Abstract
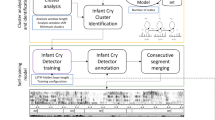
Since babies cannot speak, they can only communicate with the outside world and express their emotions and needs through crying. Considering the variety of reasons why babies cry, it is a challenging task to accurately understand the meaning of baby crying. In this paper, we propose a baby cry recognition method based on acoustic segment model (ASM). Firstly, based on Gaussian mixtures models - hidden Markov models (GMM-HMMs), baby cry recordings are transcribed into ASM sequences composed of ASM units. In this way, different baby cry recordings are segmented in more detail, which can better capture the similarities and differences between acoustic segments. Then, by using latent semantic analysis (LSA), these ASM sequences are converted into feature vectors, and the term-document matrix is obtained. Finally, a simple classifier is adopted to distinguish different types of baby crying. The effectiveness of the proposed method is evaluated on two infant crying databases. The ASM-based approach can achieve higher accuracy compared with the approach based on residual network (ResNet). And through experiments, we analyze the reasons for the better performance of the ASM-based method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drummond, J.E., McBride, M.L., Wiebe, C.F.: The development of mothers’ understanding of infant crying. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2(4), 396–410 (1993)
Garcia, J.O., Garcia, C.R.: Mel-frequency cepstrum coefficients extraction from infant cry for classification of normal and pathological cry with feed-forward neural networks. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 3140–3145 (2003)
Rusu, M.S., Diaconescu, Ş.S., Sardescu, G., Brătilă, E.: Database and system design for data collection of crying related to infant’s needs and diseases. In: 2015 International Conference on Speech Technology and Human-Computer Dialogue (SpeD), pp. 1–6 (2015)
Wasz-Höckert, O., Partanen, T.J., Vuorenkoski, V., Michelsson, K., Valanne, E.: The identification of some specific meanings in infant vocalization. Experientia 20(3), 154–154 (1964)
Orlandi, S., et al.: Study of cry patterns in infants at high risk for autism. In: Seventh International Workshop on Models and Analysis of Vocal Emissions for Biomedical Applications (2011)
Farsaie Alaie, H., Tadj, C.: Cry-based classification of healthy and sick infants using adapted boosting mixture learning method for gaussian mixture models. Model. Simul. Eng. 2012(9), 55 (2012)
Chittora, A., Patil, H.A.: Classification of pathological infant cries using modulation spectrogram features. In: The 9th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing, pp. 541–545 (2014)
Bğnicğ, I.A., Cucu, H., Buzo, A., Burileanu, D., Burileanu, C.: Baby cry recognition in real-world conditions. In: 2016 39th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), pp. 315–318 (2016)
Bănică, I.A., Cucu, H., Buzo, A., Burileanu, D., Burileanu, C.: Automatic methods for infant cry classification. In: 2016 International Conference on Communications (COMM), pp. 51–54 (2016)
Abdulaziz, Y., Ahmad, S.M.S.: Infant cry recognition system: a comparison of system performance based on mel frequency and linear prediction cepstral coefficients. In: 2010 International Conference on Information Retrieval & Knowledge Management (CAMP), pp. 260–263 (2010)
Reyes-Galaviz, O.F., Reyes-Garcia, C.A.: A system for the processing of infant cry to recognize pathologies in recently born babies with neural networks. In: 9th Conference Speech and Computer, pp. 552–557 (2004)
Chang, C.Y., Li, J.J.: Application of deep learning for recognizing infant cries. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), pp. 1–2 (2016)
Yong, B.F., Ting, H.N., Ng, K.H.: Baby cry recognition using deep neural networks. In: World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2018, pp. 809–813 (2019)
Lee, C.H., Soong, F.K., Juang, B.H.: A segment model based approach to speech recognition. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 501–502 (1988)
Lee, H.Y., et al.: Ensemble of machine learning and acoustic segment model techniques for speech emotion and autism spectrum disorders recognition. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 215–219 (2013)
Zheng, S., Du, J., Zhou, H., Bai, X., Lee, C.H., Li, S.: Speech emotion recognition based on acoustic segment model. In: 2021 12th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), pp. 1–5 (2021)
Tsao, Y., Sun, H., Li, H., Lee, C.H.: An acoustic segment model approach to incorporating temporal information into speaker modeling for text-independent speaker recognition. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 4422–4425 (2010)
Riley, M., Heinen, E., Ghosh, J.: A text retrieval approach to content-based audio retrieval. In: International Society for Music Information Retrieval (ISMIR), pp. 295–300 (2008)
Bai, X., Du, J., Wang, Z.R., Lee, C.H.: A hybrid approach to acoustic scene classification based on universal acoustic models. In: Interspeech, pp. 3619–3623 (2019)
Svendsen, T., Soong, F.: On the automatic segmentation of speech signals. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 77–80 (1987)
Hu, H., Siniscalchi, S.M., Wang, Y., Bai, X., Du, J., Lee, C.H.: An acoustic segment model based segment unit selection approach to acoustic scene classification with partial utterances. In: INTERSPEECH, pp. 1201–1205 (2020)
Rabiner, L.R.: A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. IEEE 77(2), 257–286 (1989)
Su, D., Wu, X., Xu, L.: GMM-HMM acoustic model training by a two level procedure with Gaussian components determined by automatic model selection. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 4890–4893 (2010)
Karpagavalli, S., Chandra, E.: Phoneme and word based model for tamil speech recognition using GMM-HMM. In: 2015 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems, pp. 1–5 (2015)
Wall, M.E., Rechtsteiner, A., Rocha, L.M.: Singular value decomposition and principal component analysis. In: A Practical Approach to Microarray Data Analysis, pp. 91–109 (2003)
Elworthy, D.: Does Baum-Welch re-estimation help taggers?. ar**v preprint cmp-lg/9410012 (1994)
Hull, D.: Improving text retrieval for the routing problem using latent semantic indexing. In: SIGIR1994, pp. 282–291 (1994)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
**e, X., Zhang, L., Wang, J.: Application of residual network to infant crying recognition. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 41(1), 233–239 (2019)
Hu, H., Yang, C.H.H., **a, X., et al.: A two-stage approach to device-robust acoustic scene classification. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 845–849 (2021)
Bottou, L.: Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In: Proceedings of COMPSTAT 2010, pp. 177–186 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, S., Du, J., Wang, Y. (2023). Baby Cry Recognition Based on Acoustic Segment Model. In: Zhenhua, L., Jianqing, G., Kai, Y., Jia, J. (eds) Man-Machine Speech Communication. NCMMSC 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1765. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2401-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2401-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2400-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2401-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)