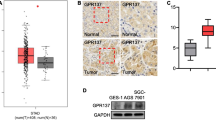
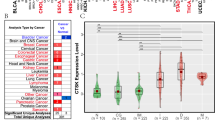
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC), a leading cancer that occupies the second position in terms of morbidity and mortality, occupies the fourth place of all cancers in terms of manifestation. Annual gastric cancer manifestations are reaching several millions of deaths along with millions of new cases. Gastric cancer which is not detected in the early stages has very poor prognosis, and the 5-year survival rate is only around 20%. Gastric cancer development includes numerous alterations at genome level leading to changes in the expression of quite a lot of genes involved in several physiological processes. Even though a number of factors showed their role in advancement of GC, a link between STAT3 and the risk of GC has become apparent in current years. Signal transducers and activators of transcriptions (STATs) which are predominantly known for their role as transcription factors are implicated in controlling numerous physiological processes such as cell propagation, differentiation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis by controlling the expression of critical genes in the pathway. Abnormal activation of STAT3 plays a key role in inflammation and transformation in numerous cancers including gastric cancer (GC). Earlier, STAT3 has never been considered as a target, and hence there is no FDA-approved STAT3 inhibitor till now. Recent advances in drug discovery and cancer biology now focused on STAT3 globally for treating different types of cancers. The present chapter summarizes the recent literature and gives an idea about involvement of STAT3 in gastric cancer initiation and progression.
The original version of this chapter was revised. The book was inadvertently published without Abstracts and Keywords, which are now included in all the chapters. An erratum to this chapter can be found at https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6728-0_39
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC (2004) Roles of fascin in cell adhesion and motility. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16(5):590–596
Akira S, Nishio Y, Inoue M, Wang XJ, We S, Matsusaka T, Kishimoto T (1994) Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell 77(1):63–71
Alberts SR, Cervantes A, Van de Velde CJH (2003) Gastric cancer: epidemiology, pathology and treatment. Ann Oncol 14(90002):31–36
Alexandrow MG, Song LJ, Altiok S, Gray J, Haura EB, Kumar NB (2012) Curcumin: a novel stat 3 pathway inhibitor for chemoprevention of lung cancer. Eur J Cancer Prev 21(5):407
Alonso A, Sasin J, Bottini N, Friedberg I, Friedberg I, Osterman A, Mustelin T (2004) Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 117(6):699–711
Alvarez RH, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE (2006) The role of Src in solid and hematologic malignancies. Cancer 107(8):1918–1929
Amin HM, McDonnell TJ, Ma Y, Lin Q, Fujio Y, Kunisada K, Medeiros LJ (2004) Selective inhibition of STAT3 induces apoptosis and G1 cell cycle arrest in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Oncogene 23(32):5426–5434
Anglesio MS, George J, Kulbe H, Friedlander M, Rischin D, Lemech C, Chakravarty P (2011) IL6-STAT3-HIF signaling and therapeutic response to the angiogenesis inhibitor sunitinib in ovarian clear cell cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17(8):2538–2548
Axon A (2006) Symptoms and diagnosis of gastric cancer at early curable stage. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 20(4):697–708
Azare J, Leslie K, Al-Ahmadie H, Gerald W, Weinreb PH, Violette SM, Bromberg J (2007) Constitutively activated STAT3 induces tumorigenesis and enhances cell motility of prostate epithelial cells through integrin β6. Mol Cell Biol 27(12):4444–4453
Aznar S, Valerón PF, del Rincon SV, Pérez LF, Perona R, Lacal JC (2001) Simultaneous tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of STAT3 transcription factor is involved in Rho A GTPase oncogenic transformation. Mol Biol Cell 12(10):3282–3294
Barnhart BC, Legembre P, Pietras E, Bubici C, Franzoso G, Peter ME (2004) CD95 ligand induces motility and invasiveness of apoptosis-resistant tumor cells. EMBO J 23(15):3175–3185
Becker S, Groner B, Müller CW (1998) Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3β homodimer bound to DNA. Nature 394(6689):145–151
Bromberg J (2002) Stat proteins and oncogenesis. J Clin Invest 109(9):1139–1142
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C, Darnell JE (1999) STAT3 as an oncogene. Cell 98(3):295–303
Bronte-Tinkew DM, Terebiznik M, Franco A, Ang M, Ahn D, Mimuro H, Jones NL (2009) Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin-associated gene A activates the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 69(2):632–639
Cabral MM, Mendes C, Castro LP, Cartelle CT, Guerra J, Queiroz DM, Nogueira AM (2006) Apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori gastritis is related to cagA status. Helicobacter 11(5):469–476
Calvet X, Ramírez Lázaro MJ, Lehours P, Mégraud F (2013) Diagnosis and epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 18(s1):5–11
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Dalton WS (1999) Constitutive activation of STAT3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity 10(1):105–115
Chan AOO, Luk JM, Hui WM, Lam SK (1999) Molecular biology of gastric carcinoma: from laboratory to bedside. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(12):1150–1160
Chang TLY, Mosoian A, Pine R, Klotman ME, Moore JP (2002) A soluble factor (s) secreted from CD8+ T lymphocytes inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication through STAT1 activation. J Virol 76(2):569–581
Chen X, Vinkemeier U, Zhao Y, Jeruzalmi D, Darnell JE, Kuriyan J (1998) Crystal structure of a tyrosine phosphorylated STAT-1 dimer bound to DNA. Cell 93(5):827–839
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR (1994) Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Sci-AAAS-Wkly Pap Ed-Incl Guid Sci Inf 264(5164):1415–1420
Deng X, Cao M, Zhang J, Hu K, Yin Z, Zhou Z, …, Zeng Y (2014) Hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of MiR-34a and doxorubicin in therapy against triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials 35(14):4333–4344
Durães C, Almeida GM, Seruca R, Oliveira C, Carneiro F (2014) Biomarkers for gastric cancer: prognostic, predictive or targets of therapy? Virchows Arch 464(3):367–378
Durbin JE, Hackenmiller R, Simon MC, Levy DE (1996) Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell 84(3):443–450
Frame MC (2002) Src in cancer: deregulation and consequences for cell behaviour. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Rev Cancer 1602(2):114–130
Fukada T, Hibi M, Yamanaka Y, Takahashi-Tezuka M, Fujitani Y, Yamaguchi T, Hirano T (1996) Two signals are necessary for cell proliferation induced by a cytokine receptor gp130: involvement of STAT3 in anti-apoptosis. Immunity 5(5):449–460
Giraud S, Bienvenu F, Avril S, Gascan H, Heery DM, Coqueret O (2002) Functional interaction of STAT3 transcription factor with the coactivator NcoA/SRC1a. J Biol Chem 277(10):8004–8011
Gray MJ, Zhang J, Ellis LM, Semenza GL, Evans DB, Watowich SS, Gallick GE (2005) HIF-1α, STAT3, CBP/p300 and Ref-1/APE are components of a transcriptional complex that regulates Src-dependent hypoxia-induced expression of VEGF in pancreatic and prostate carcinomas. Oncogene 24(19):3110–3120
Guo C, Yang G, Khun K, Kong X, Levy D, Lee P, Melamed J (2009) Activation of STAT3 in renal tumors. Am J Transl Res 1(3):283–290
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Müller-Newen G, Schaper F, Graeve L (1998) Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem J 334(2):297–314
Hirano T, Ishihara K, Hibi M (2000) Roles of STAT3 in mediating the cell growth, differentiation and survival signals relayed through the IL-6 family of cytokine receptors. Oncogene 19(21):2548–2556
Huang Y, Yang M, Yang H, Zeng Z (2010) Upregulation of the GRIM-19 gene suppresses invasion and metastasis of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell line. Exp Cell Res 316(13):2061–2070
Improta T, Pine R (1997) Susceptibility to virus infection is determined by a Stat-mediated response to the autocrine effect of virus-induced type I interferon. Cytokine 9(6):383–393
Jackson CB, Judd LM, Menheniott TR, Kronborg I, Dow C, Yeomans ND, Giraud AS (2007) Augmented gp130-mediated cytokine signalling accompanies human gastric cancer progression. J Pathol 213(2):140–151
Judd LM, Bredin K, Kalantzis A, Jenkins BJ, Ernst M, Giraud AS (2006) STAT3 activation regulates growth, inflammation, and vascularization in a mouse model of gastric tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 131(4):1073–1085
Kanda N, Seno H, Konda Y, Marusawa H, Kanai M, Nakajima T, Sekikawa A (2004) STAT3 is constitutively activated and supports cell survival in association with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 23(28):4921–4929
Kaplan MH, Grusby MJ (1998) Regulation of T helper cell differentiation by STAT molecules. J Leukoc Biol 64(1):2–5
Kaplan MH, Sun YL, Hoey T, Grusby MJ (1996) Impaired IL-12 responses and enhanced development of Th2 cells in Stat4-deficient mice. Nature 382(6587):174
Kuo CT, Leiden JM (1999) Transcriptional regulation of T lymphocyte development and function. Annu Rev Immunol 17(1):149–187
Lai SY, Johnson FM (2010) Defining the role of the JAK-STAT pathway in head and neck and thoracic malignancies: implications for future therapeutic approaches. Drug Resist Updat 13(3):67–78
Lee JH, Kaminski N, Dolganov G, Grunig G, Koth L, Solomon C, …, Sheppard D (2001) Interleukin-13 induces dramatically different transcriptional programs in three human airway cell types. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25(4):474–485
Levy DE, Darnell JE (2002) Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(9):651–662
Li M, Liu W, Zhu YF, Chen YL, Zhang BZ, Wang R (2006) Correlation of COX-2 and K-ras expression to clinical outcome in gastric cancer. Acta Oncol 45(8):1115–1119
Lo HW, Hsu SC, **a W, Cao X, Shih JY, Wei Y, …, Hung MC (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression. Cancer Res 67(19):9066–9076
Macha MA, Matta A, Kaur J, Chauhan SS, Thakar A, Shukla NK, Ralhan R (2011) Prognostic significance of nuclear pSTAT3 in oral cancer. Head Neck 33(4):482–489
Machesky LM, Li A (2010) Fascin: invasive filopodia promoting metastasis. Commun Integr Biol 3(3):263–270
Mali SB (2015) Review of STAT3 (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 51(6):565–569
Mao X, Ren Z, Parker GN, Sondermann H, Pastorello MA, Wang W, Chen X (2005) Structural bases of unphosphorylated STAT1 association and receptor binding. Mol Cell 17(6):761–771
Matsuda T, Nakamura T, Nakao K, Arai T, Katsuki M, Heike T, Yokota T (1999) STAT3 activation is sufficient to maintain an undifferentiated state of mouse embryonic stem cells. EMBO J 18(15):4261–4269
Mohrs M, Lacy DA, Locksley RM (2003) Stat signals release activated naive Th cells from an anergic checkpoint. J Immunol 170(4):1870–1876
Mora LB, Buettner R, Seigne J, Diaz J, Ahmad N, Garcia R, Muro-Cacho C (2002) Constitutive activation of STAT3 in human prostate tumors and cell lines direct inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 62(22):6659–6666
Moriggl R, Topham DJ, Teglund S, Sexl V, McKay C, Wang D, …, Grosveld GC (1999) Stat5 is required for IL-2-induced cell cycle progression of peripheral T cells. Immunity 10(2):249–259
Murray PJ (2007) The JAK-STAT signaling pathway: input and output integration. J Immunol 178(5):2623–2629
Ning ZQ, Li J, McGuinness M, Arceci RJ (2001) STAT3 activation is required for Asp816 mutant c-Kit induced tumorigenicity. Oncogene 20(33):4528
Owen-Schaub LB, Meterissian S, Ford RJ (1993) Fas/APO-1 expression and function on malignant cells of hematologic and nonhematologic origin. J Immunother 14(3):234–241
Pan H, Hong F, Radaeva S, Gao B (2004) Hydrodynamic gene delivery of interleukin-22 protects the mouse liver from concanavalin A-, carbon tetrachloride-, and Fas ligand-induced injury via activation of STAT3. Cell Mol Immunol 1(1):43–49
Schindler C, Plumlee C (2008) Interferons pen the JAK–STAT pathway. In: Seminars in cell & developmental biology, vol. 19, no. 4. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 311–318
Schindler C, Levy DE, Decker T (2007) JAK-STAT signaling: from interferons to cytokines. J Biol Chem 282(28):20059–20063
Seidel HM, Milocco LH, Lamb P, Darnell JE, Stein RB, Rosen J (1995) Spacing of palindromic half sites as a determinant of selective STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92(7):3041–3045
Shah NG, Trivedi TI, Tankshali RA, Goswami JV, Jetly DH, Shukla SN, Verma RJ (2009) Prognostic significance of molecular markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a multivariate analysis. Head Neck 31(12):1544–1556
Shaulian E (2010) AP-1 – the Jun proteins: oncogenes or tumor suppressors in disguise? Cell Signal 22(6):894–899
Sheen-Chen SM, Huang CC, Tang RP, Chou FF, Eng HL (2008) Prognostic value of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 17(9):2286–2290
Shimoda K, van Deursen J, Sangster MY, Sarawar SR, Carson RT, Tripp RA, Chu C, Quelle FW, Nosaka T, Vignali DA, Doherty PC, Grosveld G, Paul WE, Ihle JN (1996) Lack of IL-4-induced Th2 response and IgE class switching in mice with disrupted Stat6 gene. Nature 380:630–633
Shinohara H, Yagita H, Ikawa Y, Oyaizu N (2000) Fas drives cell cycle progression in glioma cells via extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cancer Res 60(6):1766–1772
Siewert JR, Böttcher K, Stein HJ, Roder JD (1998) Relevant prognostic factors in gastric cancer: ten-year results of the German Gastric Cancer Study. Ann Surg 228(4):449
Silva CM (2004) Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 23(48):8017–8023
Siveen KS, Sikka S, Surana R, Dai X, Zhang J, Kumar AP, Bishayee A (2014) Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Rev Cancer 1845(2):136–154
Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD (1998) How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem 67(1):227–264
Stephanou A, Latchman DS (2003) STAT-1: a novel regulator of apoptosis. Int J Exp Pathol 84(6):239–244
Su CC, Lin HC, Lin YP, Shan YS, Yang BC (2013) Expression of Th17-related genes in PHA/IL-2-activated human T cells by Fas signaling via caspase-1-and Stat3-dependent pathway. Cell Immunol 281(2):101–110
Subramaniam A, Shanmugam MK, Perumal E, Li F, Nachiyappan A, Dai X, Hui KM (2013) Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Rev Cancer 1835(1):46–60
Takeda K, Akira S (2000) STAT family of transcription factors in cytokine-mediated biological responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 11(3):199–207
Takeda K, Noguchi K, Shi W, Tanaka T, Matsumoto M, Yoshida N, Akira S (1997) Targeted disruption of the mouse STAT3 gene leads to early embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94(8):3801–3804
Takeda K, Tanaka T, Shi W, Matsumoto M (1996) Essential role of Stat6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature 380(6575):627
Takemoto S, Ushijima K, Kawano K, Yamaguchi T, Terada A, Fujiyoshi N, Kage M (2009) Expression of activated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 predicts poor prognosis in cervical squamous-cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 101(6):967–972
Thierfelder WE, van Deursen JM, Yamamoto K, Tripp RA (1996) Requirement for Stat4 in interleukin-12-mediated responses of natural killer and T cells. Nature 382(6587):171
Tkach M, Rosemblit C, Rivas MA, Proietti CJ, Flaqué MCD, Mercogliano MF, Deza EG (2013) p42/p44 MAPK-mediated Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation is required for progestin-induced full activation of STAT3 and breast cancer growth. Endocr Relat Cancer 20(2):197–212
Trauzold A, Röder C, Sipos B, Karsten K, Arlt A, Jiang P, Siebert R (2005) CD95 and TRAF2 promote invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. FASEB J 19(6):620–622
Turkson J, Bowman T, Garcia R, Caldenhoven E, De Groot RP, Jove R (1998) STAT3 activation by Src induces specific gene regulation and is required for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol 18(5):2545–2552
Uchiyama T, Takahashi H, Endo H, Sugiyama M, Sakai E, Hosono K, Nakajima A (2011) Role of the long form leptin receptor and of the STAT3 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer progression. Int J Oncol 39(4):935
Udy GB, Towers RP, Snell RG, Wilkins RJ, Park SH, Ram PA, Davey HW (1997) Requirement of STAT5b for sexual dimorphism of body growth rates and liver gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94(14):7239–7244
Visconti R, Gadina M, Chiariello M, Chen EH, Stancato LF, Gutkind JS, O’Shea JJ (2000) Importance of the MKK6/p38 pathway for interleukin-12–induced STAT4 serine phosphorylation and transcriptional activity. Blood 96(5):1844–1852
Walford HH, Doherty TA (2013) STAT6 and lung inflammation. Jak-stat 2(4):e25301
Wang Y, Qu A, Wang H (2015) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 in liver diseases. Int J Biol Sci 11(4):448
Ward AC, Barry A, O’Sullivan LA (2009) Suppressors of cytokine signaling: functions in normal biology and roles in disease. In: Stephanou A (ed) Jak-stat pathway in disease. Landes Bioscience, Austin, pp 10–23
Weidemann A, Johnson RS (2008) Biology of HIF-1α. Cell Death Differ 15(4):621–627
Wurster AL, Tanaka T, Grusby MJ (2000) The biology of Stat4 and Stat6. Oncogene 19(21):2577
Yang E, Lerner L, Besser D, Darnell JE (2003) Independent and cooperative activation of chromosomal c-fos promoter by STAT3. J Biol Chem 278(18):15794–15799
Yang J, Liao X, Agarwal MK, Barnes L, Auron PE, Stark GR (2007) Unphosphorylated STAT3 accumulates in response to IL-6 and activates transcription by binding to NFκB. Genes Dev 21(11):1396–1408
Yokogami K, Wakisaka S, Avruch J, Reeves SA (2000) Serine phosphorylation and maximal activation of STAT3 during CNTF signaling is mediated by the rapamycin target mTOR. Curr Biol 10(1):47–50
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R (2009) STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 9(11):798–809
Yuan ZL, Guan YJ, Chatterjee D, Chin YE (2005) STAT3 dimerization regulated by reversible acetylation of a single lysine residue. Science 307(5707):269–273
Zhang J, Zhang D, Hua Z (2004) FADD and its phosphorylation. IUBMB Life 56:395–402
Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell JE Jr (1994) Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 264(5155):95–99
Zhu MH, John S, Berg M, Leonard WJ (1999) Functional association of Nmi with Stat5 and Stat1 in IL-2-and IFN γ-mediated signaling. Cell 96(1):121–130
Acknowledgment
The author gratefully acknowledges DST-SERB, Government of India, for the financial support in the form of DST-Young Scientist under the SERB File No. YSS/2015/000860.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pinjari, A.B., Meerza, A.R. (2017). Role of STAT3 in Gastric Cancer Initiation, Development, and Progression. In: Nagaraju, G., Bramhachari, P. (eds) Role of Transcription Factors in Gastrointestinal Malignancies. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6728-0_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6728-0_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-6727-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-6728-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)