Introduction
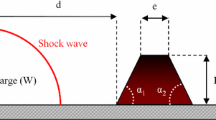
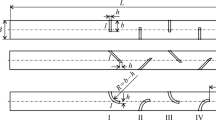
Major resources have being invested in the last two decades in an effort to find and utilize efficient protective technologies against terror attacks. Most of the resources have been directed to civil and military structures and protection of civil population from explosion induced blast wave loads. Explosive devices exploding inside a bus or an airplane and bombs exploding in the entrance of military bunkers are examples in which a blast wave will be initiated, propagating in a corridor-type structure, causing injuries to human and damage to structures and equipment. Barriers of different sizes and shapes inside a tunnel can cause the incident shock wave to diffract, leaving behind it a complex flow field that changes the impact on the target wall at the end of the tunnel. Several ways to reduce shock-wave loads propagating inside tunnels are based on forcing abrupt changes in the tunnel as in a bent duct [1], passing through particle suspensions [2], or passing through perforated tube walls [3]. In a pioneering experimental work by Dosanjh [4], shadowgraph photography was used to investigate the wave pattern that resulted from the head-on collision of an incident shock wave with a grid like obstacle. Britan et al. [5] investigated the attenuation of a shock wave by grid and orifice plates. In their study, the interaction of shock waves (1.35 < M s < 1.7) with porous barriers of different geometries and porosities was examined. The barrier inside the test section of a shock tube initiated the development of a complex wave pattern following the interaction between the incident shock wave and the barrier. They proposed a one-dimensional (1D), inviscid flow model for predicting the flow that results from the collision of an incident shock wave with the barrier. They showed that the over-pressure acting on an endwall protected by a barrier reduces almost linearly with increasing distance between the end-wall and the barrier. Ohtomo et al. [6] investigated the attenuation of a shock wave propagating through arrayed baffle plates. Two baffle plate arrays, oblique and staggered, were tested. In both arrays, the effect of baffle plate arrangements on the shock attenuation was significant. They found that shock attenuation occurs quicker over the oblique one than over the staggered one. This trend was accentuated with increased shock Mach number. The main objective of the present study is to better understand the physical elements governing the induced flow behind the shock wave propagating through a barrier, and optimizing the barrier geometry for better shock wave attenuation. To carry out the overall research plan, a combined (numerical and experimental) approach has been offered: in the first stage, an experimental study was carrying out to check the feasibility of barrier geometry effect on shock wave attenuation. In the second stage, a numerical investigation is being carried out, using experiments to calibrate a reliable numerical code. In the third stage, a comprehensive study will be performed, investigating the physical elements governing the induced flow behind the shock wave while implementing a barrier geometry optimization. This stage will include local experiments to support the numerical findings. The first and second stages of a broader research of shock wave and rigid barrier interaction are presented.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Igra, O., Wu, X., Falcovitz, J., Meguro, T., Takayama, K.: Experimental and theoretical study of shock wave propagation through double-bend ducts. J. Fluid Mech. 437, 255–282 (2001)
Elperin, T., Ben-Dor, G., Igra, O.: Head-on collision of normal shock waves in dusty gases. Int. J. Heat and Fluid Flow 8(4), 303–308 (1987)
Sasoh, A., Matsuoka, K., Nakashio, K., Timofeev, E., Takayama, K., Voinovich, P., Saito, T., Hirano, S., Ono, S.: Attenuation of weak shock waves along pseudoperforated walls. Shock Waves, 149–159 (1998)
Dosanjh, D.S.: Interaction of grids with traveling shock waves. NACA TN 3680 (1956)
Britan, A., Igra, O., Ben-Dor, G., Shapiro, H.: Shock wave attenuation by grids and orifice plates. Shock Waves, 1–15 (2006)
Ohtomo, F., Ohtani, K., Takayama, K.: Attenuation of shock waves propagating over arrayed baffle plates. Shock Waves 14(5/6), 379–390 (2005)
Berger, S., Sadot, O., Ben-Dor, G.: Experimental investigation on the shock-wave load attenuation by geometrical means. Shock Waves 20, 29–40 (2010)
Kivity, Y., Falcovich, J., Ben-David, Y., Bar-On, E.: Dynamic drag of a sphere subjected to shock wave: validation of four hydro-codes. In: MABS 21 -International Symposium of Military Aspects Os Shock and Blast, Jerusalem, Israel (October 2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Berger, S., Sadot, O., Ben-Dor, G. (2012). Numerical Investigation of Shock-Wave Load Attenuation by Barriers. In: Kontis, K. (eds) 28th International Symposium on Shock Waves. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25688-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25688-2_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-25687-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-25688-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)