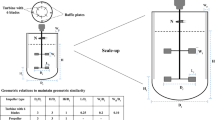
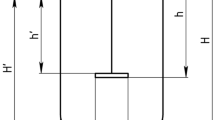
Abstract
Bioreactor or fermenter is the heart of a process. Scaling up a bioreactor and maintaining the same optimized process in a recombinant enzyme production in a higher scale is an engineering challenge. Scale-up is about mixing and mass transfer, a combination of art and science. It is more to methodological approach with some combination of rules of thumb, experience and/or trial and error. This chapter presented several bioreactor or fermenter modes and types before encompasses four different scale-up strategies. The scale-up strategies related to mass transfer involving constants scale-up of; (i)volumetric transfer coefficient (KLa), (ii) power input per liquid volume (P/V), (iii) impeller tip speed (Vi), and (iv) mixing time (t m) are described and discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Junker BH (2004) Scale-up methodologies for Escherichia coli and yeast fermentation processes. J Biosci Bioeng 97:347–364
Papagianni M (2011) Methodologies for scale-down of microbial bioprocess. Microb Biochem Technol 2011:1–7
Präve PFU, Sittig W, Sukatsch DA (1987) Fundamentals of biotechnology. VCH Publisher, New York
Smith R (2005) Chemical process design and integration. Wiley, England
Godoy A, Amorim HV, Lopes ML, Oliviera AJ (2008) Continuous and batch fermentation processes: advantages and disadvantages of these processes in the Brazilian ethanol production. Int Sugar J 110:175–181
Zhao Y, Lin YH (2003) Growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a chemostat under high glucose conditions. Biotechnol Lett 25:1151–1154
Doran PM (2009) Bioprocess engineering principles. Academic, United Kingdom
Soni AS (2002) A multi-scale approach to fed-batch bioreactor control. University of Pittsburgh, United State of America: Master thesis
Bayrock DP, Michael Ingledew W (2001) Application of multistage continuous fermentation for production of fuel alcohol by very-high-gravity fermentation technology. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 27:87–93
Huang T-K, McDonald KA (2009) Bioreactor engineering for recombinant protein production in plant cell suspension cultures. Biochem Eng J 45:168–184
Kracke-Helm HA, Rinas U, Hitzmann B, Schügerl K (1991) Cultivation of recombinant E. coli and production of fusion protein in 60-l bubble column and airlift tower loop reactors. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:554–564
Farrell P, Sun J, Gao M, Sun H, Pattara B, Zeiser A et al (2012) Development of a scaled-down aerobic fermentation model for scale-up in recombinant protein vaccine manufacturing. Vaccine 30:5695–5698
Singh RS, Yadav M (2013) Enhanced production of recombinant aspartase of Aeromonas media NFB-5 in a stirred tank reactor. Bioresour Technol 145:217–223
De León A, Hernández V, Galindo E, Ramı amp x et al (2003) Effects of dissolved oxygen tension on the production of recombinant penicillin acylase in Escherichia coli. Enzyme Microb Technol 33:689–697
Glazyrina J, Materne E-M, Dreher T, Storm D, Junne S, Adams T et al (2010) High cell density cultivation and recombinant protein production with Escherichia coli in a rocking-motion-type bioreactor. Microb Cell Fact 9:42
Dubey KK, Haque S, Jawed A, Singh BP, Behera BK (2010) Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli for enhanced bioconversion of colchicine into 3-demethylated colchicine at 70 l bioreactor level. Process Biochem 45:1036–1042
Garcia-Ochoa F, Gomez E (2009) Bioreactor scale-up and oxygen transfer rate in microbial processes: an overview. Biotechnol Adv 27:153–176
Standbury PF, Whitaker A, Hall SJ (2003) Principles of fermentation technology. Butterworth-Heinemanh, Massachusetts
Bhattacharya S, Gupta VS, Prabhune AA, SivaRaman H, Debnath M, Ranjekar PK (1993) Studies of operational variables in batch mode for genetically engineered Escherichia coli cells containing penicillin acylase. Enzyme Microb Technol 15:1070–1073
Bhattacharya SK, Dubey AK (1997) Effects of dissolved oxygen and oxygen mass transfer on overexpression of target gene in recombinant E. coli. Enzyme Microb Technol 20:355–360
Kapat A, Jung JK, Park YH (2001) Enhancement of glucose oxidase production in batch cultivation of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae: optimization of oxygen transfer condition. J app microbiol 90:216–222
Mel M, Karim MIA, Salleh HM (2010) The evaluation of kLa values for recombinant Escherichia coli fermentation producing b-glucuronidase enzyme. J App Sci 10(4):325–330
Amid A (2013) 30 L bromelain production. Kuala Lumpur, (Personal Communication)
Lin SJ, Hsieh YF, Lai LA, Chao ML, Chu WS (2008) Characterization and large-scale production of recombinant Streptoverticillium platensis transglutaminase. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:981–990
Anane E, van Rensburg E, Görgens JF (2013) Optimisation and scale-up of α-glucuronidase production by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae in aerobic fed-batch culture with constant growth rate. Biochem Eng J 81:1–7
Junker BH (2004) Scale-up methodologies for E.coli and yeast fermentation processes. J Biosci Bioeng 97(6):347–364
Flickinger MC, Greenstein M, Bremmon C, Conlin J (1993) Strain selection, medium development and scale-up of toyocamycin production by Streptomyces chrestomyceticus. Bioprocess Eng 5:143–153
Bartholomew WH (1960) Scale-up of submerged fermentations. Adv App Micro 2:289–300
Banks GT (1979) Scale-up of fermentation processes. Topics in enzyme and fermentation biotechnology. Wiley, New York, pp 170–266
Oosterhuis NMG (1984) Scale-up of bioreactors: a scale down approach. Suike Unie, Netherland
Imamoglu E, Sukan FV (2013) Scale-up and kinetic modeling for bioethanol production. Bioresour Technol 144:311–320
Lee TS (2009) A methodological approach to scaling up fermentation and primary recovery processes to the manufacturing scale for vaccine production. Vaccine 27:6439–6443
Rao DG (2010) Introduction to biochemical engineering. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Kim HJ, Kim YH, Roh YH, Seong BL, Shin CS (2005) Optimization of enterokinase fermentation using a recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Process Biochem 40:717–722
Kay M. Frey FBO-S, Schmidt H, Steinbüchel A (2002) Technical-Scale production of cyanophycin with recombinant strains of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3377–3384
Marques MPC, Cabral JMS, Fernandes P Bioprocess scale-up: quest for the parameters to be used as criterion to move from microreactors to lab-scale. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:1184–1198
Caşcaval D, Galaction AI, Cămăruţ S (2011) Scale-up of aerobic stirred bioreactors using the mixing time criteria 1. Simulated broths. Chem Biochem Eng Q 25:43–54
Singh V (1999) Disposable bioreactor for cell culture using wave-induced agitation. Cytotechnology 30:149–158
Pollard DJ, Kirschner TF, Hunt GR, Tong IT, Stieber R, Salmon PM (2007) Scale up of a viscous fungal fermentation: application of scale-up criteria with regime analysis and operating boundary conditions. Biotechnol bioeng 96:307–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Azmi, A., Sulaiman, S., Amin, N., Ali, F. (2015). Scaling-Up Recombinant Enzyme Fermentation. In: Amid, A. (eds) Recombinant Enzymes - From Basic Science to Commercialization. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12397-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12397-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-12396-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-12397-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)