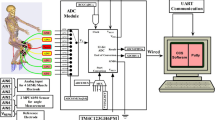
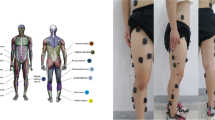
Abstract
Surface electromyography (sEMG) signal is widely used in lower limb exoskeleton system because it can reflect human motion intention. Aiming at the problem of low decoding accuracy of joint motion angle of lower limb exoskeleton robot, a knee motion angle prediction method based on sEMG signal is proposed. Firstly, in order to solve the problem of high time efficiency and insufficient stability of single time domain feature extraction method for sEMG signal, the eigenvalues are extracted from time domain, frequency domain and time-frequency domain respectively, and the prediction error of different channel sEMG signal feature parameter combination model is analyzed. Then, an innovative particle swarm optimization LSTM deep learning algorithm (PSO-LSTM) is proposed to establish the map** model between sEMG signal and knee joint angle, and determine the PSO-LSTM model corresponding to the optimal feature parameter combination to realize the accurate prediction of knee joint angle. Finally, the experimental results show that the predicted results of the model are highly consistent with the real angle values, which is helpful to improve the human-computer cooperation of the lower limb exoskeleton system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luh, G.C., Cai, J.J., Lee, Y.S.: Estimation of elbow motion intension under varing weight in lifting movement using an EMG-Angle neural network model. In: 2017 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), vol. 2, pp. 640–645. IEEE (2017)
Chen, Y., Zhao, X., Han, J.: Hierarchical projection regression for online estimation of elbow joint angle using EMG signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 23(3.4), 1129–1138 (2013)
Zhang, F., Li, P., Hou, Z.G., et al.: sEMG-based continuous estimation of joint angles of human legs by using BP neural network. Neurocomputing 78(1), 139–148 (2012)
Ngeo, J., Tamei, T., Shibata, T.: Continuous estimation of finger joint angles using muscle activation inputs from surface EMG signals. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, vol. 2012, pp. 2756–2759. IEEE (2012)
Raj, R., Rejith, R., Sivanandan, K.S.: Real time identification of human forearm kinematics from surface EMG signal using artificial neural network models. Procedia Technol. 25, 44–51 (2016)
Wang, S., Gao, Y., Zhao, J., et al.: Prediction of sEMG-based tremor joint angle using the RBF neural network. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, pp. 2103–2108. IEEE (2012)
Ren, J.L., Chien, Y.H., Chia, E.Y., et al.: Deep Learning based motion prediction for exoskeleton robot control in upper limb rehabilitation. In: 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5076–5082. IEEE (2019)
Kwon, S., Kim, J.: Real-time upper limb motion estimation from surface electromyography and joint angular velocities using an artificial neural network for human-machine cooperation. IEEE Trans. Inf Technol. Biomed. 15(4), 522–530 (2011)
Ying, S.: Measurement of human joint angle and neural network prediction based on sEMG signal recognition. Tian** University (2005)
Li, X., Yang, J., Shi, Y., et al.: Identification of arm motion state based on EMG signal. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 24(4), 416–420 (2005)
Fitzpatrick, R., Burke, D., Gandevia, S.C.: Task-dependent re-exresponses and movement illusions evoked by galvanic vestibular stimulation in standing humans. J. Physiol. 478(Pt 2), 363–372 (1994)
Fitzpatrick, R., Mccloskey, D.I.: Proprioceptive, visual and vestibular thresholds for the perception of sway during standing in humans. J. Physiol. 478(Pt 1), 173–186 (1994)
Simoneau, G.G., Derr, J.A., Ulbrecht, J.S., et al.: Diabetic sensory neuropathy effect on ankle joint movement perception. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 77(5), 453–460 (1996)
Winter, D.A., Patla, A.E., Prince, F., et al.: Stiffness control of balance in quiet standing. J. Neurophysiol. 80(3), 1211–1221 (1998)
Yanji, J.: Research on Key Technologies of Multi-sensor Data Fusion. Harbin Engineering University (2010)
Li, S., Luo, Z., Meng, M.: Lower limb motion information acquisition method based on acceleration sensor. Mech. Electr. Eng. 26(1), 5–7, 16 (2009)
Gottschall, J.S., Kram, R.: Energy cost and muscular activity required for propulsion during walking. J. Appl. Physiol. 94(5), 1766–1772 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, J., Tao, Y., Huang, Y., Zhao, Z., Zhou, S. (2022). Joint Angle Prediction of Lower Extremity Exoskeleton Based on sEMG Signal. In: Jia, Y., Zhang, W., Fu, Y., Yu, Z., Zheng, S. (eds) Proceedings of 2021 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 804. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6324-6_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6324-6_68
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-6323-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-6324-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)