Abstract
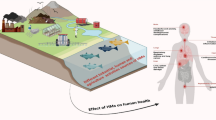
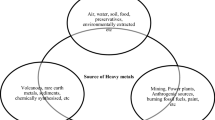
Heavy metals (HMs) accumulate in milieu due to various human activities that persist leading to biomagnification in food chains and cause unpleasant effects on human health and environment. Pollutants such as organic matter and HMs are remediated traditionally by chemical precipitation, electrochemical treatment, adsorption, reverse osmosis, ion exchange, coagulation, and photo-catalyzation, remained ineffective. Use of nanomaterials conjugated with various compounds showed significant reduction in several contaminated sites. However, existing implication of nanotechnology works with nanoparticles (NPs) synthesis majorly involved the use of chemical raw materials and physical methods which are relatively toxic and unstable. Aforesaid difficulties made researchers and entrepreneurs to reconnoitre effective, newer, and novel synthesis approaches for the replacement over older version. During the past decade, to overcome these issues plant-derived NPs are extensively used because of its less cost, efficiency, and eco-friendly in nature. Hence, advanced alternative technology like phytoremediation using nanomaterials with innovative techniques has been a boon for HM remediation. Efficiency of green synthesized NPs is based on redox reactions which makes metals stable facilitated by flavonoids and polyphenols responding to HM-stress. Several metal complexation processes are known to produce phytochelatins or other metal-chelating peptides hel** the bioremediation of HMs. Current chapter throws light on adaptive mechanism employed by NPs coupled with plant or microbial extracts in overcoming the HM stress. Furthermore, here we also focus on the possible mechanism and interaction between NPs and HM in minimizing severity of polluted sites with many examples.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal H, Venkat Kumar S, Rajeshkumar S (2017) A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles—an eco-friendly approach. Resour Efficient Technol 3:406–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2017.03.002
Ahmad J, Ikram S, Ahmad F, Rehman IU, Mushtaq M (2020) SARS-CoV-2 RNA Dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) – A drug repurposing study. Heliyon 6:e04502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04502
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang M-Q (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9030042
Ali MdA, Ahmed T, Wu W, Hossain A, Hafeez R, Islam Masum MdM, Wang Y, An Q, Sun G, Li B (2020) Advancements in plant and microbe-based synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity against plant pathogens. Nanomaterials 10:1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061146
Alloway BJ (2013) Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In: Heavy metals in soils, pp 11–50. Springer, Dordrecht
Ananda A, Ramakrishnappa T, Archana S, Reddy Yadav LS, Shilpa BM, Nagaraju G, Jayanna BK (2022) Green synthesis of MgO nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica for Evans blue degradation and antibacterial activity. Mater Today Proc 49:801–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.340
Andreotti F, Rocca B, Husted S, Ajjan RA, ten Berg J, Cattaneo M, Collet J-P, De Caterina R, Fox KAA, Halvorsen S, Huber K, Hylek EM, Lip GYH, Montalescot G, Morais J, Patrono C, Verheugt FWA, Wallentin L, Weiss TW, Storey RF, ESC Thrombosis Working Group (2015) Antithrombotic therapy in the elderly: expert position paper of the European society of cardiology working group on thrombosis. Eur Heart J 36:3238–3249. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv304
Annamalai J, Ummalyma SB, Pandey A, Bhaskar T (2021) Recent trends in microbial nanoparticle synthesis and potential application in environmental technology: a comprehensive review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:49362–49382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15680-x
Archana S, Jayanna BK, Ananda A, Shilpa BM, Pandiarajan D, Muralidhara HB, Kumar KY (2021) Synthesis of nickel oxide grafted graphene oxide nanocomposites—a systematic research on chemisorption of heavy metal ions and its antibacterial activity. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100486
Cangemi DJ, Kuo B (2019) Practical perspectives in the treatment of nausea and vomiting. J Clin Gastroenterol 53:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000001164
Chakraborty S, Chowdhury S, Das Saha P (2011) Adsorption of crystal violet from aqueous solution onto NaOH-modified rice husk. Carbohyd Polym 86:1533–1541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.058
Chen A, Contreras LM, Keitz BK (2017) Imposed environmental stresses facilitate cell-free nanoparticle formation by deinococcus radiodurans. Appl Environ Microbiol 83. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00798-17
Chowdhury SR, Yanful EK, Pratt AR (2011) Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by mixed magnetite–maghemite nanoparticles. Environ Earth Sci 64:411–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0865-z
Chung I-M, Park I, Seung-Hyun K, Thiruvengadam M, Rajakumar G (2016) Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1257-4
Coelho J, Mendoza-Sánchez B, Pettersson H, Pokle A, McGuire EK, Long E, McKeon L, Bell AP, Nicolosi V (2015) Manganese oxide nanosheets and a 2D hybrid of graphene–manganese oxide nanosheets synthesized by liquid-phase exfoliation. 2D Mater 2:025005. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1583/2/2/025005
Das P, Ghosh S, Ghosh R, Dam S, Baskey M (2018) Madhuca longifolia plant mediated green synthesis of cupric oxide nanoparticles: a promising environmentally sustainable material for waste water treatment and efficient antibacterial agent. J Photochem Photobiol B 189:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.09.023
Das PK, Das BP, Dash P (2021) Chromite mining pollution, environmental impact, toxicity and phytoremediation: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:1369–1381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01102-w
Dipaolo JA, Nelson RL, Casto BC (1978) In vitro neoplastic transformation of Syrian hamster cells by lead acetate and its relevance to environmental carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer 38:452–455. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1978.228
Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F, Barzegar-Jalali M, Zarrintan MH, Adibkia K (2014) Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 44:278–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.08.031
Ebrahimbabaie P, Meeinkuirt W, Pichtel J (2020) Phytoremediation of engineered nanoparticles using aquatic plants: Mechanisms and practical feasibility. J Environ Sci 93:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.03.034
Fair RJ, Tor Y (2014) Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st century. Perspect Medicin Chem 6:PMC.S14459. https://doi.org/10.4137/PMC.S14459
Fajardo C, Sánchez-Fortún S, Costa G, Nande M, Botías P, García-Cantalejo J, Mengs G, Martín M (2020) Evaluation of nanoremediation strategy in a Pb, Zn and Cd contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 706:136041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136041
Fayiga AO, Ma LQ, Zhou Q (2007) Effects of plant arsenic uptake and heavy metals on arsenic distribution in an arsenic-contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 147:737–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.09.010
Gade A, Gaikwad S, Duran N, Rai M (2014) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Phoma glomerata. Micron 59:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2013.12.005
Gahlawat G, Choudhury AR (2019) A review on the biosynthesis of metal and metal salt nanoparticles by microbes. RSC Adv 9:12944–12967. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA10483B
Glenn JB, White SA, Klaine SJ (2012) Interactions of gold nanoparticles with freshwater aquatic macrophytes are size and species dependent: Interactions of AuNPs with freshwater aquatic plants. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.728
Huang M, Zhu Y, Li Z, Huang B, Luo N, Liu C, Zeng G (2016) Compost as a soil amendment to remediate heavy metal-contaminated agricultural soil: mechanisms, efficacy, problems, and strategies. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3068-8
Huang G, Zhang M, Liu C, Li L, Chen Z (2018) Heavy metal (loid) s and organic contaminants in groundwater in the pearl river delta that has undergone three decades of urbanization and industrialization: distributions, sources, and driving forces. Sci Total Environ 635:913–925
Hussain A, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Ali S (2019) Seed priming with silicon nanoparticles improved the biomass and yield while reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat grains. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:7579–7588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04210-5
Iavicoli I, Fontana L, Leso V, Bergamaschi A (2013) The effects of nanomaterials as endocrine disruptors. IJMS 14:16732–16801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816732
Inoue KI (2013) Heavy metal toxicity. J Clinic Toxicol S 3:2161–2495
Jadimurthy R, Mayegowda SB, Nayak SC, Mohan CD, Rangappa KS (2022) Esca** mechanisms of ESKAPE pathogens from antibiotics and their targeting by natural compounds. Biotechnol Rep 34:e00728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2022.e00728
Kabir MH, Islam MS, Hoq ME, Tusher TR, Islam MS (2020) Appraisal of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Shitalakhya River in Bangladesh using pollution indices, geo-spatial, and multivariate statistical analysis. Arab J Geosci 13(21):1–13
Kapahi M, Sachdeva S (2019) Bioremediation options for heavy metal pollution. J Health Pollut 9:191203. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-9.24.191203
Karthiga D, Anthony SP (2013) Selective colorimetric sensing of toxic metal cations by green synthesized silver nanoparticles over a wide pH range. RSC Adv 3:16765. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra42308e
Kaur S, Roy A (2021) Bioremediation of heavy metals from wastewater using nanomaterials. Environ Dev Sustain 23:9617–9640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01078-1
Khan M, Shaik MR, Khan ST, Adil SF, Kuniyil M, Khan M, Al-Warthan AA, Siddiqui MRH, Nawaz Tahir M (2020) Enhanced antimicrobial activity of biofunctionalized zirconia nanoparticles. ACS Omega 5:1987–1996. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03840
Kieta KA, Owens PN (2019) Phosphorus release from shoots of Phleum pretense L. after repeated freeze-thaw cycles and harvests. Ecol Eng 127:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.11.024
Kulkarni RR, Shaiwale NS, Deobagkar DN, Deobagkar DD (2015) Synthesis and extracellular accumulation of silver nanoparticles by employing radiation-resistant Deinococcus radiodurans, their characterization, and determination of bioactivity. Int J Nanomedicine 10:963–974. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S72888
Kumar M, Nagdev R, Tripathi R, Singh VB, Ranjan P, Soheb M, Al R (2019) Geospatial and multivariate analysis of trace metals in tubewell water using for drinking purpose in the upper Gangetic basin, India: Heavy metal pollution index. Groundw Sustain Dev 8:122–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.10.001
Kumar D (2020) An analysis of earth system approach to the global pact for the environment-international environmental law-making and diplomacy review 2019 Chapter 4. Int Environ Law Making Diplomacy Rev 2019
Lawal AO (2017) Air particulate matter induced oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis: The role of Nrf2 and AhR-mediated pathways. Toxicol Lett 270:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.01.017
Li J, Li Q, Ma X, Tian B, Li T, Yu J, Dai S, Weng Y, Hua Y (2016) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by the extreme bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans and an evaluation of their antibacterial properties. Int J Nanomedicine 11:5931–5944
Liu W, Liu L, Kou G, Zheng Y, Ding Y, Ni W, Wang Q, Tan L, Wu W, Tang S, **ong Z, Zheng S (2020) Evaluation of nucleocapsid and spike protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. J Clin Microbiol 58:e00461-e520. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00461-20
Maiti S, Barman G, Konar Laha J (2016) Detection of heavy metals (Cu+2, Hg+2) by biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 6:529–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0452-4
Mayegowda SB, Ng M, Alghamdi S, Atwah B, Alhindi Z, Islam F (2022) Role of antimicrobial drug in the development of potential therapeutics. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2022:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2500613
Mehta VN, Kumar MA, Kailasa SK (2013) Colorimetric detection of copper in water samples using dopamine dithiocarbamate-functionalized au nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:4414–4420. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie302651f
Mohammed YMM, Khedr YI (2021) Applications of Fusarium solani YMM20 in bioremediation of heavy metals via enhancing extracellular green synthesis of nanoparticles. Water Environ Res 93:1600–1607. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1542
Mohd Yusof H, Mohamad R, Zaidan UH, Abdul Rahman NA (2019) Microbial synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential application as an antimicrobial agent and a feed supplement in animal industry: a review. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 10:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-019-0368-z
Mujaddidi N, Nisa S, Al Ayoubi S, Bibi Y, Khan S, Sabir M, Qayyum A (2021) Pharmacological properties of biogenically synthesized silver nanoparticles using endophyte Bacillus cereus extract of Berberis lyceum against oxidative stress and pathogenic multidrug-resistant bacteria. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(11):6432–6440
Mulware SJ (2013) Trace elements and carcinogenicity: a subject in review. 3 Biotech 3:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-012-0072-6
Naghdi M, Taheran M, Brar SK, Kermanshahi-pour A, Verma M, Surampalli RY (2019) Fabrication of nanobiocatalyst using encapsulated laccase onto chitosan-nanobiochar composite. Int J Biol Macromol 124:530–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.234
Nagore P, Ghotekar S, Mane K, Ghoti A, Bilal M, Roy A (2021) Structural properties and antimicrobial activities of polyalthia longifolia leaf extract-mediated CuO nanoparticles. BioNanoScience 11:579–589
Omidifar N, Nili-Ahmadabadi A, Nakhostin-Ansari A, Lankarani KB, Moghadami M, Mousavi SM, Hashemi SA, Gholami A, Shokripour M, Ebrahimi Z (2021) The modulatory potential of herbal antioxidants against oxidative stress and heavy metal pollution: plants against environmental oxidative stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:61908–61918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16530-6
Omran BA, Whitehead KA, Baek K-H (2021) One-pot bioinspired synthesis of fluorescent metal chalcogenide and carbon quantum dots: applications and potential biotoxicity. Colloids Surf B 200:111578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111578
Pandit C, Roy A, Ghotekar S, Khusro A, Islam MN, Emran TB, Bradley DA (2022) Biological agents for synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications. J King Saud Univ Sci:101869
Patil PM, Mahamuni PP, Shadija PG, Bohara RA (2019) Conversion of organic biomedical waste into value added product using green approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:6696–6705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4001-z
Pattanayak DS, Pal D, Thakur C, Kumar S, Devnani GL (2021) Bio-synthesis of iron nanoparticles for environmental remediation: Status till date. Mater Today Proc 44:3150–3155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.821
Priyadarshini E, Priyadarshini SS, Cousins BG, Pradhan N (2021) Metal-fungus interaction: review on cellular processes underlying heavy metal detoxification and synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Chemosphere 274:129976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129976
Rahman Z, Singh VP (2020) Bioremediation of toxic heavy metals (THMs) contaminated sites: concepts, applications and challenges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:27563–27581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08903-0
Raval NP, Kumar M (2021) Geogenic arsenic removal through core–shell based functionalized nanoparticles: groundwater in-situ treatment perspective in the post–COVID anthropocene. J Hazard Mater 402:123466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123466
Roy A, Singh V, Sharma S, Ali D, Azad AK, Kumar G, Emran TB (2022) Antibacterial and dye degradation activity of green synthesized iron nanoparticles. J Nanomaterials
Roy A, Elzaki A, Tirth V, Kajoak S, Osman H, Algahtani A, Bilal M (2021) Biological synthesis of nanocatalysts and their applications. Catalysts 11(12):1494
Roychoudhury A (2020) Yeast-mediated green synthesis of nanoparticles for biological applications. Indian J Pharm Bio Res 8(03):26–31
Sebastian A, Nangia A, Prasad MNV (2018) A green synthetic route to phenolics fabricated magnetite nanoparticles from coconut husk extract: Implications to treat metal contaminated water and heavy metal stress in Oryza sativa L. J Clean Prod 174:355–366
Shafi I, Liang E, Li B (2021) Ultrafine chromium oxide (Cr2O3) nanoparticles as a pseudocapacitive electrode material for supercapacitors. J Alloy Compd 851:156046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156046
Shamsul Harumain ZA (2016) Phytomining of precious metals from mine wastes. Doctoral dissertation, University of York
Sharma P, Kumar S (2021) Bioremediation of heavy metals from industrial effluents by endophytes and their metabolic activity: recent advances. Biores Technol 339:125589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125589
Shittu KO, Ihebunna O (2017) Purification of simulated waste water using green synthesized silver nanoparticles of Piliostigma thonningii aqueous leave extract. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:045003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6254/aa8536
Singh J, Vashisht AK, Sharma M (2016) Efficiency analysis of indian commercial banks: a DEA approach. Int J Banking Risk Insur 4(2):27
Sytar O, Kumari P, Yadav S, Brestic M, Rastogi A (2019) Phytohormone priming: regulator for heavy metal stress in plants. J Plant Growth Regul 38:739–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9886-8
Tak YK, Pal S, Naoghare PK, Rangasamy S, Song JM (2015) Shape-dependent skin penetration of silver nanoparticles: does it really matter? Sci Rep 5:16908. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16908
Tang SCN, Lo IMC (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles: essential factors for sustainable environmental applications. Water Res 47:2613–2632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.02.039
Tiquia-Arashiro S, Rodrigues DF (2016) Extremophiles: applications in nanotechnology. Springer, Cham
Tiwari S, Lata C (2018) Heavy metal stress, signaling, and tolerance due to plant-associated microbes: an overview. Front Plant Sci 9:452. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00452
Thakare M, Sarma H, Datar S, Roy A, Pawar P, Gupta K, Prasad R (2021) Understanding the holistic approach to plant-microbe remediation technologies for removing heavy metals and radionuclides from soil. Current Res Biotechnol 3:84–98
Uchimiya M, Bannon D, Nakanishi H, McBride MB, Williams MA, Yoshihara T (2020) Chemical speciation, plant uptake, and toxicity of heavy metals in agricultural soils. J Agric Food Chem 68:12856–12869. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00183
Varjani S, Rakholiya P, Ng HY, You S, Teixeira JA (2020) Microbial degradation of dyes: an overview. Biores Technol 314:123728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123728
Varun BV, Prabhu KR (2014) Regioselective thiolation of arenes and heteroarenes: C–H functionalization strategy for C–S bond formation. J Org Chem 79:9655–9668. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo501793q
Verma A, Bharadvaja N (2021) Plant-mediated synthesis and characterization of silver and copper oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial and heavy metal removal activity. J Clust Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02091-8
Vijayan SR, Santhiyagu P, Singamuthu M, Kumari Ahila N, Jayaraman R, Ethiraj K (2014) Synthesis and characterization of silver and gold nanoparticles using aqueous extract of seaweed, turbinaria conoides, and their antimicrofouling activity. Sci World J 2014:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/938272
Wu F, Zhang J, **ao A, Gu X, Lee WL, Armas F, Kauffman K, Hanage W, Matus M, Ghaeli N, Endo N, Duvallet C, Poyet M, Moniz K, Washburne AD, Erickson TB, Chai PR, Thompson J, Alm EJ (2020) SARS-CoV-2 titers in wastewater are higher than expected from clinically confirmed cases. mSystems 5. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00614-20
Yadav LSR, Shilpa BM, Suma BP, Venkatesh R, Nagaraju G (2021) Synergistic effect of photocatalytic, antibacterial and electrochemical activities on biosynthesized zirconium oxide nanoparticles. Eur Phys J plus 136:764. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01606-6
Yu G, Wang X, Liu J, Jiang P, You S, Ding N, Guo Q, Lin F (2021) Applications of nanomaterials for heavy metal removal from water and soil: a review. Sustainability 13:713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020713
Yue L, Lian F, Han Y, Bao Q, Wang Z, **ng B (2019) The effect of biochar nanoparticles on rice plant growth and the uptake of heavy metals: implications for agronomic benefits and potential risk. Sci Total Environ 656:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.364
Zou L, Zhu F, Long Z, Huang Y (2021) Bacterial extracellular electron transfer: a powerful route to the green biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials for multifunctional applications. J Nanobiotechnol 19:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00868-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shilpa, B.M., Rashmi, R., Manjula, N.G., Sreekantha, A. (2022). Bioremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Sites Using Phytogenic Nanoparticles. In: Shah, M.P., Roy, A. (eds) Phytonanotechnology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4811-4_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4811-4_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-4810-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-4811-4
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)