Abstract
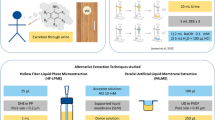
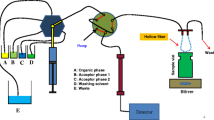
This chapter discusses microextraction using liquid membranes immobilized in a porous support membrane, including two- and three-phase hollow fibre liquid-phase microextraction (HF-LPME), 96-well LPME (or parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction (PALME)), and electromembrane extraction (EME). These techniques are essentially two- or three-phase liquid extraction systems, but downscaled to the level where the consumption of organic solvent per sample is less than 10 µL. Such microextraction systems are interesting for several reasons. First, they are ideal for green sample preparation, and therefore they are expected to be important in the near future in the context of sustainability. In addition, due to size and technical arrangement, they are easily implemented in microchip systems. Recently, several research papers have been investigating such microchip systems in combination with smartphone detection. This research has the potential to move analytical measurements out of today’s specialized laboratories. The fundamentals are discussed, to underline that microextraction with liquid membranes can be performed in partition-based systems, or in systems controlled by an external electrical field. In addition, this chapter discusses novel developments and new applications, based on examples from recent literature. The chapter is not comprehensive but is intended to give a flavour of the field.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EME:
-
Electromembrane extraction
- HF-LPME:
-
Hollow-fibre liquid-phase microextraction
- LPME:
-
Liquid-phase microextraction
- SDME:
-
Single drop microextraction
- SPME:
-
Solid-phase microextraction
References
Arthur CL, Pawliszyn J (1990) Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal Chem 62(19):2145–2148. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00218a019
Liu H, Dasgupta PK (1996) Analytical chemistry in a drop. Solvent extraction in a microdrop. Anal Chem 68(11):1817–1821. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac960145h
Jeannot MA, Cantwell FF (1996) Solvent microextraction into a single drop. Anal Chem 68(13):2236–2240. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac960042z
Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Rasmussen KE (1999) Liquid−Liquid−Liquid microextraction for sample preparation of biological fluids prior to capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 71(14):2650–2656. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac990055n
Lopes D, Morés L, da Silva M, Schneider M, Merib J, Carasek E (2022) Determination of hormones in urine by hollow fiber microporous membrane liquid–liquid extraction associated with 96-well plate system and HPLC-FLD detection. J Chromatogr B 1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2022.123406
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Parmer MP, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2013) Parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction: micro-scale liquid-liquid-liquid extraction in the 96-well format. Bioanalysis 5(11):1377–1385. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.13.59
Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Rasmussen KE (2006) Electrokinetic migration across artificial liquid membranes: new concept for rapid sample preparation of biological fluids. J Chromatogr A 1109(2):183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.01.025
Goh SXL, Goh HA, Lee HK (2018) Automation of ionic liquid enhanced membrane bag-assisted-liquid-phase microextraction with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of glucocorticoids in water. Anal Chim Acta 1035:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.07.031
Jiang X, Lee HK (2004) Solvent bar microextraction. Anal Chem 76(18):5591–5596. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac040069f
Fashi A, Salarian AA, Zamani A (2018) Solvent-stir bar microextraction system using pure tris-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate as supported liquid membrane: a new and efficient design for the extraction of malondialdehyde from biological fluids. Talanta 182:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.02.002
Pantůčková P, Kubáň P (2017) In-line coupling of supported liquid membrane extraction to capillary electrophoresis for simultaneous analysis of basic and acidic drugs in urine. J Chromatogr A 1519:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.08.084
Lopes D, Dias AN, Simão V, Carasek E (2017) Determination of emerging contaminants in aqueous matrices with hollow fiber-supported dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (HF-DLLME) and separation/detection by liquid chromatography: diode array detection. Microchem J 130:371–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.10.011
Asl YA, Yamini Y, Seidi S (2016) Development of a microfluidic-chip system for liquid–phase microextraction based on two immiscible organic solvents for the extraction and preconcentration of some hormonal drugs. Talanta 160:592–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.07.063
Berijani S, Assadi Y, Anbia M, Milani Hosseini MR, Aghaee E (2006) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography-flame photometric detection. Very simple, rapid and sensitive method for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water. J Chromatogr A 1123(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.05.010
Gjelstad A, Andersen TM, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2007) Microextraction across supported liquid membranes forced by pH gradients and electrical fields. J Chromatogr A 1157(1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.05.007
Ocaña-González JA, Aranda-Merino N, Pérez-Bernal JL, Ramos-Payán M (2023) Solid supports and supported liquid membranes for different liquid phase microextraction and electromembrane extraction configurations: a review. J Chromatogr A 1691:463825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2023.463825
Huang CX, Gjelstad A, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2016) Organic solvents in electromembrane extraction: recent insights. Rev Anal Chem 35(4):169–183. https://doi.org/10.1515/revac-2016-0008
Ho TS, Vasskog T, Anderssen T, Jensen E, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2007) 25,000-fold pre-concentration in a single step with liquid-phase microextraction. Anal Chim Acta 592(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.04.014
Wang P, **ao Y, Liu W, Wang J, Yang Y (2015) Vortex-assisted hollow fibre liquid-phase microextraction technique combined with high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection for the determination of oestrogens in milk samples. Food Chem 172:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.092
Seyfinejad B, Ozkan SA, Jouyban A (2021) Ultrasound-assisted electromembrane extraction of clonazepam from plasma and determination using capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr B 1181:122928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122928
Shang Q, Mei H, Feng X, Huang C, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Shen X (2021) Ultrasound-assisted electromembrane extraction with supported semi-liquid membrane. Anal Chim Acta 1184:339038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339038
Román-Hidalgo C, Martín-Valero MJ, Fernández-Torres R, Bello-López MÁ (2018) Use of polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs) as support for electromembrane extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and highly polar acidic drugs. Talanta 179:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.11.066
Alsharif AMA, Tan G-H, Choo Y-M, Lawal A (2017) Efficiency of hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction chromatography methods in the separation of organic compounds: a review. J Chromatogr Sci 55(3):378–391. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmw188
Romero A, Santos A, Tojo J, Rodríguez A (2008) Toxicity and biodegradability of imidazolium ionic liquids. J Hazard Mater 151(1):268–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.079
Hansen FA, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2020) Emerging extraction strategies in analytical chemistry. Anal Chem 92(1):2–15. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04677
Wang J, Huang S, Wang P, Yang Y (2016) Method development for the analysis of phthalate esters in tea beverages by ionic liquid hollow fibre liquid-phase microextraction and liquid chromatographic detection. Food Control 67:278–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.03.015
Sun JN, Chen J, Shi YP (2014) Ionic liquid-based electromembrane extraction and its comparison with traditional organic solvent based electromembrane extraction for the determination of strychnine and brucine in human urine. J Chromatogr A 1352:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.037
Sun JN, Shi YP, Chen J (2015) Development of ionic liquid based electromembrane extraction and its application to the enrichment of acidic compounds in pig kidney tissues. RSC Adv 5(47):37682–37690. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra01029b
De Boeck M, Dubrulle L, Dehaen W, Tytgat J, Cuypers E (2018) Fast and easy extraction of antidepressants from whole blood using ionic liquids as extraction solvent. Talanta 180:292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.12.044
Andruch V, Makoś-Chełstowska P, Płotka-Wasylka J (2022) Remarks on use of the term “deep eutectic solvent” in analytical chemistry. Microchem J 179:107498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107498
Abbott AP, Capper G, Davies DL, Rasheed RK, Tambyrajah V (2003) Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem Commun 1:70–71. https://doi.org/10.1039/B210714G
van Osch DJGP, Zubeir LF, van den Bruinhorst A, Rocha MAA, Kroon MC (2015) Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem 17(9):4518–4521. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC01451D
van Osch DJGP, Dietz CHJT, van Spronsen J, Kroon MC, Gallucci F, van Sint AM, Tuinier R (2019) A search for natural hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents based on natural components. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(3):2933–2942. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03520
Makoś P, Przyjazny A, Boczkaj G (2018) Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as “green” extraction media for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. J Chromatogr A 1570:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.07.070
Makoś P, Słupek E, Gębicki J (2020) Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in microextraction techniques: a review. Microchem J 152:104384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104384
Seidi S, Alavi L, Jabbari A, Shanehsaz M (2019) Three-phase carrier-mediated hollow fiber microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent followed by HPLC–UV for determination of raloxifene and ethinylestradiol in pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plants. J Iran Chem Soc 16(5):1007–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-018-01572-4
Zhang SM, Zhang XX, Chen X, Hu S, Bai XH (2020) Deep eutectic solvent-based hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction for quantification of Q-markers of cinnamic acid derivatives in traditional Chinese medicines and research of their plasma protein binding rates. Microchem J 155:104696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104696
Hansen FA, Santigosa-Murillo E, Ramos-Payán M, Muñoz M, Leere Øiestad E, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2021) Electromembrane extraction using deep eutectic solvents as the liquid membrane. Anal Chim Acta 1143:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.11.044
Hansen FA, Tirandaz S, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2021) Selectivity and efficiency of electromembrane extraction of polar bases with different liquid membranes—link to analyte properties. J Sep Sci 44(13):2631–2641. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202100167
Hay AO, Trones R, Herfindal L, Skrede S, Hansen FA (2022) Determination of methotrexate and its metabolites in human plasma by electromembrane extraction in conductive vials followed by LC-MS/MS. Adv Sample Prep 2:100011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sampre.2022.100011
Rye TK, Martinovic G, Eie LV, Hansen FA, Halvorsen TG, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2021) Electromembrane extraction of peptides using deep eutectic solvents as liquid membrane. Anal Chim Acta 1175:338717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338717
Ballesteros-Gómez A, Sicilia MD, Rubio S (2010) Supramolecular solvents in the extraction of organic compounds: a review. Anal Chim Acta 677(2):108–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.07.027
Rezaei F, Yamini Y, Moradi M, Daraei B (2013) Supramolecular solvent-based hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction of benzodiazepines. Anal Chim Acta 804:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.10.026
Li X, Huang A, Liao X, Chen J, **ao Y (2020) Restricted access supramolecular solvent based magnetic solvent bar liquid-phase microextraction for determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in human serum coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1634:461700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461700
Rubio S (2020) Twenty years of supramolecular solvents in sample preparation for chromatography: achievements and challenges ahead. Anal Bioanal Chem 412(24):6037–6058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02559-y
Nemulenzi O, Mhaka B, Cukrowska E, Ramström O, Tutu H, Chimuka L (2009) Potential of combining of liquid membranes and molecularly imprinted polymers in extraction of 17β-estradiol from aqueous samples. J Sep Sci 32(11):1941–1948. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800659
Yaripour S, Nojavan S, Khoshayand MR, Mohammadi A (2020) Electromembrane extraction of phenytoin from biological fluids: a survey on the effects of molecularly imprinted polymer and carbon nanotubes on extraction efficiency. Microchem J 156:104800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104800
Worawit C, Alahmad W, Miró M, Varanusupakul P (2020) Combining graphite with hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction for improving the extraction efficiency of relatively polar organic compounds. Talanta 215:120902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120902
Tahmasebi Z, Davarani SSH, Asgharinezhad AA (2018) Highly efficient electrochemical determination of propylthiouracil in urine samples after selective electromembrane extraction by copper nanoparticles-decorated hollow fibers. Biosens Bioelectron 114:66–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.014
López-Lorente ÁI, Pena-Pereira F, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Zuin VG, Ozkan SA, Psillakis E (2022) The ten principles of green sample preparation. Trends Anal Chem 148:116530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2022.116530
Poole C, Mester Z, Miró M, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Pawliszyn J (2016) Glossary of terms used in extraction (IUPAC Recommendations 2016). Pure Appl Chem 88(5):517–558. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2015-0903
Cabal LFR, Medina DAV, Costa JL, Lanças FM, Santos-Neto ÁJ (2019) Determination of ring-substituted amphetamines through automated online hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction-liquid chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(29):7889–7897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02196-0
Fuchs D, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Jensen H, Rand KD, Honore Hansen S, Petersen NJ (2016) Fully automated electro membrane extraction autosampler for LC-MS systems allowing soft extractions for high-throughput applications. Anal Chem 88(13):6797–6804. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01243
Lopes D, Dias AN, Merib J, Carasek E (2018) Hollow-fiber renewal liquid membrane extraction coupled with 96-well plate system as innovative high-throughput configuration for the determination of endocrine disrupting compounds by high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence and diode array detection. Anal Chim Acta 1040:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.07.032
Luo G, Li Y, Bao JJ (2016) Development and application of a high-throughput sample cleanup process based on 96-well plate for simultaneous determination of 16 steroids in biological matrices using liquid chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(4):1137–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9213-1
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Parmer MP, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2013) Parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction: micro-scale liquid–liquid–liquid extraction in the 96-well format. Bioanalysis 5(11):1377–1385. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio.13.59
Drouin N, Mandscheff JF, Rudaz S, Schappler J (2017) Development of a new extraction device based on parallel-electromembrane extraction. Anal Chem 89(12):6346–6350. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01284
Restan MS, Jensen H, Shen X, Huang C, Martinsen OG, Kuban P, Gjelstad A, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2017) Comprehensive study of buffer systems and local pH effects in electromembrane extraction. Anal Chim Acta 984:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.06.049
Miková B, Dvořák M, Ryšavá L, Kubáň P (2020) Hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction at-line coupled to capillary electrophoresis for direct analysis of human body fluids. Anal Chem 92(10):7171–7178. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00697
Zhou WL, Ding L, Cheng YH, Xu Z, Chen ML, Fu XS (2022) Application of an improved hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction technique coupled to LC-MS/MS to studying migration of fluorescent whitening agents from plastic food contact materials. Food Addit Contam Part A 39(7):1337–1347. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2022.2066192
Drobnjak M, Hansen F, Øiestad EL, Løvli T, Trones R, Martinsen ØG, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2020) Electromembrane extraction with vials of conducting polymer. LCGC North Am 38(8):435–439
Skaalvik TG, Øiestad EL, Trones R, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Hegstad S (2021) Determination of psychoactive drugs in serum using conductive vial electromembrane extraction combined with UHPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 1183:122926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122926
Zarghampour F, Yamini Y, Alipanahpour Dil E, Shokrollahi A, Javadian G (2023) A new microfluidic-chip device followed by sensitive image analysis of smart phone for simultaneous determination of dyes with different acidic–basic properties. Talanta 254:124168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.124168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hansen, F.A., Pedersen-Bjergaard, S. (2024). Hollow-Fibre Liquid-Phase Microextraction. In: Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á., Socas-Rodríguez, B., Herrera-Herrera, A.V. (eds) Microextraction Techniques. Integrated Analytical Systems. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50527-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50527-0_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-50526-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-50527-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)