Abstract
The reactive oxygen species or ROS, a cumulative term for reactive oxygen containing molecules in biological system, can provide molecular signatures in diseases. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a fundamental role in cellular processes. Produced as a result of biological process, the ROS levels and signaling are affected in diseased state. ROS modeling using mathematical models and further improving design of scavengers or sensitizers using computer-aided drug design (CADD) are promising and powerful technologies for relatively quicker, cheaper, and successful drug discovery by essentially drop** the overall cost and time required. This chapter aims to highlight the emerging scope of computer-aided drug design and bioinformatics in targeting ROS for efficient cancer therapy. Herein, we discuss the different in vitro ROS measurement/testing methods to build predictive models. An introduction of computational-mathematical modeling approaches, mainly focusing on the simulation of ROS dynamics, is followed by the description of the software tools. The integration of omics studies and high-throughput biological data created from a wide diversity of cancer type is discussed subsequently.
Graphical Abstract

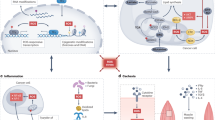
An illustration to depict various methods for (a) ROS signaling pathways and (b) ROS modeling and in silico drug design. The genome sequence and epigenomic and transcriptomic data contribute to the understanding of signaling pathways. This information when integrated with ROS modeling can aid in drug design and study ROS dynamics that can be validated using in vitro estimation
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal V, Tuli HS, Varol A, Thakral F, Year MB, Sak K et al (2019) Role of reactive oxygen species in cancer progression: molecular mechanisms and recent advancements. Biomol Ther 9(11):735
An BC, Choi YD, Oh IJ, Kim JH, Park JI, Lee SW (2018) GPx3-mediated redox signaling arrests the cell cycle and acts as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One 13(9):e0204170
Bergmann FT, Hoops S, Klahn B, Kummer U, Mendes P, Pahle J, Sahle S (2017) COPASI and its applications in biotechnology. J Biotechnol 261:215–220
Cao Y, Li H, Petzold L (2004) Efficient formulation of the stochastic simulation algorithm for chemically reacting systems. J Chem Phys 121(9):4059–4067
Chakraborty S, Balan M, Flynn E, Zurakowski D, Choueiri TK, Pal S (2019) Activation of c-Met in cancer cells mediates growth-promoting signals against oxidative stress through Nrf2-HO-1. Oncogene 8(2):1–12
Cid TP, Garcıa JC, Alvarez FC, De Arriba G (2003) Antioxidant nutrients protect against cyclosporine A nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 189(1–2):99–111
Dalle Pezze P, Le Novère N (2017) SBpipe: a collection of pipelines for automating repetitive simulation and analysis tasks. BMC Syst Biol 11(1):1–5
Dalle Pezze P, Nelson G, Otten EG, Korolchuk VI, Kirkwood TB, von Zglinicki T, Shanley DP (2014) Dynamic modelling of pathways to cellular senescence reveals strategies for targeted interventions. PLoS Comput Biol 10(8):e1003728
Dalmasso G, Marin Zapata PA, Brady NR, Hamacher-Brady A (2017) Agent-based modeling of mitochondria links sub-cellular dynamics to cellular homeostasis and heterogeneity. PLoS One 12(1):e0168198
de Sá Junior PL, Câmara DAD, Porcacchia AS, Fonseca PMM, Jorge SD, Araldi RP, Ferreira AK (2017) The roles of ROS in cancer heterogeneity and therapy. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:2467940
Deng X, Feng N, Zheng M, Ye X, Lin H, Yu X et al (2017) PM2. 5 exposure-induced autophagy is mediated by lncRNA loc146880 which also promotes the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg (BBA)-Gen Sub 1861(2):112–125
Drawert B, Hellander A, Bales B, Banerjee D, Bellesia G, Daigle BJ Jr et al (2016) Stochastic simulation service: bridging the gap between the computational expert and the biologist. PLoS Comput Biol 12(12):e1005220
Echizen K, Oshima H, Nakayama M, Oshima M (2018) The inflammatory microenvironment that promotes gastrointestinal cancer development and invasion. Adv Biol Regul 68:39–45
Gauthier LD, Greenstein JL, Cortassa S, O’Rourke B, Winslow RL (2013) A computational model of reactive oxygen species and redox balance in cardiac mitochondria. Biophys J 105(4):1045–1056
Gopalakrishnan V, Kim M, An G (2013) Using an agent-based model to examine the role of dynamic bacterial virulence potential in the pathogenesis of surgical site infection. Adv Wound Care 2(9):510–526
Griendling KK, Touyz RM, Zweier JL, Dikalov S, Chilian W, Chen YR et al (2016) Measurement of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, and redox-dependent signaling in the cardiovascular system: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Res 119(5):e39–e75
Hu Y, Zhang HR, Dong L, Xu MR, Zhang L, Ding WP et al (2019) Enhancing tumor chemotherapy and overcoming drug resistance through autophagy-mediated intracellular dissolution of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 11(24):11789–11807
Hui KF, Yeung PL, Chiang AK (2016) Induction of MAPK-and ROS-dependent autophagy and apoptosis in gastric carcinoma by combination of romidepsin and bortezomib. Oncotarget 7(4):4454
Kadayat TM, Kim MJ, Nam TG, Park PH, Lee ES (2014) Thieny/furanyl-hydroxyphenylpropenones as inhibitors of LPS-induced ROS and NO production in RAW 264.7 macrophages, and their structure-activity relationship study. Bull Kor Chem Soc 35(8):2481–2486
Kansestani AN, Mansouri K, Hemmati S, Zare ME, Moatafaei A (2019) High glucose-reduced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is mediated by activation of NF-κB. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 18(2):153–162
Kembro JM, Aon MA, Winslow RL, O’Rourke B, Cortassa S (2013) Integrating mitochondrial energetics, redox and ROS metabolic networks: a two-compartment model. Biophys J 104(2):332–343
Khlebnikov AI, Schepetkin IA, Domina NG, Kirpotina LN, Quinn MT (2007) Improved quantitative structure–activity relationship models to predict antioxidant activity of flavonoids in chemical, enzymatic, and cellular systems. Bioorg Med Chem 15(4):1749–1770
Kim C, Song HS, Park H, Kim B (2018) Activation of ER stress-dependent miR-216b has a critical role in Salvia miltiorrhiza ethanol-extract-induced apoptosis in U266 and U937 cells. Int J Mol Sci 19(4):1240
Kolodkin AN, Sharma RP, Colangelo AM, Ignatenko A, Martorana F, Jennen D et al (2020) ROS networks: designs, aging, Parkinson’s disease and precision therapies. NPJ Syst Biol Appl 6(1):1–20
Kuznetsov AV, Kehrer I, Kozlov AV, Haller M, Redl H, Hermann M et al (2011) Mitochondrial ROS production under cellular stress: comparison of different detection methods. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(8):2383–2390
Lazo JS, Sharlow ER (2016) Drugging undruggable molecular cancer targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 56:23–40
Lee SH, Gupta MK, Bang JB, Bae H, Sung HJ (2013) Current progress in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive materials for biomedical applications. Adv Healthc Mater 2(6):908–915
Lee SY, Ju MK, Jeon HM, Lee YJ, Kim CH, Park HG et al (2019) Reactive oxygen species induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition, glycolytic switch, and mitochondrial repression through the Dlx-2/Snail signaling pathways in MCF-7 cells. Mol Med Rep 20(3):2339–2346
Li S, Zhuang Z, Wu T, Lin JC, Liu ZX, Zhou LF et al (2018) Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase-mediated redox homeostasis promotes tumor growth and metastasis in gastric cancer. Redox Biol 18:246–255
Li Y, Guo F, Guan Y, Chen T, Ma K, Zhang L et al (2020) Novel anthraquinone compounds inhibit colon cancer cell proliferation via the reactive oxygen species/JNK pathway. Molecules 25(7):1672
Liang W, Zhang Y, Song L, Li Z (2019) 2, 3′ 4, 4′, 5-Pentachlorobiphenyl induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through pyruvate kinase M2-dependent glycolysis. Toxicol Lett 313:108–119
Lim JB, Langford TF, Huang BK, Deen WM, Sikes HD (2016) A reaction-diffusion model of cytosolic hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med 90:85–90
Markevich NI, Markevich LN, Hoek JB (2020) Computational modeling analysis of generation of reactive oxygen species by mitochondrial assembled and disintegrated complex II. Front Physiol 11:1212
Martin-Cordero C, Jose Leon-Gonzalez A, Manuel Calderon-Montano J, Burgos-Moron E, Lopez-Lazaro M (2012) Pro-oxidant natural products as anticancer agents. Curr Drug Targets 13(8):1006–1028
Meng Y, Chen CW, Yung MM, Sun W, Sun J, Li Z et al (2018) DUOXA1-mediated ROS production promotes cisplatin resistance by activating the ATR-Chk1 pathway in ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett 428:104–116
Moraru II, Schaff JC, Slepchenko BM, Loew LM (2002) The virtual cell: an integrated modeling environment for experimental and computational cell biology. Ann N Y Acad Sci 971(1):595–596
Park J, Lee J, Choi C (2011) Mitochondrial network determines intracellular ROS dynamics and sensitivity to oxidative stress through switching inter-mitochondrial messengers. PLoS One 6(8):e23211
Pradhan AK, Bhoopathi P, Talukdar S, Scheunemann D, Sarkar D, Cavenee WK et al (2019) MDA-7/IL-24 regulates the miRNA processing enzyme DICER through downregulation of MITF. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(12):5687–5692
Reed MC, Thomas RL, Pavisic J, James SJ, Ulrich CM, Nijhout HF (2008) A mathematical model of glutathione metabolism. Theor Biol Med Model 5(1):1–16
Rodrigues C, Pimpão C, Mósca AF, Coxixo AS, Lopes D, da Silva IV et al (2019) Human aquaporin-5 facilitates hydrogen peroxide permeation affecting adaption to oxidative stress and cancer cell migration. Cancer 11(7):932
Sarkar J, Dwivedi G, Chen Q, Sheu IE, Paich M, Chelini CM et al (2018) A long-term mechanistic computational model of physiological factors driving the onset of type 2 diabetes in an individual. PLoS One 13(2):e0192472
Sarkar R, Kishida S, Kishida M, Nakamura N, Kibe T, Karmakar D et al (2019) Effect of cigarette smoke extract on mitochondrial heme-metabolism: An in vitro model of oral cancer progression. Toxicol in Vitro 60:336–346
Sun HF, Yang XL, Zhao Y, Tian Q, Chen MT, Zhao YY, ** W (2019) Loss of TMEM126A promotes extracellular matrix remodeling, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and breast cancer metastasis by regulating mitochondrial retrograde signaling. Cancer Lett 440:189–201
The, I. C. G. C., of Whole, T. P. C. A., & Genomes Consortium (2020) Pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes. Nature 578(7793):82
Tomita M, Hashimoto K, Takahashi K, Shimizu TS, Matsuzaki Y, Miyoshi F et al (1999) E-CELL: software environment for whole-cell simulation. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 15(1):72–84
Vaneev AN, Gorelkin PV, Garanina AS, Lopatukhina HV, Vodopyanov SS, Alova AV et al (2020) In vitro and in vivo electrochemical measurement of reactive oxygen species after treatment with anticancer drugs. Anal Chem 92(12):8010–8014
Wang N, Zhan T, Ke T, Huang X, Ke D, Wang Q, Li H (2014) Increased expression of RRM2 by human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein promotes angiogenesis in cervical cancer. Br J Cancer 110(4):1034–1044
Wang C, Shao L, Pan C, Ye J, Ding Z, Wu J et al (2019) Elevated level of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species via fatty acid β-oxidation in cancer stem cells promotes cancer metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Stem Cell Res Ther 10(1):1–16
Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, Shaw KRM, Ozenberger BA, Ellrott K et al (2013) The cancer genome atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat Genet 45(10):1113–1120
Xu Y, Cui J, Puett D (2014) Cancer bioinformatics. Springer, New York, pp 1–362
Zhou L, Aon MA, Almas T, Cortassa S, Winslow RL, O'Rourke B (2010) A reaction-diffusion model of ROS-induced ROS release in a mitochondrial network. PLoS Comput Biol 6(1):e1000657. (RIRR)
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Zhou W, Chen T, Wu Q, Chutturghoon VK et al (2019) YAP promotes multi-drug resistance and inhibits autophagy-related cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma via the RAC1-ROS-mTOR pathway. Cancer Cell Int 19(1):1–15
Zhu B, Li Y, Lin Z, Zhao M, Xu T, Wang C, Deng N (2016a) Silver nanoparticles induce HePG-2 cells apoptosis through ROS-mediated signaling pathways. Nanoscale Res Lett 11(1):1–8
Zhu D, Shen Z, Liu J, Chen J, Liu Y, Hu C et al (2016b) The ROS-mediated activation of STAT-3/VEGF signaling is involved in the 27-hydroxycholesterol-induced angiogenesis in human breast cancer cells. Toxicol Lett 264:79–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
Sharma, D., Chaturvedi, S., Chaudhary, V., Kaul, A., Mishra, A.K. (2022). Emerging Scope of Computer-Aided Drug Design in Targeting ROS in Cancer Therapy. In: Chakraborti, S. (eds) Handbook of Oxidative Stress in Cancer: Therapeutic Aspects. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5422-0_143
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5422-0_143
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-5421-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-5422-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences