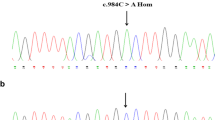
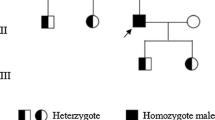
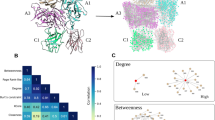
Abstract
Human coagulation factor V (FV) provides an essential function in the coagulation pathway. As a non-enzymatic cofactor of the prothrombinase complex, it is required for the rapid generation of thrombin [1, 2]. The gene for coagulation FV is located on chromosome 1q24.2 and spans more then 80 kilobases (kb) [3]. It consists of 25 exons encoding a 25 amino acids leader peptide and 2196 amino acids mature protein organized in A1-A2-B-A3-C1-C2 domain structure [4]. The activated factor Va is composed of a heavy chain (domains A1 and A2, Ala1-Arg709) and a light chain (domains A3, C1, and C2, Ser1546-Tyr2196), noncovalently associated in the presence of divalent metal ions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mann, K. G., and Kalafatis, M. (2003) Factor V: a combination of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde, Blood 101, 20–30
Kalafatis, M., Egan, J. O., van’t Veer, C., Cawthern, K. M., and Mann, K. G. (1997) The regulation of clotting factors, Crit. Re V. Eukaryotic Gene Expression 7, 241–280
Koeleman BP, Reitsma PH, Bakker E, Bertina RM. Location on the human genetic linkage map of 26 genes involved in blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1997;77:873–878
Kane WH, Davie EW. Blood coagulation factors V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to hemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood. 1988;71:539–555
Peyvandi F, Duga S, Akhavan S, Mannucci PM. Rare coagulation deficiencies. Haemophilia. 2002;8:308–321
Macedo-Ribeiro S, Bode W, Huber R, et al. Crystal structures of the membrane-binding C2 domain of human coagulation factor V. Nature. 1999;402:434–439
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Delev, D., Pavlova, A., Seifried, E., Oldenburg, J. (2008). Structural Investigation of Two Novel Mutations in Coagulation Factor V by Molecular Modeling. In: Scharrer, I., Schramm, W. (eds) 37th Hemophilia Symposium. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73535-9_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73535-9_49
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-73534-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-73535-9
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)