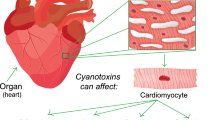
Abstract
Cyanobacteria produce a wide range of toxins with different chemical composition and molecular targets. Cyanobacterial neurotoxins comprise a variety of compounds acting either on acetylcholine receptors or acetylcholinesterase, on voltage-gated sodium channels and on excitatory neuronal synapses. Acute intoxications can be lethal and they mainly present as paralytic shellfish poisoning. Chronic exposure may lead to neurodegenerative disorders. Hepatotoxins and neurotoxins present two main groups of cyanobacterial toxins that affect human health. Nodularin and microcystins are hepatotoxins characterized by the presence of non-proteinogenic β-amino acid ADDA in cyclic penta- or heptapeptide structure. Best known acute lethal intoxications of humans have occurred in Brazil, but chronic exposure to these toxins leading to multi-organ failure is a more serious and widespread health problem. Microcystins are also tumor promoters, and there are several reports showing harmful effects of long-term exposure to microcystins in highly populated regions of China and other parts of the world. Cyanobacterial toxins must be considered as a serious threat, and high safety measures must be followed in monitoring the quality of water and food used in human nutrition, medical care, and recreational activities.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araoz R, Molgo J, Tandeau de Marsac N. Neurotoxic cyanobacterial toxins. Toxicon. 2010;56(5):813–28.
Batista T, de Sousa G, Suput JS, Rahmani R, Suput D. Microcystin-LR causes the collapse of actin filaments in primary human hepatocytes. Aquat Toxicol. 2003;65(1):85–91.
Byth S. Palm Island mystery disease. Med J Aust. 1980;2(1):40. 42.
Carmichael WW, Azevedo SM, An JS, Molica RJ, Jochimsen EM, Lau S, Rinehart KL, Shaw GR, Eaglesham GK. Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: chemical and biological evidence for cyanotoxins. Environ Health Perspect. 2001;109(7):663–8.
Chen Y, Xu J, Li Y, Han X. Decline of sperm quality and testicular function in male mice during chronic low-dose exposure to microcystin-LR. Reprod Toxicol. 2011;31(4):551–7.
Chen DN, Zeng J, Wang F, Zheng W, Tu WW, Zhao JS, Xu J. Hyperphosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins is involved in microcystin-LR-induced toxicity in HL7702 cells. Toxicol Lett. 2012;214(2):192–9.
Cox PA, Richer R, Metcalf JS, Banack SA, Codd GA, Bradley WG. Cyanobacteria and BMAA exposure from desert dust: a possible link to sporadic ALS among Gulf War veterans. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2009;10 Suppl 2:109–17.
Ding WX, Shen HM, Ong CN. Pivotal role of mitochondrial Ca(2+) in microcystin-induced mitochondrial permeability transition in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;285(5):1155–61.
Ding WX, Shen HM, Ong CN. Calpain activation after mitochondrial permeability transition in microcystin-induced cell death in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;291(2):321–31.
Ding XS, Li XY, Duan HY, Chung IK, Lee JA. Toxic effects of Microcystis cell extracts on the reproductive system of male mice. Toxicon. 2006;48(8):973–9.
Eriksson JE, Toivola D, Meriluoto JA, Karaki H, Han YG, Hartshorne D. Hepatocyte deformation induced by cyanobacterial toxins reflects inhibition of protein phosphatases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;173(3):1347–53.
Falconer IR, Humpage AR. Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2005;2(1):43–50.
Falconer IR, Smith JV, Jackson AR, Jones A, Runnegar MT. Oral toxicity of a bloom of the Cyanobacterium microcystis Aeruginosa administered to mice over periods up to 1 year. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1988;24(3):291–305.
Farrer D, Counter M, Hillwig R, Cude C. Health-based cyanotoxin guideline values allow for cyanotoxin-based monitoring and efficient public health response to cyanobacterial blooms. Toxins (Basel). 2015;7(2):457–77.
Feuerbach D, Lingenhohl K, Dobbins P, Mosbacher J, Corbett N, Nozulak J, Hoyer D. Coupling of human nicotinic acetylcholine receptors alpha 7 to calcium channels in GH3 cells. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48(2):215–27.
Feurstein D, Kleinteich J, Heussner AH, Stemmer K, Dietrich DR. Investigation of microcystin congener-dependent uptake into primary murine neurons. Environ Health Perspect. 2010;118(10):1370–5.
Feurstein D, Stemmer K, Kleinteich J, Speicher T, Dietrich DR. Microcystin congener- and concentration-dependent induction of murine neuron apoptosis and neurite degeneration. Toxicol Sci. 2011;124(2):424–31.
Filipič M, Žegura B, Sedmak B, Horvat-Žnidaršič I, Milutinovič A, Šuput D. Subchronic exposure of rats to sublethal dose of microcystin-YR induces DNA damage in multiple organs. Radiol Oncol. 2007;41(1):15–22.
Fischer WJ, Altheimer S, Cattori V, Meier PJ, Dietrich DR, Hagenbuch B. Organic anion transporting polypeptides expressed in liver and brain mediate uptake of microcystin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005;203(3):257–63.
Fischer A, Hoeger SJ, Stemmer K, Feurstein DJ, Knobeloch D, Nussler A, Dietrich DR. The role of organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs/SLCOs) in the toxicity of different microcystin congeners in vitro: a comparison of primary human hepatocytes and OATP-transfected HEK293 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;245(1):9–20.
Fladmark KE, Brustugun OT, Mellgren G, Krakstad C, Boe R, Vintermyr OK, Schulman H, Doskeland SO. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is required for microcystin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(4):2804–11.
Frangez R, Zuzek MC, Mrkun J, Suput D, Sedmak B, Kosec M. Microcystin-LR affects cytoskeleton and morphology of rabbit primary whole embryo cultured cells in vitro. Toxicon. 2003;41(8):999–1005.
French RJ, Worley 3rd JF, Krueger BK. Voltage-dependent block by saxitoxin of sodium channels incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1984;45(1):301–10.
Guzman RE, Solter PF. Hepatic oxidative stress following prolonged sublethal microcystin LR exposure. Toxicol Pathol. 1999;27(5):582–8.
Guzman RE, Solter PF, Runnegar MT. Inhibition of nuclear protein phosphatase activity in mouse hepatocytes by the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR. Toxicon. 2003;41(7):773–81.
Herfindal L, Myhren L, Kleppe R, Krakstad C, Selheim F, Jokela J, Sivonen K, Doskeland SO. Nostocyclopeptide-M1: a potent, nontoxic inhibitor of the hepatocyte drug transporters OATP1B3 and OATP1B1. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(2):360–7.
Humpage AR, Fontaine F, Froscio S, Burcham P, Falconer IR. Cylindrospermopsin genotoxicity and cytotoxicity: role of cytochrome P-450 and oxidative stress. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2005;68(9):739–53.
Irie K, Yanagita RC, Nakagawa Y. Challenges to the development of bryostatin-type anticancer drugs based on the activation mechanism of protein kinase C delta. Med Res Rev. 2012;32(3):518–35.
Ito E, Kondo F, Terao K, Harada K. Neoplastic nodular formation in mouse liver induced by repeated intraperitoneal injections of microcystin-LR. Toxicon. 1997;35(9):1453–7.
Ito E, Kondo F, Harada K. Intratracheal administration of microcystin-LR, and its distribution. Toxicon. 2001;39(2–3):265–71.
Ito E, Satake M, Yasumoto T. Pathological effects of lyngbyatoxin A upon mice. Toxicon. 2002;40(5):551–6.
Jabba SV, Prakash A, Dravid SM, Gerwick WH, Murray TF. Antillatoxin, a novel lipopeptide, enhances neurite outgrowth in immature cerebrocortical neurons through activation of voltage-gated sodium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;332(3):698–709.
Jarde T, Evans RJ, McQuillan KL, Parry L, Feng GJ, Alvares B, Clarke AR, Dale TC. In vivo and in vitro models for the therapeutic targeting of Wnt signaling using a Tet-ODeltaN89beta-catenin system. Oncogene. 2013;32(7):883–93.
Jochimsen EM, Carmichael WW, An JS, Cardo DM, Cookson ST, Holmes CE, Antunes MB, de Melo Filho DA, Lyra TM, Barreto VS, Azevedo SM, Jarvis WR. Liver failure and death after exposure to microcystins at a hemodialysis center in Brazil. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(13):873–8.
Kamachi H, Tanaka K, Yanagita RC, Murakami A, Murakami K, Tokuda H, Suzuki N, Nakagawa Y, Irie K. Structure-activity studies on the side chain of a simplified analog of aplysiatoxin (aplog-1) with anti-proliferative activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013;21(10):2695–702.
Kao CY, Nishiyama A. Actions of saxitoxin on peripheral neuromuscular systems. J Physiol. 1965;180(1):50–66.
Kato Y, Scheuer PJ. Aplysiatoxin and debromoaplysiatoxin, constituents of the marine mollusk Stylocheilus longicauda (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824). J Am Chem Soc. 1974;96(7):2245–6.
Khan SA, Wickstrom ML, Haschek WM, Schaeffer DJ, Ghosh S, Beasley VR. Microcystin-LR and kinetics of cytoskeletal reorganization in hepatocytes, kidney cells, and fibroblasts. Nat Toxins. 1996;4(5):206–14.
Kisby G, Palmer V, Lasarev M, Fry R, Iordanov M, Magun E, Samson L, Spencer P. Does the cycad genotoxin MAM implicated in Guam ALS-PDC induce disease-relevant changes in mouse brain that includes olfaction? Commun Integr Biol. 2011;4(6):731–4.
Konst H, McKercher PD, Gorham PR, Robertson A, Howell J. Symptoms and pathology produced by toxic Microcystis aeruginosa NRC-1 in laboratory and domestic animals. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1965;29(9):221–8.
Krakstad C, Herfindal L, Gjertsen BT, Boe R, Vintermyr OK, Fladmark KE, Doskeland SO. CaM-kinaseII-dependent commitment to microcystin-induced apoptosis is coupled to cell budding, but not to shrinkage or chromatin hypercondensation. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(7):1191–202.
Kujbida P, Hatanaka E, Vinolo MA, Waismam K, Cavalcanti DM, Curi R, Farsky SH, Pinto E. Microcystins -LA, −YR, and -LR action on neutrophil migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;382(1):9–14.
Lankoff A, Carmichael WW, Grasman KA, Yuan M. The uptake kinetics and immunotoxic effects of microcystin-LR in human and chicken peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. Toxicology. 2004;204(1):23–40.
Li Y, Sheng J, Sha J, Han X. The toxic effects of microcystin-LR on the reproductive system of male rats in vivo and in vitro. Reprod Toxicol. 2008;26(3–4):239–45.
Li G, Cai F, Yan W, Li C, Wang J. A proteomic analysis of MCLR-induced neurotoxicity: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Toxicol Sci. 2012;127(2):485–95.
Ling B. Health impairments arising from drinking water polluted with domestic sewage and excreta in China. Schriftenr Ver Wasser Boden Lufthyg. 2000;105:43–6.
Liu Y, **e P, Qiu T, Li HY, Li GY, Hao L, **ong Q. Microcystin extracts induce ultrastructural damage and biochemical disturbance in male rabbit testis. Environ Toxicol. 2010;25(1):9–17.
Marchi M, Lupinacci M, Bernero E, Bergaglia F, Raiteri M. Nicotinic receptors modulating ACh release in rat cortical synaptosomes: role of Ca2+ ions in their function and desensitization. Neurochem Int. 1999;34(4):319–28.
Mikhailov A, Harmala-Brasken AS, Hellman J, Meriluoto J, Eriksson JE. Identification of ATP-synthase as a novel intracellular target for microcystin-LR. Chem Biol Interact. 2003;142(3):223–37.
Milutinovic A, Zivin M, Zorc-Pleskovic R, Sedmak B, Suput D. Nephrotoxic effects of chronic administration of microcystins -LR and -YR. Toxicon. 2003;42(3):281–8.
Mucenski ML, Nation JM, Thitoff AR, Besnard V, Xu Y, Wert SE, Harada N, Taketo MM, Stahlman MT, Whitsett JA. Beta-catenin regulates differentiation of respiratory epithelial cells in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;289(6):L971–9.
Nakagawa Y, Yanagita RC, Hamada N, Murakami A, Takahashi H, Saito N, Nagai H, Irie K. A simple analogue of tumor-promoting aplysiatoxin is an antineoplastic agent rather than a tumor promoter: development of a synthetically accessible protein kinase C activator with bryostatin-like activity. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131(22):7573–9.
Nakagawa Y, Kikumori M, Yanagita RC, Murakami A, Tokuda H, Nagai H, Irie K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the 12,12-dimethyl derivative of Aplog-1, an anti-proliferative analog of tumor-promoting aplysiatoxin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(6):1167–73.
Nishiwaki-Matsushima R, Ohta T, Nishiwaki S, Suganuma M, Kohyama K, Ishikawa T, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H. Liver tumor promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1992;118(6):420–4.
Pouria S, de Andrade A, Barbosa J, Cavalcanti RL, Barreto VT, Ward CJ, Preiser W, Poon GK, Neild GH, Codd GA. Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. Lancet. 1998;352(9121):21–6.
Qiu T, **e P, Liu Y, Li G, **ong Q, Hao L, Li H. The profound effects of microcystin on cardiac antioxidant enzymes, mitochondrial function and cardiac toxicity in rat. Toxicology. 2009;257(1–2):86–94.
Shen X, Lam PK, Shaw GR, Wickramasinghe W. Genotoxicity investigation of a cyanobacterial toxin, cylindrospermopsin. Toxicon. 2002;40(10):1499–501.
Soliakov L, Wonnacott S. Voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels involved in nicotinic receptor-mediated [3H]dopamine release from rat striatal synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1996;67(1):163–70.
Spencer PS, Fry RC, Palmer VS, Kisby GE. Western Pacific ALS-PDC: a prototypical neurodegenerative disorder linked to DNA damage and aberrant proteogenesis? Front Neurol. 2012;3:180.
Straser A, Filipic M, Gorenc I, Zegura B. The influence of cylindrospermopsin on oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis induction in HepG2 cells. Chemosphere. 2013;92(1):24–30.
Su Z, Sheets M, Ishida H, Li F, Barry WH. Saxitoxin blocks L-type ICa. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;308(1):324–9.
Suput D, Zorc-Pleskovic R, Petrovic D, Milutinovic A. Cardiotoxic injury caused by chronic administration of microcystin-YR. Folia Biol (Praha). 2010;56(1):14–8.
Takumi S, Komatsu M, Furukawa T, Ikeda R, Sumizawa T, Akenaga H, Maeda Y, Aoyama K, Arizono K, Ando S, Takeuchi T. p53 Plays an important role in cell fate determination after exposure to microcystin-LR. Environ Health Perspect. 2010;118(9):1292–8.
Theiss WC, Carmichael WW, Wyman J, Bruner R. Blood pressure and hepatocellular effects of the cyclic heptapeptide toxin produced by the freshwater cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Microcystis aeruginosa strain PCC-7820. Toxicon. 1988;26(7):603–13.
Turner PC, Gammie AJ, Hollinrake K, Codd GA. Pneumonia associated with contact with cyanobacteria. BMJ. 1990;300(6737):1440–1.
Wagh PK, Zinser GM, Gray JK, Shrestha A, Waltz SE. Conditional deletion of beta-catenin in mammary epithelial cells of Ron receptor, Mst1r, overexpressing mice alters mammary tumorigenesis. Endocrinology. 2012;153(6):2735–46.
Yoshizawa S, Matsushima R, Watanabe MF, Harada K, Ichihara A, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H. Inhibition of protein phosphatases by microcystins and nodularin associated with hepatotoxicity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1990;116(6):609–14.
Yu SZ. Primary prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995;10(6):674–82.
Yuan M, Carmichael WW, Hilborn ED. Microcystin analysis in human sera and liver from human fatalities in Caruaru, Brazil 1996. Toxicon. 2006;48(6):627–40.
Zegura B, Sedmak B, Filipic M. Microcystin-LR induces oxidative DNA damage in human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Toxicon. 2003;41(1):41–8.
Zhang XX, Zhang Z, Fu Z, Wang T, Qin W, Xu L, Cheng S, Yang L. Stimulation effect of microcystin-LR on matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 expression in mouse liver. Toxicol Lett. 2010;199(3):377–82.
Zhou L, Yu H, Chen K. Relationship between microcystin in drinking water and colorectal cancer. Biomed Environ Sci. 2002;15(2):166–71.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Research Agency of Slovenia (ARRS); grant P3-0019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this entry
Cite this entry
Šuput, D. (2016). Effects of Cyanotoxins: Sea and Freshwater Toxins. In: Gopalakrishnakone, P., Haddad Jr., V., Tubaro, A., Kim, E., Kem, W. (eds) Marine and Freshwater Toxins. Toxinology. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6419-4_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6419-4_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-6418-7
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-6419-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences