Abstract
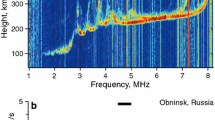
The regularity and coupling mechanism of typhoon-induced ionospheric disturbances are still unclear. In this paper, three typhoons that made landfall over China in 2016 are selected as typical cases. The morphological characteristics of ionospheric disturbances affected by typhoons are comprehensively analyzed using ionospheric TEC extracted from ground-based GPS, ionospheric scintillation data, and digital ionosonde data. The results show that the ionospheric TEC shows positive anomalies and the ionospheric scintillation intensity increases before typhoon’s landfall. On the vertical scale, anomalies have occurred in E, F1 and F2 layers of the ionosphere too. It is analyzed that the movement of the turbulent layer and the gravity waves generated by the interaction between the typhoon and the ground cause changes in the electric field and then cause ionospheric disturbances.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arikan, F., Nayir, H., Sezen, U., et al.: Estimation of single station inter frequency receiver bias using GPS-TEC. Radio Sci. 43(4), 1–13 (2008)
Bauer, S.J.: An apparent ionospheric response to the passage of hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. 63(1), 265–269 (1958)
Chou, M.Y., Lin, C.H., Yue, J., Chang, L.C., Tsai, H.F., Chen, C.H.: Medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances triggered by super typhoon Nepartak (2016). Geophys. Res. Lett. 44, 7569–7577 (2017)
Davies, K., Jones, J.E.: Ionospheric disturbances in the F2 region associated with severe thunderstorms. J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 254–262 (1971)
Huang, Y.N., Cheng, K., Chen, S.W.: On the detection of acoustic-gravity waves generated by typhoon by use of real time HF Doppler frequency shift sounding system. Radio Sci. 20(4), 897–906 (1985)
Hung, R.J., Phan, T., Smith, R.E.: Observation of gravity waves during the extreme tornado outbreak of 3 April 1974. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 40(7), 831–843 (1978)
Ke, F.Y., Wang, J.L., Tu, M.H., et al.: Characteristics and coupling mechanism of GPS ionospheric scintillation responses to the tropical cyclones in Australia. GPS Solutions 23(2), 34 (2019)
Ke, F.Y., Wang, J.L., Tu, M.H., et al.: Enhancing reliability of seism-ionospheric anomaly detection with the linear correlation between total electron content and the solar activity index F10.7: Nepal earthquake 2015. J. Geodyn. 121, 88–95 (2018)
Liu, Y.M., Wang, J.S., **ao, Z., Suo, Y.C.: A possible mechanism of typhoon effects on the ionospheric F2 layer. Chin. J. Space Sci. 26(2), 92–97 (2006)
Liu, Y.M.: The influence of typhoon on the F2 layer of the ionosphere and the integral difference method for predicting the ionospheric TEC. Peking University (2006b)
Luo, X., Lou, Y., **ao, Q., et al.: Investigation of ionospheric scintillation effects on BDS precise point positioning at low-latitude regions. GPS Solutions 22(3), 63 (2018)
Sezen, U., Arikan, F., Arikan, O., et al.: Online, automatic, near-real time estimation of GPS-TEC: IONOLAB-TEC. Space Weather 11(5), 297–305 (2013)
Shen, C.S.: The correlations between the typhoon and the foF2 of ionosphere. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2, 335–340 (1982)
Song, Q., Ding, F., Zhang, X., Mao, T.: GPS detection of the ionospheric disturbances over China due to impacts of Typhoon Rammasum and Matmo. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phy. 122, 1055–1063 (2017)
Vanina-Dart, L.B., Sharkov, E.A.: Main results of recent investigations into the physical mechanisms of the interaction of tropical cyclones and the ionosphere. Izvestiya Atmos. Oceanic Phys. 52(9), 1120–1127 (2016)
Wang, J.S.: Chronic or Permanent coupling (CoP coupling) between the lower and upper martian atmospheres. Geophys. Res. Abs. 7, 05855 (2005)
Wang, X., Ke, F., Cao, Y.C., et al.: Combination of GPS, HY-2A and COSMIC observations to establish global ionospheric map. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 47(05), 1000–1010 (2018)
**ao, Z., **ao, S., Hao, Y., et al.: Morphological features of ionospheric response to typhoon. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112(A4) (2007)
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41674036).
We acknowledge the use of data from the Chinese Meridian Project, China Meteorological Administration and Hong Kong Geodetic Survey Services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, J., Ke, F., Zhao, X., Qi, X. (2020). Characteristics of the Ionospheric Disturbances Caused by Typhoon Using GPS and Ionospheric Sounding. In: Shen, J., Chang, YC., Su, YS., Ogata, H. (eds) Cognitive Cities. IC3 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1227. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6113-9_57
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6113-9_57
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-6112-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-6113-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)