Abstract
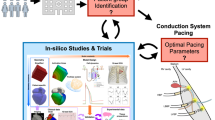
In this work, we report on the application of a closed-loop system, composed of a 2D reaction-diffusion heart model and a pace-maker model, for assessing pacemaker-heart interactions.
To demonstrate the potential of our approach, we replicated a clinical case report in which a ventricular pacing-minimizing strategy promoted the onset of Pacemaker-Mediated Tachycardia (PMT). To replicate the clinical case, we simulated an atrioventricular (AV) block condition and set the same pacemaker programming reported in the clinical case study. Our study aims to show the usability and potential of our framework by exploring different pacemaker settings coupled with specific electro-physiological heart conditions, thus allowing the assessment of the safety and efficacy of a particular pacing algorithm. The results from our heart model highlighted that the refractoriness of the AV node, in addition to the pacemaker setting (e.g., AV delay and Post Ventricular Atrial Refractory period), plays a crucial role in the onset of PMTs in patients with pacemakers programmed with an AV delay hysteresis algorithm. We believe that our closed-loop system could represent a valuable auxiliary tool for a preliminary assessment and comparison of various pacing algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lloyd, M., El Chami, M., Langberg, J.: Pacing features that mimic malfunction: a review of current programmable and automated device functions that cause confusion in the clinical setting. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 20, 453–460 (2009)
Jankelson, L., Bordachar, P., Strik, M., Ploux, S., Chinitz, L.: Reducing right ventricular pacing burden: algorithms, benefits, and risks. EP Europace. 21, 539–547 (2019)
Sweeney, M., et al.: Minimizing ventricular pacing to reduce atrial fibrillation in sinus-node disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 1000–1008 (2007)
Perez, M., Al-Ahmad, A., Wang, P., Turakhia, M.: Inappropriate pacing in a patient with managed ventricular pacing: what is the cause? Heart Rhythm 7, 1336–1337 (2010)
Calton, R., Hariya, M., Calton, R., Bali, R., Varshney, S.: Pacemaker-Mediated tachycardia leading to ventricular tachycardia and syncope. IHJ Cardiovasc Case Rep. (CVCR) 6, 45–49 (2022)
Bauer, A., Vermeulen, J., Toivonen, L., Voitk, J., Barr, C., Peytchev, P.: Minimizing right ventricular pacing in pacemaker patients with intact and compromised atrioventricular conduction: Results from the EVITA trial. Herzschrittmachertherapie Elektrophysiologie. 26, 359–366 (2015)
Barold, S., Stroobandt, R.: Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia initiated by an atrioventricular search algorithm to minimize right ventricular pacing. J. Electrocardiol. 45, 336–339 (2012)
Dennis, M., Sparks, P.: Pacemaker mediated tachycardia as a complication of the autointrinsic conduction search function. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 27, 824–826 (2004)
Ai, W., Patel, N., Roop, P., Malik, A., Trew, M.: Closing the loop: validation of implantable cardiac devices with computational heart models. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 24, 1579–1588 (2019)
Jiang, Z., Pajic, M., Mangharam, R.: Cyber–physical modelling of implantable cardiac medical devices. Proc. IEEE 100, 122–137 (2011)
Biasi, N., Seghetti, P., Mercati, M., Tognetti, A.: A reaction-diffusion heart model for the closed-loop evaluation of heart-pacemaker interaction. IEEE Access 10, 121249–121260 (2022)
Biasi, N., Tognetti, A.: A computationally efficient dynamic model of human epicardial tissue. PLoS ONE 16, e0259066 (2021)
Fenton, F., Cherry, E., Karma, A., Rappel, W.: Modelling wave propagation in realistic heart geometries using the phase-field method. Chaos Interdisc. J. Nonlinear Sci. 15, 013502 (2005)
Yu, H., Chen, H., Thornton, K.: Extended smoothed boundary method for solving partial differential equations with general boundary conditions on complex boundaries. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 20, 075008 (2012)
Jiang, Z., Pajic, M., Connolly, A., Dixit, S. Mangharam, R.: Real-time heart model for implantable cardiac device validation and verification. In 2010 22nd Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems, pp. 239–248 (2010)
Dehghani, M., Soleimani, A., Nasab, M.: Clinical and electrophysiological predictors of ventriculoatrial conduction in patients under evaluation for ventricular tachyarrhythmia. J. Tehran Heart Center. 5, 179 (2010)
Lemery, R., et al.: Normal atrial activation and voltage during sinus rhythm in the human heart: an endocardial and epicardial map** study in patients with a history of atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 18, 402–408 (2007)
Josephson, M.: Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology: Techniques and Interpretations. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2008)
Durrer, D., Van Dam, R., Freud, G., Janse, M., Meijler, F., Arzbaecher, R.: Total excitation of the isolated human heart. Circulation 41, 899–912 (1970)
Inada, S., Hancox, J., Zhang, H., Boyett, M.: One-dimensional mathematical model of the atrioventricular node including atrio-nodal, nodal, and nodal-his cells. Biophys. J. 97, 2117–2127 (2009)
Ryzhii, M., Ryzhii, E.: A compact multi-functional model of the rabbit atrioven-tricular node with dual pathways. Front. Physiol. 14 (2023)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from the lab “Cloud Computing, Big Data and Cybersecurity” of the Information Engineering Department of the University of Pisa (CrossLab project, Departments of Excellence, Italian Ministry of University and Research). The work is partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Education and Research (MIUR) in the framework of the FoReLab project (Departments of Excellence).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mercati, M., Biasi, N., Seghetti, P., Tognetti, A. (2024). In Silico Closed-Loop System for the Assessment of Cardiac Pacing Algorithms. In: Badnjević, A., Gurbeta Pokvić, L. (eds) MEDICON’23 and CMBEBIH’23. MEDICON CMBEBIH 2023 2023. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 94. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49068-2_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49068-2_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-49067-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-49068-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)