Abstract
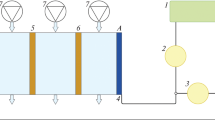
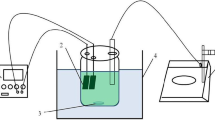
Nickel is a silvery-white metal that is in high demand for a variety of commercial applications due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments. However, the widespread use of nickel compounds in many applications has resulted serious environmental pollutions if they are not properly treated before discharging. The electro-precipitation technique for depositing nickel from industrial waste has become one of the most favorable treatment methods because of its simplicity and low environmental requirements. In this study, the efficiency of nickel deposition from industrial electronic waste with relation to power supply variation (5A and 10A) was explored using various parameters such as electrode type and reaction time. The experiments were conducted in a 500 mL batch reactor with dual electrodes: aluminum (Al) as and stainless-steel (SS) as the anode and the cathode. The results show that the optimum condition of electro-precipitation process of nickel removal efficiency of 99.9% was obtained at 5 A, for 45 min. This research could pave the way for a low-power treatment of industrial nickel wastes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muchlis D, Ardeniswan M (2018) Nickel removal from electroplating wastewater using electrocoagulation. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, vol 160, pp 12–16
Dermentzis K, Christoforidis A, Valsamidou E (2011) Removal of nickel, copper, zinc and chromium from synthetic and industrial wastewater by electrocoagulation. Int J Environ Sci 1(5):697–710
Tibebe D, Kassa Y, Bhaskarwar AN (2019) Treatment and characterization of phosphorus from synthetic wastewater using aluminum plate electrodes in the electrocoagulation process. BMC Chem 13(107)
Hall DS, Lockwood DJ, Bock C, MacDougall BR (2015) Nickel hydroxides and related materials: a review of their structures, synthesis and properties. Proc R Soc A 471:20140792
Liu YX, Wu XY, Yuan DX, Yan JM (2013) Removal of nickel from aqueous solution using cathodic deposition of nickel hydroxide at a modified electrode. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88(12)
Guo M, Feng L, Liu Y, Zhang L (2020) Electrochemical simultaneous denitrification and removal of phosphorus from the effluent of a municipal wastewater treatment plant using cheap metal electrodes. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 4
Bazrafshan E, Mohammadi L, Moghaddam AA, Mahvi AH (2015) Heavy metals removal from aqueous environments by electrocoagulation process- a systematic review. J Environ Health Sci Eng 13(74)
Raval NP, Shah PU, Shah NK (2016) Adsorptive removal of Nickel (II) ions from aqueous environment: a review. J Environ Manag 179:1–20
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from University-Private Matching Fund under a grant number of 9001-00674 from Universiti Malaysia Perlis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hassan, H., Ahmad, M.M., Hui, G.X., Sabri, M.S.A.M., Ismail, M., Ali, U.F.M. (2023). Impact of Power Supply on Electro-Precipitation of Nickel Hydroxide from Industrial Electronic Waste. In: Shukor, H., Halim, H.N.A., Ong, H.L., Lee, BB., Pisal, M.H.M. (eds) Emerging Technologies for Future Sustainability . ICoBiomasSE 2022. Green Energy and Technology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1695-5_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1695-5_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1694-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1695-5
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)