Abstract
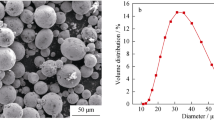
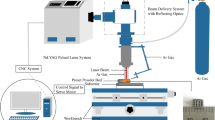
In this paper, direct metal laser sintering process was used to produce AlSi10Mg components by employing different parametric combinations. Laser intensity, scan speed, and hatch distance were regarded as the autonomous parameters. A laser energy density (led) function expressed these three parameters. Fabricated component’s density was evaluated by the Archimedes principle. Measured densities were demonstrated as relative density (rd) by indicating it as percentage of the actual density of the alloy (2.67 gm/cm3). In our study, the led–rd–structure relationship is discussed. The highest led of 93.43 J/mm3 yielded the least rd of 95.88%. Its microstructure showed numerous irregularly shaped pores; its surface topography also revealed a large amount of balling and satellite formation, whereas for the sample with the maximum rd value of 99.63%, which was fabricated by employing a led of 61.11 J/mm3, it showed very few pores and almost negligible balling formation. The above analysis revealed that surface topography also had an impactful role in determining the density of the component. This study also showed an interrelation between relative density and tensile strength of the alloy; the component with the best relative density showed a higher ultimate tensile strength value than the component with the least relative density value. A superior tensile strength property of the dog bone sample with the highest relative density was found when it was compared with the tensile strength properties of the A360 die-cast material.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yakout, M, Elbestawi MA, Veldhuis SC (2019). Density and mechanical properties in selective laser melting of Invar 36 and stainless steel 316L. J Mater Process Technol 266:403
Read N, Wang W, Essa K, Attallah MM (2015) Selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg alloy: process optimisation and mechanical properties development. Mater Des 65:417
Wang L-Z, Chen T, Wang S (2017) Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced AlSi10Mg composites fabricated by selective laser melting. Optik 143:175
Kempen K, Thijs L, Yasa E, Badrossamay M, Verheecke W, Kruth J-P (2011). Process optimization and microstructural analysis for selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg. In: Solid freeform fabrication symposium. Texas, USA, Aug 2011
Aboulkhair NT, Everitt NM, Ashcroft I, Tuck C (2014) Reducing porosity in AlSi10Mg parts processed by selective laser melting. Addit Manuf 1:83
Krishnan M, Atzen E, Canali R, Calignano F, Manfredi D, Ambrosio EP, Luliano L (2014) On the effect of process parameters on properties of AlSi10Mg parts produced by DMLS. Rapid Prototy** J 20:(16)
Kempen K, Thijs L, Van Humbeeck J, Kruth J-P (2012) Mechanical properties of AlSi10Mg produced by selective laser melting. Phys Procedia 39:441
Aboulkhaira NT, Maskerya I, Tucka C, Ashcrofta I, Everittb NM (2016) On the formation of AlSi10Mg single tracks and layers in selective laser melting: Microstructure and nano-mechanical properties. J Mater Process Technol 230:92
Shah RK, Dey PP (2019) Process parameter optimization of dmls process to produce AlSi10Mg components. In: 2nd International conference on new frontiers in engineering, science & technology (NFEST), Kurukshetra, India, Journal of physics: conference series, 18–22 Feb 2019
Yang S, Evans JRG (2007) Metering and dispensing of powder; the quest for new solid freeforming techniques. Powder Technol 178(1):57
Molina JM, Voytovychb R, Louisa E, Eustathopoulos N (2007) The surface tension of liquid aluminium in high vacuum: The role of surface condition. Int J Adhes Adhes 27:396
Liu YJ, Liu Z, Jiang Y, Wang GW, Yang Y, Zhang LC (2017) Gradient in microstructure and mechanical property of selective laser melted AlSi10Mg. J Alloys Compound 735:11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shah, R.K., Dey, P.P. (2023). Mechanical Properties, Microstructural and Surface Topography Evaluation of AlSi10Mg Alloy Produced by DMLS Process. In: Sudarshan, T.S., Pandey, K.M., Misra, R.D., Patowari, P.K., Bhaumik, S. (eds) Recent Advancements in Mechanical Engineering. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-3266-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-3266-3_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-3265-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-3266-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)