Abstract
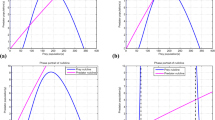
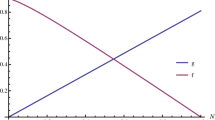
A mathematical model on predator–prey dynamics is analyzed in this study. In traditional models, prey refuge is usually taken constant which is nearly impossible in real-life scenario. We have considered nonlinear prey refuge which depends on both prey and predator. We have performed various dynamical studies incorporating Holling type-II functional response. The system can perceive at most three equilibria. The boundedness of all the solutions, stability–instability conditions, and bifurcation analysis are demonstrated in this work. All the analytical findings are verified with numerical simulations. Additionally, a model comparison is performed which helps to understand the dynamical changes due to nonlinear refuge.
Supported by organization National Institute of Technology Agartala.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holling, C.S.: The components of predation as revealed by a study of small-mammal predation of the european pine sawfly1. Can. Entomol. 91(5), 293–320 (1959)
Holling, C.S.: Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism1. Can. Entomol. 91(7), 385–398 (1959)
Holling, C.S.: The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 97(S45), 5–60 (1965)
Ji, L., Wu, C.: Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with constant-rate prey harvesting incorporating a constant prey refuge. Nonlinear Anal.: Real World Appl. 11(4), 2285–2295 (2010)
Molla, H., Sarwardi, S., Sajid, M.: Predator-prey dynamics with allee effect on predator species subject to intra-specific competition and nonlinear prey refuge. J. Math. Comput. Sci 25, 150–165 (2021)
Mondal, S., Samanta, G.: Dynamics of a delayed predator-prey interaction incorporating nonlinear prey refuge under the influence of fear effect and additional food. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 53(29), 295601 (2020)
Mondal, S., Samanta, G., Nieto, J.J.: Dynamics of a predator-prey population in the presence of resource subsidy under the influence of nonlinear prey refuge and fear effect. Complexity 2021 (2021)
Samaddar, S., Dhar, M., Bhattacharya, P.: Effect of fear on prey–predator dynamics: Exploring the role of prey refuge and additional food. Chaos: Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 30(6), 063129 (2020)
Samaddar, S., Dhar, M., Bhattacharya, P.: Supplement of additional food: dynamics of self-competitive prey-predator system incorporating prey refuge. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A: Sci. 44(1), 143–153 (2020)
Samaddar, S., Dhar, M., Bhattacharya, P.: Impact of refuge to the heterogeneous interaction of species in food chain model: a holistic approach. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A: Sci. 45(1), 221–233 (2021)
Wang, J., Cai, Y., Fu, S., Wang, W.: The effect of the fear factor on the dynamics of a predator-prey model incorporating the prey refuge. Chaos: Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 29(8), 083109 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Samaddar, S., Dhar, M., Bhattacharya, P. (2023). Effect of Nonlinear Prey Refuge on Predator–Prey Dynamics. In: Som, T., Ghosh, D., Castillo, O., Petrusel, A., Sahu, D. (eds) Applied Analysis, Optimization and Soft Computing. ICNAAO 2021. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol 419. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0597-3_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0597-3_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-0596-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-0597-3
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)