Abstract
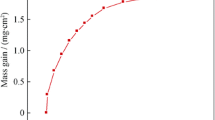
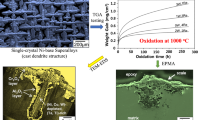
To understand the role of rare earth elements in influencing high-temperature oxidation behavior of the Ni-based single crystal superalloy, a high Mo-containing nickel-based single crystal superalloy and the derivative alloy modified by Ce and Dy were designed. The results of oxidation tests conducted at 1100 °C indicated that do** 0.022 wt% Ce or 0.042 wt% Dy significantly improved the oxidation resistance of the alloy by reducing the oxide scale growth rate and enhancing the scale adhesion. The positive effects are probably because the doped trace of Dy or Ce can combine with O2− more quickly and reduce the oxygen contents on the oxide surface which decreases the oxidation rate. At the same time, it decreases the thickness of oxide scale which results in the reduction of the elastic strain energy and the weaker tendency to spallation of the oxide scale. But too high concentration of Dy or Ce was deleterious because its high oxidation rate results in much more defects which induce cracks easily.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Raffaitin, D. Monceau, E. Andrieu, F. Crabos, Cyclic oxidation of coated and uncoated singlecrystal nickel-based superalloy MC2 analyzed by continuous thermogravimetry analysis, Acta Mater.54 (2006) 4473–4487.
Y.G. Zhang, Y.F. Han, G.L. Chen, J.T. Guo, X.J. Wan, and D. Feng, Intermetallic Structural Materials,National Defence Industry Press, (2001) 551.
Y.F. Zhang, S.S. Li, and Y.F. Han, Effect of yttrium on oxidation behavior of Ni3Al-based single crystal alloys, Rare Metals, 30 (2011) 538–543.
Q. Feng, B. Tryon, L.J. Carroll, T.M. Pollock, Cyclic oxidation of Ru-containing single crystal superalloys at 1100 °C, Mater. Sci. Eng. 458 (2007) 184–194.
C.A. Barrett, Effect of 0.1 at.% zirconium on the cyclic oxidation resistance of β-NiAl, Oxid. Met. 30 (1988) 361–390.
P. Prescott, D.F. Mitchell, M.J. Graham, J. Doychak, Oxidation mechanisms of β-NiAl + Zr determined by SIMS, Corros. Sci. 37 (1995) 1341–1364.
A. Strawbridge, P.Y. Hou, The role of rare earth elements in oxide scale adhesion, Mater. High Temp. 12 (1994) 177–181.
B.A. Pint, The role of chemical composition on the oxidation performance of aluminide coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol. 188–189 (2004) 71–78.
X. Tan, X. Peng, F. Wang, The effect of grain refinement on the adhesion of an alumina scale on an aluminide coating, Corros. Sci. 85 (2014) 280–286.
B.A. Pint, Experimental observations in support of the dynamic-segregation theory to explain the reactive-element effect, Oxid. Met. 45 (1996) 1–37.
P.Y. Hou, K. Priimak, Interfacial segregation, pore formation, and scale adhesion on NiAl alloys, Oxid. Met. 63 (2005) 113–130.
J.T. Guo, C. Yun, J.H. Huo, Effects of Rare Earth Elements on NiAl based Alloys, Science Press. 2008, vol.44, 513–520.
J. He, Z. Zhang, H. Peng, S.K. Gong, H.B. Guo, The role of Dy and Hf do** on oxidation behavior of two-phase (γ’ + β) Ni-Al alloys, Corros. Sci. 98 (2015) 699–707.
H.B. Guo,X.Y. Wang, J. Li, S.X. Wang, S.K. Gong, Effects of Dy on cyclic oxidation resistance of NiAl alloy, Science Direct, Trans Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 19 (2009) 1185–1189.
P.Y. Hou, K.F. McCarty, Surface and interface segregation in β-NiAl with and without Pt addition. Scripta Mater. 54 (2006) 937–941.
B.A. Pint, I.G. Wright, W.Y. Lee, Y. Zhang, K.B. Alexander, Substrate and bond coat compositions: factors affecting alumina scale adhesion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A245 (1998) 201–211.
B.A. Pint, On the formation of interfacial and internal voids inα-Al2O3,Oxid. Met. 48 (1997) 303–328.
C.M. Cotell, G.J. Yurek, R.J. Hussey, D.F. Mitchell, M.J. Graham, The influence ofgrain-boundary segregation of Y in Cr2O3 on the oxidation of Cr metal,Oxid. Met. 34 (1990) 173–200.
B.A. Pint, Experimental observations in support of the dynamic-segregation theory to explain the reactive-element effect, Oxid. Met. 45(1996) 1–37.
D.R. Mumm, G.A. Evans, Mechanisms Controlling the Performance and Durability of Thermal Barrier Coatings, Key Eng. Mater. 197 (2001) 199–0.
M. Ohring, the Materials Science of Thin Films, Academic Press, SanDiego, 1992.
P.K. Wright, A.G. Evans, Mechanisms governing the performance of thermal barrier coatings, Curr. Opin. Solid St. M. 4 (1999) 255–265.
A. Janotti, M. Krcˇmar,C.L. Fu, and R.C. Reed, Solute Diffusion in Metals: lager atoms can move faster, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 (2004) 085901.
Q. Wu, S.S. Li, Y. Ma, S.K. Gong, First principles calculations of alloying element diffusion coefficients in Ni using the five-frequency model, Chinese. Phys. B. 21 (2012) 109102.
O. Kubaschewski and B.E. Hopkins: Oxidation of Metals and Alloys, 2nd ed, Butterworths, London, (1962) 8–33.
Acknowledgements
This research is sponsored by National Nature Science Foundations of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 51671015 and U1435207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bai, J. et al. (2018). Effects of Ce and Dy on the Cyclic Oxidation Behavior of a Ni-Based Single Crystal Superalloy. In: Han, Y. (eds) High Performance Structural Materials. CMC 2017. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0104-9_85
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0104-9_85
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-0103-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-0104-9
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)