Abstract
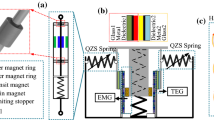
A bird-inspired nonlinear oscillator (BINO) is proposed for low-frequency vibration control and energy harvesting of bridges. By integrating the spring into the oscillator, the space utilization rate and reliability are further improved. Theoretical analysis and experimental results show that BINO with triboelectric nanogenerator damper (BINO-TENGD) with quasi-zero stiffness (QZS) has excellent low-frequency vibration isolation performance and stable output voltage. In addition, BINO-TENG can produce resonance phenomenon in the frequency range of 3-8 Hz under bistable condition, and obtain high output. Finally, BINO-TENGD under QZS condition is applied to the beam bridge, and the results show that adding BINO-TENGD to the beam bridge is beneficial to suppress vibration. Therefore, BINO has a certain application prospect in the fields of bridge low-frequency vibration control, vibration detection and energy harvesting.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, H., Jasim, A., Chen, X.: Energy harvesting technologies in roadway and bridge for different applications - a comprehensive review. Appl. Energy 212, 1083–1094 (2018)
Bouna, H.S., Nbendjo, B., Woafo, P.: Isolation performance of a quasi-zero stiffness isolator in vibration isolation of a multi-span continuous beam bridge under pier base vibrating excitation. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(2), 1125–1141 (2020)
Li, M., **g, X.: Novel tunable broadband piezoelectric harvesters for ultralow-frequency bridge vibration energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 255, 113829 (2019)
Zhang, Y., **e, J., Peng, J., Li, H., Huang, Y.: A deep neural network-based vehicle re-identification method for bridge load monitoring. Adv. Struct. Eng. 24(16), 3691–3706 (2021)
Chen, Q., et al.: Vertical deformation monitoring of the suspension bridge tower using GNSS: a case study of the forth road bridge in the UK. Remote Sens. 10(3), 364 (2018)
Lovett, G.M., Burns, D.A., Driscoll, C.T., Jenkins, J.C., Mitchell, M.J.: Who needs environmental monitoring?. Front. Ecol. Environ. 5(5), 253–260 (2007)
Tsukada, T., Minakuchi, S., Takeda, N.: Identification of process-induced residual stress/strain distribution in thick thermoplastic composites based on in situ strain monitoring using optical fiber sensors. J. Compos. Mater. 53(24), 3445–3458 (2019)
A. Zona, F.: Vision-based vibration monitoring of structures and infrastructures: an overview of recent applications. Infrastructures 6(1), 4 (2020)
Yertutanol, K., Akgün, H., Sopacı, E.: Displacement monitoring, displacement verification and stability assessment of the critical sections of the Konak tunnel, İzmir, Turkey. Tunnel. Underground Space Technol. 101, 103357 (2020)
Margielewicz, J., Gaska, D., Litak, G., Wolszczak, P., Yurchenko, D.: Nonlinear dynamics of a new energy harvesting system with quasi-zero stiffness. Appl. Energy 307, 118159 (2022)
Rezaei, M., Talebitooti, R., Liao, W.: Exploiting bi-stable magneto-piezoelastic absorber for simultaneous energy harvesting and vibration mitigation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 207, 106618 (2016)
Rezaei, M., Talebitooti, R.: Investigating the performance of tri-stable magneto-piezoelastic absorber in simultaneous energy harvesting and vibration isolation. Appl. Math. Model. 102, 661–693 (2022)
Lu, Z., Zhao, L., Ding, H., Chen, L.: A dual-functional metamaterial for integrated vibration isolation and energy harvesting. J. Sound Vib. 509, 116251 (2021)
Zhou, J., Wang, X., Xu, D., Bishop, S.: Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with cam-roller-spring mechanisms. J. Sound Vib. 346, 53–69 (2015)
Chai, Y., **g, X., Chao, X.: X-shaped mechanism based enhanced tunable QZS property for passive vibration isolation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 218, 107077 (2022)
Hao, Z., Cao, Q., Wiercigroch, M.: Nonlinear dynamics of the quasi-zero-stiffness SD oscillator based upon the local and global bifurcation analyses. Nonlinear Dyn. 87, 987–1014 (2017)
Xu, D., Yu, Q., Zhou, J., Bishop, S.R.: Theoretical and experimental analyses of a nonlinear magnetic vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 332, 3377–3389 (2013)
Ding, H., Ji, J., Chen, L.: Nonlinear vibration isolation for fluid-conveying pipes using quasi-zero stiffness characteristics. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 121, 675–688 (2019)
Han, Y., et al.: Wind-driven soft-contact rotary triboelectric nanogenerator based on rabbit fur with high performance and durability for smart farming. In: Advanced Functional Materials. CONFERENCE 2021, LNCS, vol. 9999, pp. 1–13. Springer, Heidelberg (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/202108580
Zhang, B., et al.: All-in-one 3D acceleration sensor based on coded liquid-metal triboelectric nanogenerator for vehicle restraint system. Mater. Today 43, 37–44 (2021)
Mathew, A.A., Chandrasekhar, A., Vivekanandan, S.: A review on real-time implantable and wearable health monitoring sensors based on triboelectric nanogenerator approach. Nano Energy 80, 105566 (2021)
Wang, P., et al.: An ultra-low-friction triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator for rotation energy harvesting and self-powered wind speed sensor. ACS Nano 12(9), 9433–9440 (2018)
Tian, J., et al.: Self-powered room-temperature ethanol sensor based on brush-shaped triboelectric nanogenerator. Research 1, 11 (2021)
Hao, Z., Wang, D., Wiercigroch, M.: Nonlinear dynamics of new magneto-mechanical oscillator. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 105, 106092 (2022)
Safaei, M., Sodano, H., Anton, S.R.: A review of energy harvesting using piezoelectric materials: state-of-the-art a decade later (2008–2018). Smart Mater. Struct. 28, 113001 (201)
Wang, Z., Jiang, T., Xu, L.: Toward the blue energy dream by triboelectric nanogenerator networks. Nano Energy 39, 9–23 (2017)
Zi, Y., Guo, H., Wen, Z., Yeh, M.H., Hu, C., Wang, Z.L.: Harvesting low-frequency (< 5 Hz) irregular mechanical energy: a possible killer application of triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 10(4), 4797–4805 (2016)
Du, Y., Deng, J., Li, P., Wen, Y.: Energy transfer and redistribution: an approach for unifying vibrational energy harvesting and vibration attenuation. Nano Energy 78, 105245 (2020)
Wu, C., Liu, R., Wang, J., Zi, Y., Lin, L., Wang, Z.L.: A spring-based resonance coupling for hugely enhancing the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting low-frequency vibration energy. Nano Energy 32, 287–293 (2017)
Yang, T., Zhou, S., Fang, S., Qin, W., Inman, D.J.: Nonlinear vibration energy harvesting and vibration suppression technologies. Appl. Phys. Rev. 8, 031317 (2021)
Huguet, T., Badel, A., Lallart, M.: Exploiting bistable oscillator subharmonics for magnified broadband vibration energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 173905 (2017)
Guan, D., Xu, G., **a, X., Wang, J., Zi, Y.: Boosting the output performance of the triboelectric nanogenerator through the nonlinear oscillator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(5), 6331–6338 (2021)
Yang, T., Zhang, Y., Zhou, S.: Multistage oscillators for ultra-low frequency vibration isolation and energy harvesting. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65, 631–645 (2022)
Yang, T., Cao, Q., Hao, Z.: A novel nonlinear mechanical oscillator and its application in vibration isolation and energy harvesting. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 155, 107636 (2021)
Luo, H., Liu, J., Yang, T., Zhang, Y., Cao, Q.: Dipteran flight-inspired bistable triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting low frequency vibration. Nano Energy. J. 103, 107755 (2022)
Feng, X., **g, X.: Human body inspired vibration isolation: beneficial nonlinear stiffness, nonlinear dam** & nonlinear inertia. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 117, 786–812 (2019)
Yan, G., Wang, S., Zou, H., Zhao, L., Gao, Q., Zhang, W.: Bio-inspired polygonal skeleton structure for vibration isolation: Des. Model. Exp. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63, 2617–2630 (2020)
Cao, Q., **ong, Y., Wiercigroch, M.: A novel model of dipteran flight mechanism. Int. J. Dyn. Control 1, 1–11 (2013)
Bouna, H.S., Nana Nbendjo, B.R., Woafo, P.: On the dynamics of two multi-span continuous beam bridges model coupled by their close environment. Int. J. Dyn. Control 6, 29–40 (2018)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Granted Nos. 12002272 and 12272293), and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Granted No. 2022A1515010967, 2023A1515012821). TY wishes to thank the supports from Hong Kong Scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, J., Cui, Y., Yang, T., **g, X. (2024). Bird-Inspired Nonlinear Oscillator with Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Vibration Control and Energy Harvesting. In: **g, X., Ding, H., Ji, J., Yurchenko, D. (eds) Advances in Applied Nonlinear Dynamics, Vibration, and Control – 2023. ICANDVC 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1152. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0554-2_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0554-2_58
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-0553-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-0554-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)