BE, Guyon IM, Vapnik VN (1992) Training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In: Proceedings of the fifth annual ACM workshop on computational learning theory. ACM Press, pp 144–152
Bronick C, Lal R (2005) Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma 124:3–22
Cai J, Luo J, Wang S et al (2018) Feature selection in machine learning: a new perspective. Neurocomputing 300:70–79
Chang CW, Laird DA (2002) Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopic analysis of soil C and N. Soil Sci 167:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200202000-00003
Chen X, Qi Z, Gui D et al (2020) Evaluation of a new irrigation decision support system in improving cotton yield and water productivity in an arid climate. Agric Water Manage 234:106139
Cheng M, Jiao X, Liu Y et al (2022) Estimation of soil moisture content under high maize canopy coverage from UAV multimodal data and machine learning. Agric Water Manag 264:107530
Clingensmith CM, Grunwald S, Wani SP (2019) Evaluation of calibration subsetting and new chemometric methods on the spectral prediction of key soil properties in a data-limited environment. Eur J Soil Sci 70:107–126. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12753
Coblinski J, Giasson É, Demattê J et al (2020) Prediction of soil texture classes through different wavelength regions of reflectance spectroscopy at various soil depths. Catena 189:104485
Comino F, Aranda V, Carcía-Ruiz R et al (2018) Infrared spectroscopy as a tool for the assessment of soil biological quality in agricultural soils under contrasting management practices. Ecol Indic 87:117–126
Cozzolino D, Cynkar WU, Dambergs RG et al (2013) In situ measurement of soil chemical composition by near-infrared spectroscopy: a tool toward sustainable vineyard management. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 44:1610–1619. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2013.768263
da Rocha Neto OC, dos Santos TA, de Oliveira Leão RA et al (2017) Hyperspectral remote sensing for detecting soil salinization using pro spec TIR-VS aerial imagery and sensor simulation. Remote Sens 9:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010042
Dalal RC, Henry RJ (1986) Simultaneous determination of moisture, organic carbon, and total nitrogen by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:120–123. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000010023x
Datta S, Taghvaeian S, Stivers J (2017) Understanding soil water content and thresholds for irrigation management. In: Oklahoma cooperative extension fact sheet BAE-1537. Oklahoma State University
Degrune F, Theodorakopoulos N, Colinet G et al (2017) Temporal dynamics of soil microbial communities below the seedbed under two contrasting tillage regimes. Front Microbiol 8:1127. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01127
Deiss L, Margenot AJ, Culman SW et al (2020) Tuning support vector machines regression models improves prediction accuracy of soil properties in MIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 365:114227
Diaz-Gonzalez FA, Vuelvas J, Correa CA et al (2022) Machine learning and remote sensing techniques applied to estimate soil indicators – review. Ecol Indic 135:108517
Du CW, Zhou JM (2009) Evaluation of soil fertility using infrared spectroscopy: a review. Environ Chem Lett 7:97–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-008-0166-x
Fernández F, Hoeft RG (2009) Managing soil pH and crop nutrients. Academia. extension.cropsciences.illinois.edu. http://extension.cropsciences.illinois.edu/handbook/pdfs/chapter08.pdf. Accessed 4 Jan 2023
Fystro G (2002) The prediction of C and N content and their potential mineralisation in heterogeneous soil samples using vis-NIR spectroscopy and comparative methods. Plant Soil 246:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020612319014
Gholizadeh A, Borůvka L, Saberioon MM et al (2015) Comparing different data preprocessing methods for monitoring soil heavy metals based on soil spectral features. Soil Wat Res 10:218–227. https://doi.org/10.17221/113/2015-SWR
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M et al (2020) Generative adversarial networks. Commun ACM 63:139–144. https://doi.org/10.1145/3422622
Greenberg I, Seidel M, Vohland M et al (2022) Performance of in situ vs laboratory mid-infrared soil spectroscopy using local and regional calibration strategies. Geoderma 409:115614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115614
Han X, Wang P, Cui C et al (2010) Influence of soil surface disposal on precision of measuring soil water by near-infrared spectroscopy. Trans Chin Soc Agric Engin 26:47–51
Hartemink AE (2008) Soils are back on the global agenda. Soil Use Manag 24:327–330. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-2743.2008.00187.x
Hartmann M, Frey B, Mayer J et al (2015) Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J 9:1177–1194
Hati K, Mandal K, Misra A et al (2006) Effect of inorganic fertilizer and farmyard manure on soil physical properties, root distribution, and water-use efficiency of soybean in vertisols of Central India. Bioresour Technol 97:2182–2188
Hinton GE (2009) Deep belief networks. Scholarpedia 4:5947
Houser JN, Richardson WB (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus in the Upper Mississippi river: transport, processing, and effects on the river ecosystem. Hydrobiologia 640:71–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10750-009-0067-4
Hu J, Peng J, Zhou Y et al (2019) Quantitative estimation of soil salinity using UAV-borne hyperspectral and satellite multispectral images. Remote Sens 11:736
Hutengs C, Eisenhauer N, Schädler M et al (2021) VNIR and MIR spectroscopy of PLFA-derived soil microbial properties and associated soil physicochemical characteristics in an experimental plant diversity. Soil Biol Biochem 160:108319
Jia S, Yang X, Zhang J et al (2014) Quantitative analysis of soil nitrogen, organic carbon, available phosphorous, and available potassium using near-infrared spectroscopy combined with variable selection. Soil Sci 179:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1097/ss.0000000000000060
John K, Isong IA, Kebonye NM et al (2020) Using machine learning algorithms to estimate soil organic carbon variability with environmental variables and soil nutrient indicators in an alluvial soil. Land 9:487. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9120487
Johnson AM, Hoyt GD (1999) Changes to the soil environment under conservation tillage. HortTechnology 9:380–393
Kaschuk G, Alberton O, Hungria M (2010) Three decades of soil microbial biomass studies in Brazilian ecosystems: lessons learned about soil quality and indications for improving sustainability. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1–13
Katuwal S, Knadel M, Norgaard T et al (2020) Predicting the dry bulk density of soils across Denmark: comparison of single-parameter, multi-parameter, and vis–NIR based models. Geoderma 361:114080
Kotroczó Z, Veres Z, Fekete I et al (2014) Soil enzyme activity in response to long-term organic matter manipulation. Soil Biol Biochem 70:237–243
Kramer O (2013) K-nearest Neighbors. In: Dimensionality reduction with unsupervised nearest Neighbors. Intelligent systems reference library 51. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38652-7_2
Kweon G, Maxton C (2013) Soil organic matter sensing with an on-the-go optical sensor. Biosyst Eng 115:66–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2013.02.004
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436–444
Lehmann A, Zheng W, Rillig MC (2017) Soil biota contributions to soil aggregation. Nature Ecol Evol 1:1828–1835
Lewis DD (1998) Naive (bayes) at forty: the independence assumption in information retrieval. In: Nédellec C, Rouveirol C (eds) Machine learning: ECML-98. ECML 1998. Lecture notes in computer science 1398. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0026666
Li Y, Cui S, Chang SX et al (2019) Liming effects on soil pH and crop yield depend on lime material type, application method and rate, and crop species: a global meta-analysis. J Soils Sediments 19:1393–1406. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11368-018-2120-2
Liu H, Motoda H (2012) Feature selection for knowledge discovery and data mining. Springer
Liu X, Herbert S, Hashemi A et al (2006) Effects of agricultural management on soil organic matter and carbon transformation-a review. Plant Soil Environ 52:531–543
Liu Y, Jiang Q, Shi T et al (2014) Prediction of total nitrogen in cropland soil at different levels of soil moisture with Vis/NIR spectroscopy. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 64:267–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2014.906644
Liu Y, Deng C, Lu YY et al (2020) Evaluating the characteristics of soil vis-NIR spectra after the removal of moisture effect using external parameter orthogonalization. Geoderma 376:114568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114568
Liu J, Zhang D, Yang L et al (2022) Develo** a generalized vis-NIR prediction model of soil moisture content using external parameter orthogonalization to reduce the effect of soil type. Geoderma 419:115877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.115877
Lloyd S (1982) Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 28:129–137. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1056489. Accessed 8 Feb 2023
Loh W-Y (2011) Classification and regression trees. WIREs 1:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.8
Lopez Pinaya WH, Vieira S, Garcia-Dias R et al (2019) Autoencoders. In: Mechelli A, Vieira S (eds) Machine learning: methods and applications to brain disorders. Academic, pp 193–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815739-8.00011-0
López-Fando C, Pardo MT (2012) Use of a partial-width tillage system maintains benefits of no-tillage in increasing total soil nitrogen. Soil Tillage Res 118:32–39
Lu Q, Tian S, Wei L (2023) Digital map** of soil pH and carbonates at the European scale using environmental variables and machine learning. Sci Total Environ 856:159171
Ludwig B, Murugan R, Parama VRR et al (2018) Use of different chemometric approaches for an estimation of soil properties at field scale with near infrared spectroscopy. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 181:704–713. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201800130
Ludwig B, Murugan R, Parama VRR et al (2019) Accuracy of estimating soil properties with mid-infrared spectroscopy: implications of different chemometric approaches and software packages related to calibration sample size. Soil Sci Soc Am J 83:1542–1552. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2018.11.0413
Maleki MR, van Holm L, Ramon H et al (2006) Phosphorus sensing for fresh soils using visible and near infrared spectroscopy. Biosyst Eng 95:425–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2006.07.015
Malley DF, Yesmin L, Eilers RG (2002) Rapid analysis of hog manure and manure-amended soils using near-infrared spectroscopy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1677–1686. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2002.1677
Martin PD, Malley DF, Manning G et al (2002) Determination of soil organic carbon and nitrogen at the field level using near-infrared spectroscopy. Can J Soil Sci 82:413–422. https://doi.org/10.4141/s01-054
Martínez-España R, Bueno-Crespo A, Soto J (2019) Develo** an intelligent system for the prediction of soil properties with a portable mid-infrared instrument. Biosyst Eng 177:101–108
Maugis C, Celeux G, Martin-Magniette ML (2009) Variable selection for clustering with gaussian mixture models. Biometrics 65:701–709. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1541-0420.2008.01160.X
Medsker LR, Jain LC (2001) Recurrent neural networks. In: Design and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Metzger K, Zhang C, Ward M et al (2020) Mid-infrared spectroscopy as an alternative to laboratory extraction for the determination of lime requirement in tillage soils. Geoderma 364:114171
Miao F, Li Y, Cui S et al (2019) Soil extracellular enzyme activities under long-term fertilization management in the croplands of China: a meta-analysis. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 114:125–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10705-019-09991-2
Miransari M (2013) Soil microbes and the availability of soil nutrients. Acta Physiol Plant 35:3075–3084. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11738-013-1338-2
Miransari M, Smith DL (2007) Overcoming the stressful effects of salinity and acidity on soybean nodulation and yields using signal molecule genistein under field conditions. J Plant Nutr 30:1967–1992. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160701700384
Mohammadi K, Heidari G, Khalesro S et al (2011) Soil management, microorganisms and organic matter interactions: a review. Afr J Biotechnol 10:19840–19849. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJBX11.006
Mouazen AM, de Baerdemaeker J, Ramon H (2006a) Effect of wavelength range on the measurement accuracy of some selected soil constituents using visual-near infrared spectroscopy. J Near Infrared Spectrosc 14:189–199
Mouazen AM, Karoui R, de Baerdemaeker J et al (2006b) Characterization of soil water content using measured visible and near infrared spectra. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1295–1302. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0297
Mouazen AM, Kuang B, de Baerdemaeker J et al (2010) Comparison among principal component, partial least squares and back propagation neural network analyses for accuracy of measurement of selected soil properties with visible and near infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 158:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.03.001
Murphy KP (2018) Machine learning: a probabilistic perspective. MIT Press. (Adaptive computation and machine learning series)
Mutuo PK, Shepherd KD, Albrecht A et al (2006) Prediction of carbon mineralization rates from different soil physical fractions using diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1658–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.11.020
Nath D, Laik R, Meena V et al (2021) Can mid-infrared (mid-IR) spectroscopy evaluate soil conditions by predicting soil biological properties? Soil Security 4:100008
Neal RM (1998) Regression and classification using gaussian process priors. In: Bernardo J, Berger J, Dawid A, AFM S (eds) Bayesian statistics, vol 6, pp 475–501
Ng W, Anggria L, Siregar A et al (2020) Develo** a soil spectral library using a low-cost NIR spectrometer for precision fertilization in Indonesia. Geoderma Reg 22:e00319
O’Shea K, Nash R (2015) An introduction to Convolutional neural networks. Cornell University. http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.08458
Olden JD, Jackson DA (2002) Illuminating the “black box”: a randomization approach for understanding variable contributions in artificial neural networks. Ecol Model 154:135–150
Omondi M, **a X, Nahayo A et al (2016) Quantification of biochar effects on soil hydrological properties using meta-analysis of literature data. Geoderma 274:28–34
Padarian J, Minasny B, McBratney AB (2019) Using deep learning to predict soil properties from regional spectral data. Geoderma Reg 16:e00198
Padarian J, Minasny B, McBratney AB (2020) Machine learning and soil sciences: a review aided by machine learning tools. Soil 6:35–52. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-6-35-2020
Peng X, Shi T, Song A et al (2014) Estimating soil organic carbon using VIS/NIR spectroscopy with SVMR and SPA methods. Remote Sens 6:2699–2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6042699
Post JL, Noble PN (1993) The near-infrared combination band frequencies of dioctahedral smectites, micas, and illites. Clay Clay Miner 41:639–644. https://doi.org/10.1346/ccmn.1993.0410601
Reeves JB (2010) Near- versus mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for soil analysis emphasizing carbon and laboratory versus on-site analysis: where are we and what needs to be done? Geoderma 158:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.04.005
Reeves JB, McCarty GW, Meisinger JJ (1999) Near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for the analysis of agricultural soils. J Near Infrared Spectrosc 7:179–193. https://doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.248
Reeves JB, Follett RF, McCarty GW et al (2006) Can near or mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy be used to determine soil carbon pools? Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 37:2307–2325. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620600819461
Rivera JI, Bonilla CA (2020) Predicting soil aggregate stability using readily available soil properties and machine learning techniques. Catena 187:104408
Robinson CA, Cruse RM, Kohler KA (1994) Soil management. In: Hatfield JL, Karlen DL (eds) Sustainable agriculture systems. CRC Press
Rosero-Vlasova OA, Vlassova L, Pérez-Cabello F et al (2019) Soil organic matter and texture estimation from visible–near infrared–shortwave infrared spectra in areas of land cover changes using correlated component regression. Land Degrad Dev 30:544–560. https://doi.org/10.1002/LDR.3250
Rossel RAV, Behrens T (2010) Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 158:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.12.025
Rossel RAV, Lark RM (2009) Improved analysis and modelling of soil diffuse reflectance spectra using wavelets. Eur J Soil Sci 60:453–464. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2009.01121.x
Rossel RAV, Walvoort DJJ, McBratney AB et al (2006) Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 131:59–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.03.007
Rossel RAV, Adamchuk VI, Sudduth KA et al (2011) Proximal soil sensing: an effective approach for soil measurements in space and time. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy, vol 113. Elsevier Academic Press Inc., San Diego, pp 237–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-386473-4.00010-5
Schloter M, Dilly O, Munch JC (2003) Indicators for evaluating soil quality. Agric Ecosyst Environ 98:255–262
Seidel M, Hutengs C, Ludwig B et al (2019) Strategies for the efficient estimation of soil organic carbon at the field scale with Vis-NIR spectroscopy: spectral libraries and spiking vs. local calibrations. Geoderma 354:113856
Seneviratne SI, Corti T, Davin EL et al (2010) Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: a review. Earth Sci Rev 99:125–161
Shao YN, He Y (2011) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium prediction in soils, using infrared spectroscopy. Soil Res 49:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1071/sr10098
Sila AM, Shepherd KD, Pokhariyal GP (2016) Evaluating the utility of mid-infrared spectral subspaces for predicting soil properties. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 153:92–105
Sithole NJ, Magwaza LS, Mafongoya PL (2016) Conservation agriculture and its impact on soil quality and maize yield: a South African perspective. Soil Tillage Res 162:55–67
Sithole NJ, Ncama K, Magwaza LS (2018) Robust vis-NIRS models for rapid assessment of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in Feralsols haplic soils from different tillage management practices. Comput Electron Agric 153:295–301
Six J, Paustian K, Elliott ET et al (2000) Aggregate and soil organic matter dynamics under conventional and no-tillage systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:681–689. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2000.642681x
Slessarev EW, Lin Y, Bingham NL et al (2016) Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale. Nature 540:567–569
Smith JL, Paul EA (1990) The significance of soil microbial biomass estimations. In: Bollag JM, Stotzky G (eds) Soil biochemistry. Routledge, New York
Smith P, Fang C, Dawson JJC et al (2008) Impact of global warming on soil organic carbon. Adv Agron 97:1–43
Soriano-Disla JM, Janik LJ, Viscarra Rossel RA et al (2014) The performance of visible, near-, and mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy for prediction of soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. Appl Spectrosc Rev 49:139–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2013.811081
Srivastava P, Shukla A, Bansal A (2021) A comprehensive review on soil classification using deep learning and computer vision techniques. Multimed Tools Appl 80:14887–14914. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11042-021-10544-5
Stenberg B, Rossel RAV, Mouazen AM et al (2010) Visible and near infrared spectroscopy in soil science. In: Sparks DL (ed) Adv Agron, vol 107. Elsevier Academic Press Inc., San Diego, pp 163–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-2113(10)07005-7
Sun Z, Zhang Y, Li J et al (2014) Spectroscopic determination of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen content in pasture soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 45:1037–1048. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2014.883628
Tang YJ, Jones E, Minasny B (2020) Evaluating low-cost portable near infrared sensors for rapid analysis of soils from South Eastern Australia. Geoderma Reg 20:e00240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2019.e00240
Wan M, Qu M, Hu W et al (2019) Estimation of soil pH using PXRF spectrometry and Vis-NIR spectroscopy for rapid environmental risk assessment of soil heavy metals. Process Saf Environ Prot 132:73–81
Wang C, Pan X (2016) Improving the prediction of soil organic matter using visible and near infrared spectroscopy of moist samples. J Near Infrared Spectrosc 24:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.1184
Wilhelm RC, van Es HM, Buckley DH (2022) Predicting measures of soil health using the microbiome and supervised machine learning. Soil Biol Biochem 164:108472
Woergoetter F, Porr B (2008) Reinforcement learning. Scholarpedia 3:1448
Wu S, Wang C, Liu Y et al (2018) Map** the salt content in soil profiles using vis-NIR hyperspectral imaging. Soil Sci Soc Am J 82:1259–1269. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2018.02.0074
**ao S, He Y (2019) Application of near-infrared spectroscopy and multiple spectral algorithms to explore the effect of soil particle sizes on soil nitrogen detection. Molecules 24:2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132486
**e S, Ding F, Chen S et al (2022) Prediction of soil organic matter content based on characteristic band selection method. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 273:120949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.120949
Xu S, Zhao Y, Wang M et al (2018a) Quantification of different forms of iron from intact soil cores of paddy fields with vis-NIR spectroscopy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 82:1497–1511. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2018.01.0014
Xu S, Zhao Y, Wang M et al (2018b) Comparison of multivariate methods for estimating selected soil properties from intact soil cores of paddy fields by vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 310:29–43
Xu X, Du C, Ma F et al (2019) Detection of soil organic matter from laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and mid-infrared spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR) coupled with multivariate. Geoderma 355:113905
Yang H, Kuang B, Mouazen AM (2012) Quantitative analysis of soil nitrogen and carbon at a farm scale using visible and near infrared spectroscopy coupled with wavelength reduction. Eur J Soil Sci 63:410–420. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2012.01443.x
Yang X, Bao N, Li W et al (2021) Soil nutrient estimation and map** in farmland based on UAV imaging spectrometry. Sensors 21:3919. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113919
Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y et al (2014) How transferable are features in deep neural networks? Cornell University. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/5347-how-transferable-are-features-in-deep-n%E2%80%A6. Accessed 3 Jan 2023
Zeraatpisheh M, Bakhshandeh E, Hosseini M et al (2020) Assessing the effects of deforestation and intensive agriculture on the soil quality through digital soil map**. Geoderma 363:114139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.114139
Zhalnina K, Hawkes C, Shade A et al (2021) Managing plant microbiomes for sustainable biofuel production. Phytobiomes J 5:3–13. https://doi.org/10.1094/PBIOMES-12-20-0090-E
Zhao Z, Morstatter F, Sharma S et al (2010) Advancing feature selection research. Academic. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=7cb7ca94930461c3ae54542d7f2358c39b3c69b8. Accessed 2 Jan 2023
Zheng H, Liu W, Zheng J et al (2018) Effect of long-term tillage on soil aggregates and aggregate-associated carbon in black soil of Northeast China. PLoS One 13:e0199523. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199523
Zhu C, Ding J, Zhang Z et al (2022) Exploring the potential of UAV hyperspectral image for estimating soil salinity: effects of optimal band combination algorithm and random forest. Spectrochim Acta Part A Molec Biomolec Spectr 279:121416
Zorb C, Senbayram M, Peiter E (2014) Potassium in agriculture - status and perspectives. J Plant Physiol 171:656–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2013.08.008
Acknowledgements
The work was funded through the project “CHN17/0019 Sinograin II: Technological innovation to support environmentally-friendly food production and food safety under a changing climate-opportunities and challenges for Norway-China cooperation” (funded by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs through the Royal Norwegian Embassy in Bei**g).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhao, J., Wan, S. (2023). Artificial Intelligence and Hyperspectral Modeling for Soil Management. In: Clarke, N., Peng, D., Clarke, J.L. (eds) Innovation for Environmentally-friendly Food Production and Food Safety in China. Sustainability Sciences in Asia and Africa(). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2828-6_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2828-6_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2827-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2828-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)