Abstract
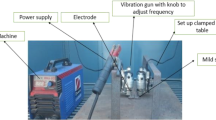
To improve the fracture toughness, “Post weld heat treatment” (PWHT) processes came into existence, but it is time-consuming, more cost, and laborious. To substitute the PWHT, Mechanical excitations are transferred throughout welding progression to enhance the weldment grain formation and fracture toughness. The vibrations are transferred to the molten state of the weld pool before it gets solidified during flux shielded manual arc welding technique (SMAW). The novel vibratory technique is introduced to vibrate the specimens mechanically and impact strength is investigated experimentally. The effect of experimental input process parameters on impact strength was compared with the conventional welding process. Results revealed the Impact strength with excitations is increased by 17% when it is compared with conventional arc welded specimen’s impact strength and the major influencing factor for improved flexural strength is a voltage at 190 V of vibrating-motor, and 18 V of D.C—Motor coupled to electrode. The microstructures of the vibratory weld joints are studied in-depth and compared with conventional prepared SMAW welded joints. Uniform and refined grain structures are identified on welded joints prepared with vibrations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker, C.A., Waddell, A.J., Johnston, D.J.: Vibratory stress relief—an investigation of the underlying processes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 209(1), 51–58 (1995)
Tewari, S.P.: Effects of transverse oscillation on tensile properties of mild steel weldments. ISIJ Int. 39(6), 570–574 (1999)
Munsi, A.S.M.Y., Waddell, A.J., Walker, C.A.: Vibratory weld conditioning—the effect of rigid body motion vibration during welding. Strain 35(4), 139–143 (1999)
Musin, A.S.M.Y., Waddell, A.J., Walker, C.A.: The influence of vibratory treatment on the fatigue life of welds: a comparison with thermal stress relief. Strain 37(4)
Munsi, A.S.M.Y., Waddell, A.J., Walker, C.A.: Vibratory stress relief—an investigation of the torsional stress effect in welded shafts. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Design 36(5), 453–464 (2001)
Sakthivel, P., Sivakumar, P.: Effect of vibration in Tig and arc welding using AISI 316 stainless steel. Int. J. Eng. Res. Sci. Technol. 3(4), 116–130 (2014)
Pučko, B., Gliha, V.: Charpy toughness of vibrated microstructures. Metalurgija 44(2), 103–106 (2005)
Rao, D.L., et al.: Reduce the residual stress of welded structures by post-weld vibration. Mater. Sci. Forum. 490 (2005)
Zhu, Z.Q., Chen, L.G., Rao, D.L.: Relieving welding residual stress by applying vibratory weld conditioning. Mater. Sci. Forum 490 (2005)
Joseph, A., et al.: Evaluation of residual stresses in dissimilar weld joints. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 82(9), 700–705 (2005)
Bade, V.S., Srinivasa Rao, P., Govinda Rao, P.: The effect of vibratory conditioning on tensile strength and microstructure of 1018 mild steel. World J. Eng. 17(6), 837–844 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/WJE-07-2020-0296
Bade, V.S., Srinivasa Rao, P., Govinda Rao, P.: Experimental investigation on influence of electrode vibrations on hardness and microstructure of 1018 mild steel weldments. World J. Eng. 17(4), 509–517 (2020)
Suresh, B.V., Shireesha, Y., Srinivasa Rao, P.: Effect of electrode vibration welding on impact and tensile strength of 1018 mild steel weld joints. In: Dave, H.K., Dixit, U.S., Nedelcu, D. (eds.) Recent Advances in Manufacturing Processes and Systems. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7787-8_26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Venkata Suresh, B., Shireesha, Y., Srinivasa Rao, P. (2023). Influence of Mechanical Vibrations on Impact Strength of 1018 Mild Steel Butt-Weld-Joints. In: Deepak, B., Bahubalendruni, M.R., Parhi, D., Biswal, B.B. (eds) Recent Trends in Product Design and Intelligent Manufacturing Systems. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4606-6_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4606-6_58
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-4605-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-4606-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)