Abstract
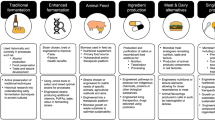
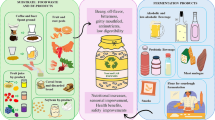
The existing food structures are based on unsustainable methods that fails to circumvent the issue of rising population and accessibility for the nutritious diet, thus embarking the new sustainable, reliable and nutritious sources such as micro-organisms. Microbes are the most suitable alternative as nutritional source as they have minimal carbon footprint, limited usage of resources such as land, water, nutrients and seasonal dependence. Additionally, with the advances in synthetic biology, potential of microbes has been raised to the next level to meet the many unmet nutritional demands. In this chapter we explore the various microbes as an additional sustainable nutritional source and impact on the recent food structure.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajpai P, Bajpai P (2017) Microorganisms used for single-cell protein production. In: Single cell protein production from lignocellulosic biomass, pp 21–30
Banks M, Johnson R, Giver L, Bryant G, Guo M (2022) Industrial production of microbial protein products. Curr Opin Biotechnol 75:102707
Change IC (2019) Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change. Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems 1– 864 (IPCC)
Choi KR, Yu HE, Lee SY (2022) Microbial food: microorganisms repurposed for our food. Micro Biotechnol 15:18–25
Ciani M, Lippolis A, Fava F, Rodolfi L, Niccolai A, Tredici MR (2021) Microbes: food for the future. Food 10(5):971
Cuskin F, Lowe EC, Temple MJ, Zhu Y, Cameron E, Pudlo NA, Porter NT, Urs K, Thompson AJ, Cartmell A, Rogowski A, Hamilton BS, Chen R, Tolbert TJ, Piens K, Bracke D, Vervecken W, Hakki Z, Speciale G, Munōz-Munōz JL, Day A, Peña MJ, McLean R, Suits MD, Boraston AB, Atherly T, Ziemer CJ, Williams SJ, Davies GJ, Abbott DW, Martens EC, Gilbert HJ (2015) Human gut Bacteroidetes can utilize yeast mannan through a selfish mechanism. Nat 517:165–169
Ercili-Cura D, Hakamies A, Sinisalo L, Vainikka P, Pitkanen J (2020) Food out of thin air. Food Sci Technol 34(2):44–48
Erdoğan E, Orhan KA, Derin E, Hava Bazlı EBCİMBÇ (2022) Proteinin Alternatif Bir Protein Kaynağı Olarak Kullanım Olanaklarının İncelenmesi. Intern J Life Sci Biotechnol 15(3):643–668
Gao R, Li Z, Zhou X, Bao W, Chemg S, Zheng L (2020) Enhanced lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica cultured with synthetic and waste-derived high-content volatile fatty acids under alkaline conditions. Biotechnol Biofuels 13:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1645-y
Graham AE, Ledesma-Amaro R (2023) The microbial food revolution. Nat Commun 14(2231):1–10
Helmy M, Elhalis H, Yan L, Chow Y, Selvarajoo K (2022) Perspective: multi-omics and machine learning help unleash the alternative food potential of microalgae. Adv Nutr 14:1–11
Jach ME, Serefko A, Ziaja M, Kieliszek M (2022) Yeast protein as an easily accessible food source. Metabol 12:63
Javourez U, O’Donohue M, Hamelin L (2021) Waste-to-nutrition: a review of current and emerging conversion pathways. Biotechnol Adv 53:107857
Jones SW, Karpol A, Friedman S, Maru BT, Tracy BP (2020) Recent advances in single cell protein use as a feed ingredient in aquaculture. Curr Opin Biotechnol 61:189–197
Linder T (2019) Making the case for edible microorganisms as an integral part of a more sustainable and resilient food production system. Food Secur 11:265–278
Marco ML, Heeney D, Binda S, Cifelli CJ, Cotter PD, Foligné B, Gänzle M, Kort R, Pasin G, Pihlanto A, Smid EJ, Hutkins R (2017) Health benefits of fermented foods: microbiota and beyond. Curr Opinion Biotechnol 44:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.11.010
Marullo P, Dubourdieu D (2022) Yeast selection for wine flavor modulation. in Managing Wine Quality (ed. Reynolds, A. G.) Elsevier, pp 371–426
McFarlin BK, Carpenter KC, Davidson T, McFarlin MA (2013) Baker’s yeast beta glucan supplementation increases salivary iga and decreases cold/flu symptomatic days after intense exercise. J Diet 10:171–183
Moreira JB, Vaz BdS, Cardias BB, Cruz CG, ACAd, Almeida, Costa JAV, MGd, Morais (2022) Microalgae polysaccharides: an alternative source for food production and sustainable agriculture. Polysacc 3(2):441–457
Pan M, Barrangou R (2020) Combining omics technologies with CRISPR-based genome editing to study food microbes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 61:198–208
Ritala A, Häkkinen ST, Toivari M, Wiebe MG (2017) Single cell protein—state-of-the-art, industrial landscape and patents 2001–2016. Front Microbiol 13:8–2009
Rockström J, Edenhofer O, Gaertner J, DeClerck F (2020) Planet-proofing the global food system. Nat Food 1:3–5
Sen T, Barrow CJ, Deshmukh SK (2019) Microbial pigments in the food industry—challenges and the way forward. Front Nutr 6:7
Sharif M, Hammad Zafar M, Islam Aqib A, Saeed M, Farag MR, Alagawany M (2021) Single cell protein: sources, mechanism of production, nutritional value and its uses in aquaculture nutrition. Aquacult 531:735885
Sousa I, Gouveia L, Batista AP, Raymundo A, Bandarra NM (2008) Microalgae in novel food products. Food Chem Res Develop 75–112
Sun Z, Sun Z, Scherer L, Tukker A, Spawn-Lee S, Brukner M, Gibbs HK (2022) Dietary change in high-income nations alone can lead to substantial double climate dividend. Nat Food 3:29–37
Tamang JP, Shin DH, Jung SJ, Chae SW (2016) Functional properties of microorganisms in fermented foods. Front Microbiol 7:578
Turnbull WH, Leeds AR, Edwards GD (1990) Effect of mycoprotein on blood lipids. Am J Clin Nutr 52(4):646–650
Wang Y, Liu L, ** Z, Zhang D (2021) Microbial cell factories for green production of vitamins. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:473
Wastyk HC, Fragiadakis GK, Perelman D, Dahan D, Merrill BD, Yu FB, Topf M, Gonzalez CG, Van Treuren W, Han S, Robinson JL, Elias JE, Sonnenburg ED, Gardner CD, Sonnenburg JL (2021) Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell 184:4137–4153
Yamada EA, Sgarbieri VC (2005) Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) protein concentrate: preparation, chemical composition, and nutritional and functional properties. J Agric Food Chem 53:3931–3936
Yuan SFF, Alper HS (2019) Metabolic engineering of microbial cell factories for production of nutraceuticals. Micro Cell Fact 18:1–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Yadav, A., Mehrotra, R., Verma, P. (2024). Microorganisms as Potential Source for Food Sustainability. In: Thakur, M. (eds) Sustainable Food Systems (Volume I). World Sustainability Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47122-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47122-3_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-47121-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-47122-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)