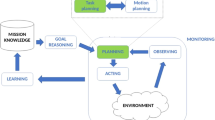
Abstract
This study presents a review of applications of Inductive Logic Programming (ILP) for robotic systems. The aim of the paper is to demonstrate the different methods of applying ILP to a robotic system and to also highlight some of the limitations that already exist. ILP can aid in the development of explainable and trustworthy robotics systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar, N., Füller, M., Kahl, B., Henne, T.: Towards iterative learning of autonomous robots using ILP. In: 2011 15th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), pp. 409–414 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAR.2011.6088625
Bratko, I.: Prolog Programming for Artificial Intelligence. Pearson Education, London (2001)
Brown, S., Sammut, C.: A relational approach to tool-use learning in robots. In: Riguzzi, F., Železný, F. (eds.) ILP 2012. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 7842, pp. 1–15. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38812-5_1
Corapi, D., Sykes, D., Inoue, K., Russo, A.: Probabilistic rule learning in nonmonotonic domains. In: Leite, J., Torroni, P., Ågotnes, T., Boella, G., van der Torre, L. (eds.) CLIMA 2011. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6814, pp. 243–258. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22359-4_17
Cropper, A., Dumančić, S.: Inductive logic programming at 30: a new introduction. ar**v preprint: ar**v:2008.07912 (2020)
Cropper, A., Dumančić, S.: Inductive logic programming at 30: a new introduction. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 74, 765–850 (2022)
Cropper, A., Morel, R.: Learning programs by learning from failures (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2005.02259
Cropper, A., Muggleton, S.H.: Logical minimisation of meta-rules within meta-interpretive learning. In: Davis, J., Ramon, J. (eds.) ILP 2014. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 9046, pp. 62–75. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23708-4_5
De Raedt, L., Kimmig, A., Toivonen, H.: ProbLog: a probabilistic prolog and its application in link discovery. In: IJCAI 2007, Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 2462–2467. IJCAI-INT JOINT CONF ARTIF INTELL (2007)
Drole, M., et al.: Learning from depth sensor data using inductive logic programming. In: 2015 XXV International Conference on Information, Communication and Automation Technologies (ICAT), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2015)
Evans, R., et al.: Making sense of raw input. Artif. Intell. 299, 103521 (2021)
Evans, R., Grefenstette, E.: Learning explanatory rules from noisy data. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 61, 1–64 (2018)
Fabisch, A., Petzoldt, C., Otto, M., Kirchner, F.: A survey of behavior learning applications in robotics-state of the art and perspectives. ar**v preprint: ar**v:1906.01868 (2019)
Garcez, A.D., Gori, M., Lamb, L.C., Serafini, L., Spranger, M., Tran, S.N.: Neural-symbolic computing: an effective methodology for principled integration of machine learning and reasoning. ar**v preprint: ar**v:1905.06088 (2019)
Garcez, A.D., et al.: Neural-symbolic learning and reasoning: a survey and interpretation. Neuro-Symbol. Artif. Intell.: State Art 342(1), 327 (2022)
Gunning, D.: Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), nd Web (2017)
Kapotoglu, M., Koc, C., Sariel, S.: Robots avoid potential failures through experience-based probabilistic planning. In: 2015 12th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO), vol. 2, pp. 111–120. IEEE (2015)
Károly, A.I., Galambos, P., Kuti, J., Rudas, I.J.: Deep learning in robotics: survey on model structures and training strategies. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybernet.: Syst. 51(1), 266–279 (2020)
Kober, J., Bagnell, J.A., Peters, J.: Reinforcement learning in robotics: a survey. Int. J. Robot. Res. 32(11), 1238–1274 (2013)
Kowalski, R., Sadri, F.: From logic programming towards multi-agent systems. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 25(3), 391–419 (1999)
Law, M., Russo, A., Broda, K.: Inductive learning of answer set programs from noisy examples. ar**v preprint: ar**v:1808.08441 (2018)
Leban, G., Žabkar, J., Bratko, I.: An experiment in robot discovery with ILP. In: Železný, F., Lavrač, N. (eds.) ILP 2008. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5194, pp. 77–90. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-85928-4_10
Moldovan, B., Moreno, P., Nitti, D., Santos-Victor, J., De Raedt, L.: Relational affordances for multiple-object manipulation. Auton. Robot. 42, 19–44 (2018)
Moldovan, B., Moreno, P., Van Otterlo, M., Santos-Victor, J., De Raedt, L.: Learning relational affordance models for robots in multi-object manipulation tasks. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4373–4378. IEEE (2012)
Muggleton, S.: Inductive logic programming. New Gener. Comput. 8(4), 295–318 (1991)
Muggleton, S.: Inverse entailment and progol. N. Gener. Comput. 13(3–4), 245–286 (1995)
Muggleton, S., Buntine, W.: Machine invention of first-order predicates by inverting resolution. In: Machine Learning Proceedings 1988, pp. 339–352. Elsevier (1988)
Muggleton, S., et al.: Efficient Induction of Logic Programs. Citeseer, San Diego (1990)
Muggleton, S., de Raedt, L.: Inductive logic programming: theory and methods. J. Logic Programm. 19–20, 629–679 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0743-1066(94)90035-3
Muggleton, S., Santos, J., Tamaddoni-Nezhad, A.: ProGolem: a system based on relative minimal generalisation. In: De Raedt, L. (ed.) ILP 2009. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5989, pp. 131–148. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13840-9_13
Muggleton, S.H., Lin, D., Tamaddoni-Nezhad, A.: Meta-interpretive learning of higher-order dyadic datalog: predicate invention revisited. Mach. Learn. 100(1), 49–73 (2015)
Müller, M.E.: ALSACE memo. On the needs for specification and verification of collaborative and concurrent robots, agents and processes, p. 74
Ranasinghe, D., Karunananda, A.: Qualitative knowledge driven approach to inductive logic programming. In: First International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems, pp. 79–83. IEEE (2006)
Rouveirol, C., Puget, J.F.: Beyond inversion of resolution. In: Machine Learning Proceedings 1990, pp. 122–130. Elsevier (1990)
Sammut, C., Sheh, R., Haber, A., Wicaksono, H.: The robot engineer. In: ILP (late breaking papers), pp. 101–106 (2015)
Sariel, S., Yildiz, P., Karapinar, S., Altan, D., Kapotoglu, M.: Robust task execution through experience-based guidance for cognitive robots. In: 2015 International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), pp. 663–668. IEEE (2015)
Solak, G., Ak, A.C., Sariel, S.: Experience-based learning of symbolic numerical constraints. In: 2016 IEEE-RAS 16th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), pp. 1264–1269. IEEE (2016)
Srinivasan, A.: The aleph manual (2001)
Stahl, I.: Predicate invention in ILP — an overview. In: Brazdil, P.B. (ed.) ECML 1993. LNCS, vol. 667, pp. 311–322. Springer, Heidelberg (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-56602-3_144
Sykes, D., Corapi, D., Magee, J., Kramer, J., Russo, A., Inoue, K.: Learning revised models for planning in adaptive systems. In: 2013 35th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE), pp. 63–71. IEEE (2013)
Vargas, B., Morales, E.F.: Learning navigation teleo-reactive programs using behavioural cloning. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2009)
Xu, D., Fekri, F.: Interpretable model-based hierarchical reinforcement learning using inductive logic programming. ar**v preprint: ar**v:2106.11417 (2021)
Zuidberg Dos Martires, P., Kumar, N., Persson, A., Loutfi, A., De Raedt, L.: Symbolic learning and reasoning with noisy data for probabilistic anchoring. Front. Robot. AI 7, 100 (2020)
Acknowledgement
This work is partially supported by a grant of the Graduate Institute and the Computer Science Department of the Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg. The authors thank the reviewers for their valuable input which helped us improving this submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Youssef, Y.M., Müller, M.E. (2023). A Review of Inductive Logic Programming Applications for Robotic Systems. In: Bellodi, E., Lisi, F.A., Zese, R. (eds) Inductive Logic Programming. ILP 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14363. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49299-0_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49299-0_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-49298-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-49299-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)