Abstract
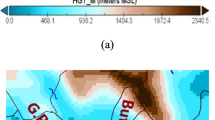
Air pollution is one of the most significant environmental concerns in China today, particularly in the highly industrialized Eastern Chinese mega cities. During the Olympic Summer Games in 2008, the air pollution in China’s capital city of Bei**g became an issue of international interest. Air pollution in Bei**g has a number of key constituent components, including anthropogenic gaseous pollutants, and small airborne particles from natural and anthropogenic sources. These often exceed WHO recommended levels. To investigate the influence of anthropogenic nitrogen oxides (NOx) and ozone (O3) on the air quality in Bei**g and its vicinity, the fully online coupled model system COSMO-ART is applied for the first time to Northern China. For this purpose a five-day simulation period from August 4th to 8th in 2008 was conducted. The simulated NOx and O3 concentrations are compared to observations from a measurement station located in Bei**g. Backward trajectories are calculated to get more information about the source areas of the air pollutants. Comparisons of measured and modeled NOx and O3 showed that the daily course of the concentrations can be reproduced by the model very well.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bangert M et al (2012) Saharan dust event impacts on cloud formation and radiation over Western Europe. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics 12:4045–4063
Draxler, R.R.a.R., G. D., HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model access via NOAA ARL READY Website (http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php). NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring, MD., 2012
Kaufman YJ, Tanré D and Boucher O (2002) A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 419(6903):215–223
Pope CA (2000) Epidemiology of fine particulate air pollution and human health: biologic mechanisms and who’s at risk? Environ Health Perspect 108(Suppl 4):713
Schleicher N et al (2012) Efficiency of mitigation measures to reduce particulate air pollution—a case study during the Olympic Summer Games 2008 in Bei**g, China. Science of The Total Environment 427–428(0):146–158
Streets DG et al (2007) Air quality during the 2008 Bei**g Olympic Games. Atmos Environ 41(3):480–492
Vogel B et al (2009) The comprehensive model system COSMO-ART—radiative impact of aerosol on the state of the atmosphere on the regional scale. Atmos Chem Phys 9(22):8661–8680
Wang Y et al (2009) Ozone air quality during the 2008 Bei**g Olympics: effectiveness of emission restrictions. Atmos Chem Phys 9:5237–5251
Wang S et al (2010) Quantifying the air pollutants emission reduction during the 2008 Olympic games in Bei**g. Environ Sci Technol 44(7):2490–2496
Wang T et al (2010) Air quality during the 2008 Bei**g Olympics: secondary pollutants and regional impact. Atmos Chem Phys 10:7603–7615
**n J et al (2012) Reductions of PM2.5 in Bei**g-Tian**-Hebei urban agglomerations during the 2008 Olympic Games. Adv Atmos Sci 29(6):1330–1342
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Helmholtz Graduate School for Climate and Environment (GRACE) at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology for financial support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Schrader, S. et al. (2013). Modeling Urban Air Quality in Bei**g during the Olympic Summer Games 2008. In: Rauch, S., Morrison, G., Norra, S., Schleicher, N. (eds) Urban Environment. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7756-9_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7756-9_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-7755-2
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-7756-9
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)