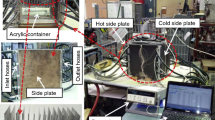
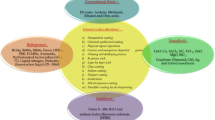
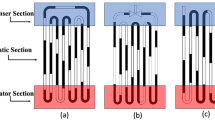
Abstract
Thermal management has a big impact on how long electronic gadgets last and how well they work. With the ever-increasing number of closely packed electronic devices, heat transport concerns in such devices are becoming increasingly common. Pulsating heat pipes (PHPs) are newly developed devices in which two-phase heat transfer occurs. The most favorable advantage of PHPs over conventional heat pipes is that the PHP does not have wick structure through which condensate returns for heating purpose. Many researchers have analyzed and performed studies on pertinent design of PHPs, but due to thermodynamics and hydrodynamics combined effect, the working mechanism of PHP is exceptionally multifaceted. Further, the use of nano-fluids has attained significant attention over the last few decades because of higher heat transfer capabilities. Researchers have suggested hybrid nano-fluids for power applications where more heating is required; however, this mechanism has not been completely explored. The present review explores the current research trends in PHPs in terms of its main features and working parameters based on experimental and numerical analysis as well as multiphase modeling.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D:
-
Diameter, m
- Eo:
-
Eotvos number
- Bo:
-
Bond number
- R:
-
Thermal resistance, K/W
- N:
-
Number of turns
- ρ density:
-
Kg/m3
- σ surface tension:
-
N/m
- h:
-
Hydraulic
- crit:
-
Critical
- l:
-
Liquid
- g:
-
Vapor
References
Akachi H (1990) Structure of heat pipe, United State Patent, no. 19, 1990
Aubin P, D’Entremont B, Cataldo F, Marcinichen JB, Amalfi RL, Thome JR (2019) Numerical simulations of pulsating heat pipes, part 1: modeling. In: 2019 18th IEEE intersociety conference on thermal and thermomechanical phenomena in electronic systems (ITherm), pp 232–242, 2019
Baitule DA (2013) Experimental analysis of closed loop pulsating heat pipe with variable filling. Int J Mech Eng Robot Res 2(3)
Chen M, Li J (2020) Nanofluid-based pulsating heat pipe for thermal management of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. J Energy Storage 32
Czajkowski C, Nowak AI, Błasiak P, Ochman A, Pietrowicz S (2020) Experimental study on a large scale pulsating heat pipe operating at high heat loads, different adiabatic lengths and various filling ratios of acetone, ethanol, and water. Appl Thermal Eng 165:114534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114534
Han X, Wang X, Zheng H, Xu X, Chen G (2016) Review of the development of pulsating heat pipe for heat dissipation. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 59:692–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.350
Jafarmadar S, Azizinia N, Razmara N, Mobadersani F (2016) Thermal analysis and entropy generation of pulsating heat pipes using nanofluids. Appl Therm Eng 103:356–364
Khandekar S (2004) Thermo- hydrodynamics of closed loop pulsating heat pipe. Universitaet Stuttgart, Germany
Kim W, Kim SJ (2020) Effect of a flow behavior on the thermal performance of closed-loop and closed-end pulsating heat pipes. Int J Heat Mass Trans 149:119251
Mohammadi M, Mohammadi M, Ghahremani AR, Shafii MB, Mohammadi N (2014) Experimental investigation of thermal resistance of a ferrofluidic closed-loop pulsating heat pipe. Heat Transfer Eng 35(1):25–33
Noh HY, Kim SJ (2020) Numerical simulation of pulsating heat pipes: parametric investigation and thermal optimization. Energy Convers Manag 203:112237
Parwani A, Gupta A (2017) CFD modeling for thermal performance of closed loop pulsating heat pipe in bottom heated mode, pp 46–50
**ng M, Yu J, Wang R (2017) Performance of a vertical closed pulsating heat pipe with hydroxylated MWNTs nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 112:81–88
Xu H, Zhang P, Yan L, Xu D, Ma W, Wang L (2019) Thermal characteristic and analysis of microchannel structure flat plate pulsating heat pipe with silver nanofluid. IEEE Access 7:51724–51734
Xu Y, Xue Y, Qi H, Cai W (2020) Experimental study on heat transfer performance of pulsating heat pipes with hybrid working fluids. Int J Heat Mass Trans 157
Yang H, Khandekar S, Groll M (2009) Performance characteristics of pulsating heat pipes as integral thermal spreaders. Int J Therm Sci 48(4):815–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2008.05.017
Zufar M, Gunnasegaran P, Kumar HM, Ng KC (2020) Numerical and experimental investigations of hybrid nanofluids on pulsating heat pipe performance. Int J Heat Mass Trans 146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Parmar, K., Parwani, A.K., Tripathi, S. (2022). A Review on Recent Advances in Pulsating Heat Pipes. In: Parwani, A.K., Ramkumar, P., Abhishek, K., Yadav, S.K. (eds) Recent Advances in Mechanical Infrastructure . Lecture Notes in Intelligent Transportation and Infrastructure. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7660-4_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7660-4_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-7659-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-7660-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)