Abstract
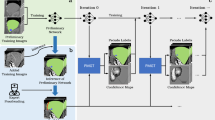
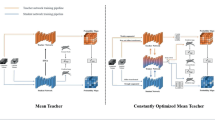
Accurate segmentation of brain tumors is crucial for cancer diagnosis, treatment planning, and evaluation. However, semi-supervised brain tumor image segmentation methods often face the challenge of mismatched distribution between labeled and unlabeled data. This study proposes a Segment Exchange Augmentation for Semi-supervised Segmentation Network (SEAS-Net) based on a teacher-student model that exchanges labeled and unlabeled data segments. This approach fosters unlabeled data to grasp general semantics from labeled data, and the consistent learning for both types notably reduces the empirical distribution gap. The SEAS-Net consists of two stages: supervised pre-training and semi-supervised segmentation. In the pre-training stage, segment exchange strategies optimize labeled images. During the semi-supervised stage, the teacher network generates pseudo-labels for unlabeled images. Subsequently, labeled and unlabeled images through segment exchange and input to the student network for generating predictive segmentation templates. Pseudo-labels and real mixed supervised signals supervise these predictions. Additionally, the discriminator after the student network enhances the reliability of prediction results. This methodology excels on the BraTS2019 and BraTS2021 datasets, effectively mitigating data distribution disparities and substantially enhancing brain tumor segmentation accuracy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alshehhi, R., Alshehhi, A.: Quantification of uncertainty in brain tumor segmentation using generative network and bayesian active learning. In: VISIGRAPP (4: VISAPP), pp. 701–709 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5220/0010341007010709
Bai, W., Oktay, O., Sinclair, M., Suzuki, H., Rajchl, M., Tarroni, G., Glocker, B., King, A., Matthews, P.M., Rueckert, D.: Semi-supervised learning for network-based cardiac MR image segmentation. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10434, pp. 253–260. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66185-8_29
Bai, Y., Chen, D., Li, Q., Shen, W., Wang, Y.: Bidirectional copy-paste for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11514–11524 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr52729.2023.01108
Bi, W.L., Hosny, A., Schabath, M.B., Giger, M.L., Birkbak, N.J., Mehrtash, A., Allison, I.F., others: Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: clinical challenges and applications 69(2), 127–157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21552, publisher: Wiley Online Library
Bortsova, G., Dubost, F., Hogeweg, L., Katramados, I., de Bruijne, M.: Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via learning consistency under transformations. In: Shen, D., Liu, T., Peters, T.M., Staib, L.H., Essert, C., Zhou, S., Yap, P.-T., Khan, A. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11769, pp. 810–818. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_90
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries 68(6), 394–424 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492, publisher: Wiley Online Library
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9901, pp. 424–432. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Dvornik, N., Mairal, J., Schmid, C.: Modeling visual context is key to augmenting object detection datasets. In: ECCV, pp. 364–380 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01258-8_23
Fan, J., Gao, B., **, H., Jiang, L.: Ucc: Uncertainty guided cross-head co-training for semi-supervised semantic segmentation (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.2205.10334
Fang, H.S., Sun, J., Wang, R., Gou, M., Li, Y.L., Lu, C.: Instaboost: boosting instance segmentation via probability map guided copy-pasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 682–691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2019.00077
Ghiasi, G., Cui, Y., Srinivas, A., Qian, R., Lin, T.Y., Cubuk, E.D., Le: Simple copy-paste is a strong data augmentation method for instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2918–2928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr46437.2021.00294
Kohl, S., et al.: Adversarial networks for the detection of aggressive prostate cancer. ar**v preprint ar**v:1702.08014 (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/ar**v.1702.08014
Li, S., Zhang, C., He, X.: Shape-aware semi-supervised 3d semantic segmentation for medical images. In: Martel, A.L., Abolmaesumi, P., Stoyanov, D., Mateus, D., Zuluaga, M.A., Zhou, S.K., Racoceanu, D., Joskowicz, L. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12261, pp. 552–561. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59710-8_54
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298965
Luo, X., Chen, J., Song, T., Wang, G.: Semi-supervised medical image segmentation through dual-task consistency. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 8801–8809 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i10.17066
Ronneberger, O.: Invited talk: u-net convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2017. I, pp. 3–3. Springer, Heidelberg (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54345-0_3
Shi, Y., Zhang, J., Ling, T., Lu, J., Zheng, Y., Yu, Q., Qi, L., Gao, Y.: Inconsistency-aware uncertainty estimation for semi-supervised medical image segmentation 41(3), 608–620 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2021.3117888, publisher: IEEE
Tarvainen, A., Valpola, H.: Mean teachers are better role models: Weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5555/3294771.3294885
Tu, P., Huang, Y., Zheng, F., He, Z., Cao, L., Shao, L.: GuidedMix-net: Semi-supervised semantic segmentation by using labeled images as reference. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, pp. 2379–2387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20137, issue: 2
Wu, Y., Wu, Z., Wu, Q., Ge, Z., Cai: exploring smoothness and class-separation for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In: MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, September 18–22, 2022, Proceedings, Part V, pp. 34–43. Springer (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_4
Yu, L., Wang, S., Li, X., Fu, C.-W., Heng, P.-A.: Uncertainty-aware self-ensembling model for semi-supervised 3D left atrium segmentation. In: Shen, D., Liu, T., Peters, T.M., Staib, L.H., Essert, C., Zhou, S., Yap, P.-T., Khan, A. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 605–613. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_67
Zülch, K.J.: Brain tumors: their biology and pathology. Springer (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-68178-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, J., Wu, W. (2024). SEAS-Net: Segment Exchange Augmentation for Semi-supervised Brain Tumor Segmentation. In: Rudinac, S., et al. MultiMedia Modeling. MMM 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14555. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53308-2_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53308-2_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-53307-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-53308-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)