Summary
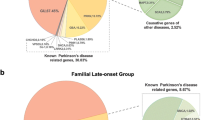
We here summarize the results of genetic investigations on a series of 82 parkinsonian patients from 60 families in Taiwan. We found 13 parkin patients in 7 families (12%), 2 PINK1 sibs from 1 family, and 1 LRRK2 patient from 1 family with I2012T mutation. We also identified SCA2 in 8 patients from 5 families (8%) and SCA3 in 3 patients from 1 family, all presenting with parkinsonian phenotype.
In the available patients with parkin, PINK1, SCA2 and SCA3, the dopamine transporter (DAT) scan revealed that the reduction of uptake was primarily observed in the bilateral putamen, basically sharing a similar pattern with that in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease.
We concluded that the genetic causes contributed to about 25% of our series of familial parkinsonism. The parkin mutations and SCA2 were the most frequent genetic causes in our series with Chinese ethnicity. The results of DAT scan indicated that bilateral putamen was essentially involved in various genetically-caused familial parkinsonism.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas N, Lücking CB, Richard S, Durr A, Bonifati V, De Michele G, Bouley S, Vaughan JR, Gasser T, Marconi R, Broussolle E, Brefel-Courbon C, Harhangi BS, Oostra BA, Fabrizio E, Bohme GA, Pradier L, Wood NW, Filla A, Meco G, Denefle P, Agid Y, Brice A, the French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group and the European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson’s Disease (1999) A wide variability of mutations in the parkin gene is responsible for autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism in Europe. French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group and the European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 8: 567–574
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MCJ, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299: 256–259
Di Fonzo A, Rohe CF, Ferreira J, Chien HF, Vacca L, Stocchi F, Guedes L, Fabrizio E, Manfredi M, Vanacore N, Goldwurm S, Breedveld G, Sampaio C, Meco G, Barbosa E, Oostra BA, Bonifati V, the Italian Parkinson Genetic Network (2005) A frequent LRRK2 gene mutation associated with autosomal dominant Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 365: 412–415
Furtado S, Farrer M, Tsuboi Y, Klimek RN, de la Fuente-Fernandez R, Hussey J, Lockhart P, Calne DB, Suchowersky O, Stoessl AJ, Wszolek ZK (2002) SCA-2 presenting as parkinsonism in an Alberta family: clinical, genetic, and PET findings. Neurology 59: 1625–1627
Gwinn-Hardy K, Chen JY, Liu HC, Liu TY, Boss M, Seltzer W, Adam A, Singleton A, Koroshetz W, Waters C, Hardy J, Farrer M (2000) Spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2) with parkinsonism in ethnic Chinese. Neurology 55: 800–805
Gwinn-Hardy K, Singleton A, O’Suilleabhain P, Boss M, Nicholl D, Adam A, Hussey J, Critchley P, Hardy J, Farrer M (2001) Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 phenotypically resembling Parkinson’s disease in a black family. Arch Neurol 58: 296–299
Hatano Y, Li Y, Sato K, Asakawa S, Yamamura Y, Tomiyama H, Yoshino H, Asahina M, Kobayashi S, Hassin-Baer S, Lu CS, Ng AR, Rosales RL, Shimizu N, Toda T, Mizuno Y, Hattori N (2004) Novel PINK1 mutations in early-onset parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 56: 424–427
Hattori N, Kidata T, Matsumine H, Asakawa S, Yamamura Y, Yoshino H, Kobayashi T, Yokochi M, Wang M, Yoritaka A, Kondo T, Kuzuhara S, Nakamura S, Shimizu N, Mizuno Y (1998) Molecular genetic analysis of a novel parkin gene in Japanese families with autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism: evidence fro variable homozygous deletion in the parkin gene in affected individuals. Ann Neurol 44: 935–941
Kidata T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minishima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392: 605–608
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 395: 451–452
Lu CS, Wu JC, Tsai CH, Chen RS, Chou Wu YH, Hattori N, Yoshino H, Mizuno Y (2001) Clinical and genetic studies on familial parkinsonism: the first report on a parkin gene mutation in a Taiwanese family. Mov Disord 16: 164–166
Lu CS, Wu Chou YH, Yen TC, Tsai CH, Chen RS, Chang HC (2002) Dopa-responsive parkinsonism phenotype of spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Mov Disord 17: 1046–1051
Lu CS, Wu Chou YH, Kuo PC, Chang HC, Weng YH (2004) The Parkinsonian phenotype of spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Arch Neurol 61: 35–38
Lücking CB, Dürr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denefle P, Wood NW, Filla A, Agid Y, Brice A, for the European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson’s Disease and the French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group (2000) Association between early onset Parkinson’s disease and mutations in the parkin gene. N Engl J Med 342: 1560–1567
Nicolas WC, Pankratz N, Hernandez D, Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Halter CA, Michaels V, Reed T, Rudolph A, Shults CW, Singleton A, Foroud T, for the Parkinson’s Study Group-PROGENI investigators (2005) Genetic screening for a single common LRRK2 mutation in familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 365: 410–412
Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evan EW, Gilks WP, Simon J, van der Brug M, deMunain AL, Aparicio S, Gil AM, Khan N, Johnson J, Martinez JR, Nicholl D, Carrera IM, Pena AS, de Silva R, Lees A, Marti-Masso JF, Perez-Tur J, Wood NW, Singleton AB (2004) Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8 linked Parkinson disease. Neuron 44: 595–600
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Bubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the a-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276: 2045–2047
Shan DI, Soong BW, Sun CM, Lee SJ, Liao KK, Liu RS (2001) Spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 presenting as familial levodopa-responsive parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 50: 812–815
Subramony SH, Hernandez D, Adam A, Smith-Jefferson S, Hussey J, Gwinn-Hardy K, Lynch T, McDaniel O, Hardy J, Farrer M, Singleton A (2002) Ethnic differences in the expression of neurodegenerative disease: Machado-Josephdisease in Africans and Caucasians. Mov Disord 17: 1068–1071
Tuite PJ, Rogaeva EA, St George-Hyslop PH, Lang AE (1995) Dopa-responsive parkinsonism phenotype of Machado-Joseph disease: confirmation of 14q CAG expansion. Ann Neurol 38: 684–687
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MMK, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG, Albanese A, Nussbaum R, Gonzalez-Maldonado R, Deller T, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW (2004) Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304: 1158–1160
Wu RM, Shan DE, Sun CM, Liu RS, Hwu WL, Tai CH, Hussey J, West A, Gwinn-Hardy K, Hardy J, Chen J, Farrer M, Lincoln S (2002) Clinical 18F-dopa PET, and genetic analysis of an ethnic Chinese kindred with early-onset parkinsonism and parkin gene mutations. Mov Disord 17: 670–675
Wu RM, Bounds R, Lincoln S, Hulihan M, Lin CH, Hwu WL, Chen J, Gwinn-Hardy K, Farrer M (2005) Parkin mutations and early-onset parkinsonism in a Taiwanese cohort. Arch Neurol 62: 82–87
Yen TC, Tzen KY, Chen MC, Wu Chou YH, Chen RS, Chen CJ, Wey SP, Ting G, Lu CS (2002) Dopamine transporter concentration is reduced in asymptomatic Machado-Joseph disease gene carriers. JNM 43: 153–159
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Muller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Storm TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44: 601–607
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lu, C.S., Wu Chou, Y.H., Weng, Y.H., Chen, R.S. (2006). Genetic and DAT imaging studies of familial parkinsonism in a Taiwanese cohort. In: Riederer, P., Reichmann, H., Youdim, M.B.H., Gerlach, M. (eds) Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa, vol 70. Springer, Vienna . https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-45295-0_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-45295-0_36
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-211-28927-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-211-45295-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)