Zusammenfassung
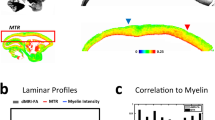
This paper presents an approach for map** the human cortical architecture in vivo based on quantitative MRI indices of myelin. We automatically construct laminar profiles in several primary cortical areas and investigate different sampling strategies. The results demonstrate that our method is able to distinguish these areas at specific cortical depths.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Vogt C, Vogt O. Allgem. Ergebnisse unserer Hirnforschung. 1. Mitteilung. Ziele und Wege unserer Hirnforschung. J Psychol Neurol. 1919;25.
Geyer S, Weiss M, Reimann K, et al. Microstructural parcellation of the human cerebral cortex–from Brodmann’s post-mortem map to in vivo map** with high-field magnetic resonance imaging. Front Hum Neurosci. 2011;5(19).
Glasser MF, Van Essen DC. Map** human cortical areas in vivo based on myelin content as revealed by T1-and T2-weighted MRI. J Neurosci. 2011;31(32):11597–616.
Clare S, Bridge H. Methodological issues relating to in vivo cortical myelography using MRI. Hum Brain Map. 2005;26(4):240–50.
Marques J, Kober T, Krueger G, et al. MP2RAGE, a self bias-field corrected sequence for improved segmentation and T1-map** at high field. NeuroImage. 2010;49(2):1271–81.
Hurley AC, Al-Radaideh A, Bai L, et al. Tailored RF pulse for magnetization inversion at ultrahigh field. MRM. 2010;63(1):51–8.
Bazin PL, Weiss M, Dinse J, et al. A computational pipeline for subject-specific, ultra-high resolution cortical analysis at 7 Tesla. Hum Brain Map. 2012;(abstract).
Sethian JA. Level set methods and fast marching methods: evolving interfaces in computational geometry, fluid mechanics, computer vision, and materials science. Cambridge University Press; 1999.
Eickhoff S, Stephan K, Mohlberg H, et al. A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. NeuroImage. 2005;25(4):1325–35.
Waehnert M,Weiss M, Streicher M, et al. Do cortical layers conform to the Laplace equation? Hum Brain Map. 2012;(abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dinse, J., Martin, P., Schäfer, A., Geyer, S., Turner, R., Bazin, PL. (2013). Quantifying Differences Between Primary Cortical Areas in Humans Based on Laminar Profiles in In-Vivo MRI Data. In: Meinzer, HP., Deserno, T., Handels, H., Tolxdorff, T. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2013. Informatik aktuell. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36480-8_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36480-8_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-36479-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-36480-8
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)