Abstract
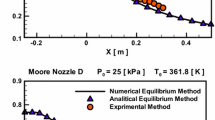
Computational fluid dynamics modelling is developed to study steam condensations within turbine blades. The numerical result is validated against experimental data available in the literature. The comparison of pressure distributions at blade pressure and suction sides demonstrates that the numerical results agree well with experimental data. The numerical result shows that the subcooling of steam can achieve 50 K which induces a maximum nucleation rate of approximately 1.77 × 1025 m−3 s−1. The produced liquid wetness reaches around 5% of the total mass of steam.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.Y. Rad, M.R. Mahpeykar, Studying the effect of convergence parameter of CUSP’s scheme in 2D modeling of novel combination of two schemes in nucleating steam flow in cascade blades. Numer. Heat Transfer Part B: Fundamentals 72(4), 325–347 (2017)
G. Zhang, F. Wang, D. Wang, T. Wu, X. Qin, Z. **, Numerical study of the dehumidification structure optimization based on the modified model. Energy Convers. Manage. 181, 159–177 (2019)
S. Dykas, M. Majkut, M. Strozik, K. Smołka, Experimental study of condensing steam flow in nozzles and linear blade cascade. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 80, 50–57 (2015)
S. Dykas, M. Majkut, K. Smołka, M. Strozik, Study of the wet steam flow in the blade tip rotor linear blade cascade. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 120, 9–17 (2018)
C. Wen, N. Karvounis, J.H. Walther, Y. Yan, Y. Feng, Y. Yang, An efficient approach to separate CO2 using supersonic flows for carbon capture and storage. Appl. Energy 238, 311–319 (2019)
Y. Yang, X. Zhu, Y. Yan, H. Ding, C. Wen, Performance of supersonic steam ejectors considering the nonequilibrium condensation phenomenon for efficient energy utilisation. Appl. Energy 242, 157–167 (2019)
J. Young, The spontaneous condensation of steam in supersonic nozzle. Physico Chem. Hydrodyn. 3(1), 57–82 (1982)
C. Wen, N. Karvounis, J.H. Walther, H. Ding, Y. Yang, Non-equilibrium condensation of water vapour in supersonic flows with shock waves. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 149, 119109 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wen, C., Zhu, X., Ding, H., Yang, Y. (2021). Numerical Modelling of Wet Steam Flows in Turbine Blades. In: Wen, C., Yan, Y. (eds) Advances in Heat Transfer and Thermal Engineering . Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4765-6_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4765-6_68
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-4764-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-4765-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)