Abstract
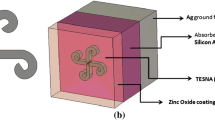
A unit cell design of a thin film solar cell incorporating turnstile diamond dipole nanoantenna as a means of light trap** structure is proposed and investigated. Diamond dipole nanoantenna (DDNA) is a transformed version of the conventional dipole nanoantenna whereby the arms of the dipole nanoantenna are replaced by diamond shaped nanoparticles. In contrast to the dipole nanoantenna, DDNA offers larger area for field confinement and it resonates in the maximum solar spectrum range. The reduction of reflection losses along with generation of localized surface plasmons leads to improved photovoltaic characteristics of the thin film solar cell. The suggested TFSC model offers 99% absorption with 1.52 times photocurrent calculated based on finite element approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kraemer, F.A., Palma, D., Braten, A.E., Ammar, D.: Operationalizing solar energy predictions for sustainable autonomous IoT device management. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(12), 11803–11814 (2020)
Pareek, P., Maurya, N.K., Singh, L., Gupta, N., Reis, M.J.C.S.: Study of smart city compatible monolithic quantum well photodetector. In: Gupta, N., Pareek, P., Reis, M. (eds.) Cognitive Computing and Cyber Physical Systems. IC4S 2022. LNICST, , vol. 472. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28975-0_18
Lee, T.D., Ebong, A.U.: A review of thin film solar cell technologies and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 70, 1286–1297 (2017)
Best Research-Cell Efficiency Chart. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html. Accessed 14 Feb 2023
Muhammad, M.H., Hameed, M.F.O., Obayya, S.S.A.: Broadband absorption enhancement in modified grating thin-film solar cell. IEEE Photon. J. 9(3), 2700314 (2017)
Catchpole, K.R., Polman, A.: Design principles for particle plasmon enhanced solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 191113 (2008)
Zhu, J., Hsu, C.-M., Yu, Z., Fan, S., Cui, Y.: Nanodome solar cells with efficient lightmanagement and self-cleaning. Nano Lett. 10, 1979–1984 (2010)
Atwater, H.A., Polman, A.: Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat. Mater. 9, 205–213 (2010)
Wu, J.L., Chen, F.C., Hasio, Y.S., Chien, F.C., Chen, P., Kuo, C.H., et al.: Surface plasmonic effects of metallic nanoparticles on the performance of polymer bulk heterojunction solar cells. ACS Nano 5(2), 959–967 (2011)
Maier, SA.: Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications, 2007th edn. Springer-Verlag, India (2007)
Green, M.A., Pillai, S.: Harnessing plasmonics for solar cells. Nat. Photon. 6, 130–132 (2012)
Muhlschlegel, P., et al.: Resonant optical antennas. Science 308, 1607–1608 (2005)
Taghian, F., Ahmadi, V., Yousefi, L.: Enhanced thin solar cells using optical nano-antenna induced hybrid plasmonic travelling-wave. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 34, 1267–1273 (2016)
Di, V.M., et al.: Plasmonic nano-antenna a-Si: H solar cell. Opt. Express 20(25), 27327–27336 (2012)
Yu, Y., et al.: Dielectric core−shell optical antennas for strong solar absorption enhancement. Nano Lett. 12(7), 3674–3681 (2012)
Pahuja, A., Parihar, M.S., Dinesh Kumar, V.: Investigation of Euler spiral nanoantenna and its application in absorption enhancement of thin film solar cell. Opt. Quant. Electron. 50(11), 1–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1665-z
Pahuja, A., Parihar, M.S., Dinesh Kumar, V.: Performance enhancement of thin-film solar cell using Yagi–Uda nanoantenna array embedded inside the anti-reflection coating. Appl. Phys. A 126(1), 1–7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3250-0
CST Studio Suite. https://www.3ds.com/products-services/simulia/products/cst-studio-suite/. Accessed 5 Jan 2023
Raether, H.: Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Johnson, P.B., Christy, R.W.: Optical constant of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 15, 4370–4379 (1972)
ASTM, Reference Solar Spectral Irradiance: Air Mass 1.5 Spectra. http://rredc.nrel.gov/solar/spectra/am1.5. Accessed 5 Dec 2023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pahuja, A., Kumar, S., Agarwal, V., Parihar, M.S., Dinesh Kumar, V. (2024). Turnstile Diamond Dipole Nanoantenna Based Smart City Compatible Thin Film Solar Cell. In: Pareek, P., Gupta, N., Reis, M.J.C.S. (eds) Cognitive Computing and Cyber Physical Systems. IC4S 2023. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 537. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48891-7_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48891-7_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-48890-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-48891-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)