Abstract
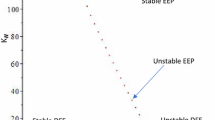
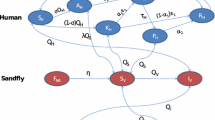
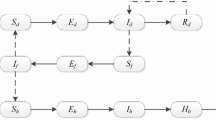
Fasciola (hepatica and gigantica) is a common liver fluke that infects cattle, causing disease and considerable production losses and might be transmitted to humans. Current control methods rely on drugs designed to kill parasites. Epidemiological modelling can be a helpful instrument for evaluating parasite control strategies. In the present paper, a mathematical model of Fasciola is established as a multi-scale 9 dimensional system of ODEs that includes the intermediate host and the larval development according to the life cycle of the disease. The model includes quarantine as a control strategy. The main purpose of this work is to establish a more realistic new model of the disease and observe the role of quarantine strategy in such systems. The model is shown to be well-posed. The disease-free equilibrium is locally asymptotically stable whenever the basic reproduction number is less than unity and unstable otherwise. Numerical simulations have been performed to show the impact of certain parameters on the spread of the disease and to confirm the analytical results of the model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cwiklinski, K., Donnelly, S., Drysdale, O., Jewhurst, H., Smith, D., Verissimo, C.D.M., Pritsch, I.C., O’Neill, S., Dalton, J.P., Robinson, M.W.: The cathepsin-like cysteine peptidases of trematodes of the genus Fasciola. Adv. Parasitol. 104, 113–164 (2019)
Krauss, H., Weber, A., Appel, M., Enders, B., Isenberg, H.D., Schiefer, H.G., Slenczka, W., von Graevenitz, A., Zahner, H.: Zoonoses: Infectious Diseases Transmissible from Animals to Humans. ASM Press, Washington, DC (2003)
WHO: Trématodoses d’origine alimentaires. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs368/fr/Aide m’emoire
Farrar, J., Hotez, P.J., Junghanss, T., Kang, G., Lalloo, D., White, N.J.: Manson’s Tropical Diseases E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences (2013)
Schillhorn, V.V.T.: Fasciolosis (f. gigantica) in West Africa. Rev. Vet. Bull 5, 229–233 (1980)
Assogba, M.N., Youssao, A.K.I.: Epidémiologie de la fasciolose à fasciola gigantica (cobbold, 1885), de la dicrocoeliose et de la paramphistomose bovines au bénin. Ann. Méd. Vét 145, 260–268 (2001)
Ka, M., Mbengue, M., Diop, B., Pouye, A., Da, J.V., Dia, D., Welle, A., Ndir, O., Diop, T.: Two unexpected cases of hepatobiliary fascioliasis in Dakar (Senegal). Dakar Med. 47(2), 202–205 (2002)
Seydi, M., Soumare, M., Sow, M., Ka, E., Diop, S., Diop, B., Sow, P.: La distomatose hepato-biliaire a fasciola hepatica: a propos du premier cas observe a la clinique des maladies infectieuses ibrahima diop mar du chu de fann a Dakar (Senegal). Med. Trop. 68(4), 431 (2008)
Spithill, T.W.: Fasciola gigantica: epidemiology, control, immunology and molecular biology. Fasciolosis, pp. 465–525 (1999)
Kaplan, R.M.: Fasciola hepatica: a review of the economic impact in cattle and considerations for control. Vet Ther 2(1), 40–50 (2001)
Malone, J., Loyacano, A., Armstrong, D., Archbald, L.: Bovine fascioliasis: economic impact and control in gulf coast cattle based on seasonal transmission [fasciola hepatica, louisiana]. J. Am. Assoc. Bovines Pract. (1982)
Saba, R., Korkmaz, M., Inan, D., Mamikoğlu, L., Turhan, Ö., Günseren, F., Cevikol, C., Kabaalioğlu, A.: Human fascioliasis (2004)
Hope-Cawdery, M.: Changing temperatures and prediction models for the liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica). J. Therm. Biol 6(4), 403–408 (1981)
Ashrafi, K., Valero, M., Panova, M., Periago, M., Massoud, J., Mas-Coma, S.: Phenotypic analysis of adults of Fasciola hepatica, Fasciola gigantica and intermediate forms from the endemic region of Gilan, Iran. Parasitol. Int. 55(4), 249–260 (2006)
Gettinby, G., Hope-Cawdery, M., Grainger, J.: Forecasting the incidence of fascioliasis from climatic data. Int. J. Biometeorol. 18(4), 319–323 (1974)
Ciddio, M., Mari, L., Sokolow, S.H., De Leo, G.A., Casagrandi, R., Gatto, M.: The spatial spread of schistosomiasis: a multidimensional network model applied to Saint-Louis region, Senegal. Adv. Water Resour. 108, 406–415 (2017)
Wilson, R., Denison, J.: The parasitic castration and gigantism of Lymnaea truncatula infected with the larval stages of Fasciola hepatica. Z. Parasitenkd. 61(2), 109–119 (1980)
Yang, X., Chen, L., Chen, J.: Permanence and positive periodic solution for the single-species nonautonomous delay diffusive models. Comput. Math. Appl. 32(4), 109–116 (1996)
Van den Driessche, P., Watmough, J.: Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180(1–2), 29–48 (2002)
Smith, G.: Density-dependent mechanisms in the regulation of Fasciola hepatica populations in sheep. Parasitology 88(3), 449–461 (1984)
Meek, A., Morrist, R.: The longevity of Fasciola hepatica metacercariae encysted on herbage. Aust. Vet. J. 55(2), 58–60 (1979)
Feng, Z., Li, C.-C., Milner, F.A.: Schistosomiasis models with density dependence and age of infection in snail dynamics. Math. Biosci. 177, 271–286 (2002)
Jain, S.K., Botsford, L.W.: Applied Population Biology, vol. 67. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Grenfell, B.T., Wilson, K., Isham, V., Boyd, H., Dietz, K.: Modelling patterns of parasite aggregation in natural populations: trichostrongylid nematode-ruminant interactions as a case study. Parasitology 111(S1), S135–S151 (1995)
Bolajoko, M.-B., Rose, H., Musella, V., Bosco, A., Rinaldi, L., van Dijk, J., Cringoli, G., Morgan, E.R.: The basic reproduction quotient (Q0) as a potential spatial predictor of the seasonality of ovine haemonchosis. Geospatial Health 333–350 (2015)
Chitnis, N., Hyman, J.M., Cushing, J.M.: Determining important parameters in the spread of malaria through the sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model. Bull. Math. Biol. 70(5), 1272 (2008)
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the support of the CEA-MITIC (Centre d’Excellence Africain en Mathématiques, Informatique et Technologie de l’Information et de la Communication) and PIED-UVS (Pôle d’Innovation et d’Expertise pour le Développement).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Diaby, M., Diop, O., Nassouri, E., Sène, A., Sène, M. (2021). Mathematical Analysis of Fasciola Epidemic Model with Treatment and Quarantine. In: Mohd, M.H., Misro, M.Y., Ahmad, S., Nguyen Ngoc, D. (eds) Modelling, Simulation and Applications of Complex Systems. CoSMoS 2019. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol 359. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2629-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2629-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2628-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2629-6
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)