Abstract
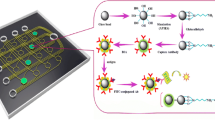
This paper describes the reduction of the size of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) utilizing microchemical reaction in a microchamber array. The microchamber array was fabricated by micromachining of a silicon chip. Glass beads of 100 µm were immobilized with antibody, and put in the microchambers of 150 p.m. As a competitive ELISA, sample solution mixed with HRP-conjugated antigens was allowed to react in the microchamber. As a sandwich assay, sample solution and HRP-conjugated antibody were sequentially added to the chamber. The addition of buffer, hydrogen peroxide, and fluorogenic substrate produced fluorescent dye, and a fluorescence microscope observed its fluorescence.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
S. P. A. Fodor, J. L. Read, M. C. Pirrung, L. Stryer, A. T. Lu, and D. Solas, “Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis”, Science,251 (1991), 767–773.
S. P. A. Fodor, R. C. Rava, X. C. Huang, A. C. Pease, C. P. Holmes, and C. L. Adams. Holmes, and C. L. Adams, “Multiplexed biochemical assays with biological chips”, Nature, 364, (1993), 555–556.
M. Schena, D. Shalon, R. W. Davis, and P. 0. Brown, “Patterns with a Complementary DNA Microarray”, Science, 270, (1995), 467–470.
Y. Murakami, K. Yokoyama, and E. Tamiya, “Miniaturization of multifunctional biosensor with enzyme-immobilized beads”, SPIE, 3258, (1998), 11–14.
Y. Murakami, K. Idegami, H. Nagai, A. Yamamura, K. Yokoyama, and E. Tamiya, “Random Fluidic Self-Assembly of Microfabricated Metal Particles”, Proc. of Transducers ’99, (1999), 1108–1111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Murakami, Y., Kikuchi, T., Yanase, M., Nagai, H., Morita, Y., Tamiya, E. (2000). Microchamber Array for Immunosensor Applications. In: van den Berg, A., Olthuis, W., Bergveld, P. (eds) Micro Total Analysis Systems 2000. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-2264-3_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-2264-3_45
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-5496-8
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-2264-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive