Abstract
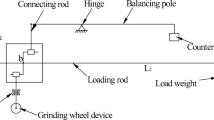
The primary goal of this research is to investigate the effect of tribo-test parameters on the coefficient of friction (COF) and wear rate of the cylinder liner and piston ring pair. The tribological studies are carried out utilizing a full factorial design (FFD) experimental scheme. Sliding speed, temperature, volume concentration, and applied force were all evaluated as important parameters that determine tribological qualities. The effects of various variables and their interactions on the dependent variables were investigated. The ANOVA analysis demonstrates that the applied load could be the most influential factor affecting the minimum amount of the friction coefficient. The minimum quantity of wear rate indicates that as the sliding speed increases, the wear rate decreases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kapsiz M, Durat M, Ficici F (2011) Friction and wear studies between cylinder liner and piston ring pair using Taguchi design method. Adv Eng Softw 42(8):595–603
Ali MKA, ** C, Turkson RF, Bicheng C (2016) Improving the tribological characteristics of piston ring assembly in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Tribol Int 103:540–554
Davim JP (2011) Tribology for engineers: a practical guide. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Arumugam S, Sriram G (2012) Effect of bio-lubricant and biodiesel-contaminated lubricant on tribological behavior of cylinder liner–piston ring combination. Tribol Trans 55(4):438–445
Nadooshan AA, Esfe MH, Afrand M (2017) Evaluation of rheological behavior of 10W40 lubricant containing hybrid nano-material by measuring dynamic viscosity. Physica E 92:47–54
Esfe MH, Saedodin S, Rejvani M, Shahram J (2017) Experimental investigation, model development and sensitivity analysis of rheological behavior of ZnO/10W40 nano-lubricants for automotive applications. Physica E 90:194–203
Wu H, Zhao J, **a W, Cheng X, He A, Yun JH, Wang L, Huang H, Jiao S, Huang L (2017) A study of the tribological behaviour of TiO2 nano-additive water-based lubricants. Tribol Int 109:398–408
Wu H, Zhao J, **a W, Cheng X, He A, Yun JH, Wang L, Huang H, Jiao S, Huang L (2017) Analysis of TiO2 nano-additive water-based lubricants in hot rolling of microalloyed steel. J Manuf Process 27:26–36
Hisham S, Kadirgama K, Ramasamy D, Noor M, Amirruddin A, Najafi G, Rahman M (2017) Waste cooking oil blended with the engine oil for reduction of friction and wear on piston skirt. Fuel 205:247–261
Wu H, Wang L, Johnson B, Yang S, Zhang J, Dong G (2018) Investigation on the lubrication advantages of MoS2 nanosheets compared with ZDDP using block-on-ring tests. Wear 394:40–49
Kakaš D, Škorić B, Mitrović S, Babić M, Terek P, Miletić A, Vilotić M (2009) Influence of load and sliding speed on friction coefficient of IBAD deposited TiN. Tribol Ind 31(3–4):3–10
Kasdekar DK, Parashar V (2018) Principal component analysis to optimize the ECM parameters of aluminium alloy. Mater Today Proc 5(2):5398–5406
Soundararajan R, Ramesh A, Sivasankaran S, Vignesh M (2017) Modeling and analysis of mechanical properties of aluminium alloy (A413) reinforced with boron carbide (B4C) processed through squeeze casting process using artificial neural network model and statistical technique. Mater Today Proc 4(2):2008–2030
Sunil B, Rajeev V, Jose S (2018) A statistical study on the dry wear and friction characteristics of Al-12.6Si-3Cu-(2–2.6 wt.%)Ni piston alloys. Mater Today Proc 5(1):1131–1137
Kamarulzaman MK, Abdullah A (2020) Multi-objective optimization of diesel engine performances and exhaust emissions characteristics of Hermetia illucens larvae oil-diesel fuel blends using response surface methodology. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Utilization Environ Effects 1–14
Ridzuan N, Adam F, Yaacob Z (2016) Screening of factor influencing wax deposition using full factorial experimental design. Pet Sci Technol 34(1):84–90
Asnida M, Hisham S, Awang N, Amirruddin A, Noor M, Kadirgama K, Ramasamy D, Najafi G, Tarlochan F (2018) Copper (II) oxide nanoparticles as additive in engine oil to increase the durability of piston-liner contact. Fuel 212:656–667
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by University Malaysia Pahang [grant number RDU192402]. “Mohd Kamal bin Kamarulzaman” is the recipient of the UMP Post-Doctoral Fellowship in Research.
Credit Authorship Contribution Statement
N. W. Awang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Visualization. Sakinah Hisham: Conceptualization, Investigation. D. Ramasamy, K. Kadirgama: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Writing—Review and Editing, Visualization, Supervision. Mohd Kamal Kamarulzaman: Conceptualization.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Awang, N.W., Hisham, S., Ramasamy, D., Kadirgama, K., Kamarulzaman, M.K. (2023). Statistical Approach to the Cellulose Nanocrystal Tribological Behavior on the Piston Liner Contact Using Full Factorial Design (FFD). In: Johari, N.H., Wan Hamzah, W.A., Ghazali, M.F., Setiabudi, H.D., Kumarasamy, S. (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd Energy Security and Chemical Engineering Congress. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4425-3_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4425-3_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-4424-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-4425-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)