Abstract
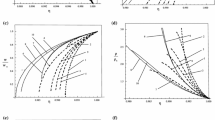
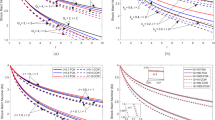
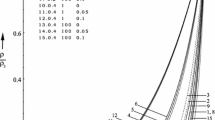
This paper investigates the effect of viscosity on the propagation of spherical shock waves in a dusty gas with a radiation heat flux and a density that grows exponentially. It is assumed that the dusty gas is a blend of fine solid particles and ideal gas. In a perfect gas, solid particles are uniformly distributed. To obtain several significant shock propagation properties, the solid particles are treated as a pseudo-fluid, and the mixture’s heat conduction is neglected. The flow’s equilibrium conditions are expected to be maintained in an optically thick gray gas model, and radiation is assumed to be of the diffusion type. The effects of modifying the viscosity parameter and time are explored, and non-similar solutions are found. The formal solution is determined by assuming that the shock wave’s velocity is variable and its total energy is not constant.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grover, R., Hardy, J.W.: The propagation of shocks in exponentially decreasing atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 143, 48 (1966)
Hayes, W.D.: Self-similar strong shocks in an exponential medium. J. Fluid Mech. 32(2), 305–315 (1968)
Deb Ray, G., Bhowmick, J.B.: Propagation of cylindrical and spherical explosion waves in an exponential medium. Defence Sci. J. 24, 9–12 (1974)
Laumbach, D.D., Probstein, R.F.: A point explosion in a cold exponential atmosphere part i. J. Fluid Mech. 35(1), 53–75 (1969)
Verma, B.G., Vishwakarma, J.P.: Axially symmetric explosion in magnetogasdynamics. Astrophys. Space Sci. 69(1), 177–188 (1980)
Laumbach, D.D., Probstein, R.F.: A point explosion in a cold exponential atmosphere part ii, radiating flow. J. Fluid Mech. 40(1), 833–858 (1970)
Laumbach, D.D., Probstein, R.F.: Self-similar strong shocks with radiation in a decreasing exponential atmosphere. Phys. Fluids 13(5), 1178–1183 (1970)
Bhowmick, J.B.: An exact analytical solution in radiation gas dynamics. Astrophys. Space Sci. 74(2), 481–485 (1981)
Singh, J.B., Srivastava, S.K.: Propagation of spherical shock waves in an exponential medium with radiation heat flux. Astrophys. Space Sci. 88(2), 277–282 (1982)
Christer, A.H., Helliwell, J.B.: Cylindrical shock and detonation waves in magnetogasdynamics. J. Fluid Mech. 39(4), 705–725 (1969)
Verma, B.G.: On a cylindrical blast ware propagating in a conducting gas. Zeitschrift fur angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP 21(1), 119–124 (1970)
Higashino, F., Suzuki, T.: The effect of particles on blast waves in a dusty gas. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 35(12), 1330–1336 (1980)
Miura, H., Israel Glass, I.: On the passage of a shock wave through a dusty-gas layer. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 385(1788), 85–105 (1983)
Popel, S.I., Gisko, A.A.: Charged dust and shock phenomena in the solar system. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 13(2), 223–229 (2006)
Pai, S.I., Menon, S., Fan, Z.Q.: Similarity solutions of a strong shock wave propagation in a mixture of a gas and dusty particles. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 18(12), 1365–1373 (1980)
Vishwakarma, J.P.: Propagation of shock waves in a dusty gas with exponentially varying density. Eur. Phys. J. B-Condensed Matter Complex Syst. 16(2), 369–372 (2000)
Singh, K.K., Vishwakarma, J.P.: Propagation of spherical shock waves in a dusty gas with radiation heat-flux. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 45(4), 801–817 (2007)
Macquorn Rankine, W.J.: Xv on the thermodynamic theory of waves of finite longitudinal disturbance. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 160, 277–288 (1870)
Rayleigh, L.: Aerial plane waves of finite amplitude. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A, Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Charact. 84(570), 247–284 (1910)
Ingram Taylor, G.: The conditions necessary for discontinuous motion in gases. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A, Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Charact. 84(571), 371–377 (1910)
Henderson, L.F., Crutchfield, W.Y., Virgona, R.J.: The effects of thermal conductivity and viscosity of argon on shock waves diffracting over rigid ramps. J. Fluid Mech. 331, 1–36 (1997)
Simeonides, G.: Generalized reference enthalpy formulations and simulation of viscous effects in hypersonic flow. Shock Waves 8(3), 161–172 (1998)
Huang, F., Matsumura, A., Shi, X.: Viscous shock wave and boundary layer solution to an inflow problem for compressible viscous gas. Commun. Math. Phys. 239(1), 261–285 (2003)
Von Neumann, J., Richtmyer, R.D.: A method for the numerical calculation of hydrodynamic shocks. J. Appl. Phys. 21(3), 232–237 (1950)
Suzuki, T., Ohyagi, S., Higashino, F., Takano, A.: The propagation of reacting blast waves through inert particle clouds. Acta Astronaut. 3(7–8), 517–529 (1976)
Narsimhulu, D., Addepalli, R., Satpathi Dipak, K.: Similarity solution of spherical shock waves-effect of viscosity. Proyecciones (Antofagasta) 35(1), 11–31 (2016)
Wang, K.C.: Approximate solution of a plane radiating “piston problem.” Phys. Fluids 9(10), 1922–1928 (1966)
Pai, S.: Two phase flows. Vol. 3, Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied Physics, pp. 56–80 (1977)
Narasimhulu Naidu, G., Venkatanandam, K., Ranga Rao, M.P.: Approximate analytical solutions for self-similar flows of a dusty gas with variable energy. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 23(1), 39–49 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Revathi, R., Narsimhulu, D., Ramu, A. (2023). Effect of Viscosity on the Spherical Shock Wave Propagation in a Dusty Gas with Radiation Heat Flux and Exponentially Varying Density. In: Sharma, R.K., Pareschi, L., Atangana, A., Sahoo, B., Kukreja, V.K. (eds) Frontiers in Industrial and Applied Mathematics. FIAM 2021. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol 410. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7272-0_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7272-0_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-7271-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-7272-0
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)