Abstract
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides strong contrast for soft tissues but requires long acquisition times, oftentimes resulting in the motion artifacts. Recent advancements in MRI reconstruction from undersampled data rely on compressed sensing (CS) and deep learning (DL) techniques, allowing for significant scan acceleration while maintaining the image quality nearly at the fully sampled level.
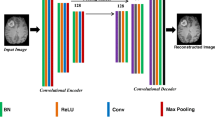
In this study, we propose to use the convolutional neural networks (CNN), such as U-net, to parametrize the objective function employed in the compressed sensing optimization problems. By doing so, our aim is to avoid unrealistic reconstructions often associated with traditional DL-based image reconstruction techniques.
To validate the proposed method, we used the CMRxRecon dataset containing cardiac raw k-space data. The results demonstrate realistic reconstruction of anatomical structures, outperforming classical CS reconstruction methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, A., Teboulle, M.: A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2(1), 183–202 (2009)
Belov, A., Stadelmann, J., Kastryulin, S., Dylov, D.V.: Towards Ultrafast MRI via Extreme k-Space Undersampling and Superresolution. In: de Bruijne, M., Cattin, P.C., Cotin, S., Padoy, N., Speidel, S., Zheng, Y., Essert, C. (eds.) MICCAI 2021. LNCS, vol. 12906, pp. 254–264. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_25
Candès, E.J., Romberg, J., Tao, T.: Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(2), 489–509 (2006)
Debatin, J.F., McKinnon, G.C.: Ultrafast MRI. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-80384-0
Griswold, M.A., et al.: Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (grappa). Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 47(6), 1202–1210 (2002)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.L.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization (2015)
Kuzmina, E., Razumov, A., Rogov, O.Y., Adalsteinsson, E., White, J., Dylov, D.V.: Autofocusing+: noise-resilient motion correction in magnetic resonance imaging. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 365–375. Springer, Heidelberg (2022), https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16446-0_35
Liu, R., Zhang, Y., Cheng, S., Luo, Z., Fan, X.: A deep framework assembling principled modules for CS-MRI: unrolling perspective, convergence behaviors, and practical modeling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(12), 4150–4163 (2020)
Lustig, M., Donoho, D., Pauly, J.M.: Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 58, 1182–1195 (2007)
Oh, G., et al.: Unpaired deep learning for accelerated MRI using optimal transport driven cycleGAN. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imag. 6, 1285–1296 (2020)
Pezzotti, N., et al.: An adaptive intelligence algorithm for undersampled knee MRI reconstruction. IEEE Access 8, 204825–204838 (2020)
Razumov, A., Rogov, O., Dylov, D.V.: Optimal MRI undersampling patterns for ultimate benefit of medical vision tasks. Magn. Reson. Imaging 103, 37–47 (2023)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Song, L., Zhang, J., Wang, Q.: MRI reconstruction based on three regularizations: total variation and two wavelets. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 30, 64–69 (2016)
Uecker, M., et al.: Espirit-an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: where sense meets grappa. Magn. Reson. Med. 71(3), 990–1001 (2014)
Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Yin, W.: A fast alternating direction method for tvl1-l2 signal reconstruction from partial Fourier data. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process. 4(2), 288–297 (2010)
Ye, J.C.: Compressed sensing MRI: a review from signal processing perspective. BMC Biomed. Eng. 1(1), 1–17 (2019)
Zbontar, J., et al.: fastMRI: an open dataset and benchmarks for accelerated MRI (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Razumov, A., Dylov, D.V. (2024). Learnable Objective Image Function for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction. In: Camara, O., et al. Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart. Regular and CMRxRecon Challenge Papers. STACOM 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14507. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-52447-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-52448-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)