Abstract
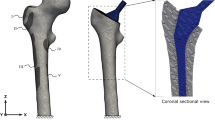
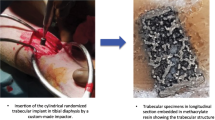
This work presents the numerical analysis by FEM of different types of biomaterials based on Hydroxyapatite and Hydroxyapatite-Titanium to estimate the values of maximum stresses in a tibial segment. The mechanical response with respect to an axial applied force of 750N on the tibial plateaus of the bone structure was analyzed. The 3D models were considered static systems. For the numerical analysis, the ANSYS tool was transmitted. The maximum stresses and total deformations in the biomaterials based on Hydroxyapatite and Hydroxyapatite-Titanium are within the range reported in the literature and confirm that the reconstruction of the 3D model used can be a good alternative in the regeneration of bone tissue. In addition, to consider reinforcing them with titanium plates, considerably increasing the stress capacity, which is important in the treatment of implants in long bones.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turnball, G.: 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. III, 1 (2017)
Zhao, Li., et al.: Bionic design and 3D printing of porous titanium alloy scaffolds for bone tissue repair. Compos. Part B: Eng. 162, 154–161 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.10.094
Kanczler, J.M., Wells, J.A., Gibbs, D.M.R., Marshall, K.M., Tang, D.K.O., Oreffo, R.O.C.: Chapter 50 - Bone tissue engineering and bone regeneration. In: Lanza, R., Langer, R., Vacanti, J.P., Atala, A. (ed.): Principles of Tissue Engineering 5th edn. pp. 917–935. Academic Press (2020) ISBN 9780128184226. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818422-6.00052-6
Niedhart, C., **smann, A., Jurgens, C., Marr, A., Blatt, R., Niethard, F.U.: Complications after harvesting of autologous bone from the ventral and dorsal iliac crest – a prospective: controlled study. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 141(4), 481–486 (2003)
Bagde, A.D., Kuthe, A.M., Nagdeve, S.R., et al.: Geometric modeling and finite element simulation for architecture design of 3D printed bio-ceramic scaffold used in bone tissue engineering. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 99, 361–374 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41745-019-00120-0
Chahal, S., Kumar, A., Hussian, F.S.J.: Development of biomimetic electrospun polymeric biomaterials for bone tissue engineering a review. J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 30(14), 1308–1355 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2019.1630699
Koons, G.L., Diba, M., Mikos, A.G.: Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 5, 584–603 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-020-0204-2
Ribas, R.G., et al.: Current advances in bone tissue engineering concerning ceramic and bioglass scaffolds: a review. Ceram. Int. 45(17), 21051–21061 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.096
Huang, M.-H., Shen, Y.-F., Hsu, T.-T., Huang, T.-H., Shie, M.-Y.: Physical characteristics, antimicrobial and odontogenesis potentials of calcium silicate cement containing hinokitiol. Mater. Sci. Eng.: C 65, 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.016
Chen, Y.-W., Ho, C.-C., Huang, T.-H., Hsu, T.-T., Shie, M.-Y.: The ionic products from mineral trioxide aggregate–induced odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp cells via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Endodontics 42(7), 1062–1069 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.04.019
Ottria, L., Lauritano, D., Andreasi Bassi, M., et al.: Mechanical, chemical and biological aspects of titanium and titanium alloys in implant dentistry. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 32(2, suppl 1), 81–90 (2018)
Soufivand, A.A., Abolfathi, N., Hashemi, S.A., Lee, S.J.: Prediction of mechanical behavior of 3D bioprinted tissue-engineered scaffolds using finite element method (FEM) analysis. Addit. Manufact. 33, 101181 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101181
Osuchukwu, O.A., et al.: Datasets on the elastic and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite: A first principle investigation, experiments, and pedagogical perspective. Data Brief 48, 109075 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2023.109075. PMID: 37020900; PMCID: PMC10068552
Flores-Sánchez, M.G., et al.: Effect of a plasma synthesized polypyrrole coverage on polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 109(11), 2199–2211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.37205. Epub 2021 Apr 26 PMID: 33904255
Abols, Y.: Biomecánica y fisiología articular subastragalina. EMC - Podología 11(1), 1–5 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1762-827X(09)70689-3
Donahue, T.L., Hull, M.L., Rashid, M.M., Jacobs, C.R.: A finite element model of the human knee joint for the study of tibio-femoral contact. J. Biomech. Eng. 124(3), 273–280 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1470171. PMID: 12071261
Kim, W.H., et al.: Optimized dental implant fixture design for the desirable stress distribution in the surrounding bone region: a biomechanical analysis. Materials (Basel). 12(17), 2749 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172749. PMID:31461942;PMCID:PMC6747764
Simon, U., Augat, P., Ignatius, A., Claes, L.: Influence of the stiffness of bone defect implants on the mechanical conditions at the interface–a finite element analysis with contact. J. Biomech. 36(8), 1079–1086 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9290(03)00114-3. PMID: 12831732
Kundu, J., Pati, F., Shim, J.-H., Cho, D.-W.: Rapid prototy** technology for bone regeneration. In: Narayan, R., (ed.) Rapid Prototy** of Biomaterials, pp. 254–284. Woodhead Publishing (2014) ISBN 9780857095992 https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857097217.254
Bruschi, S., Bertolini, R., Ghiotti, A.: Coupling machining and heat treatment to enhance the wear behaviour of an additive manufactured Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Tribol. Int. 116, 58–68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.07.004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Romo, M.F.T., Sánchez, M.F., Sierra, H.A., Aguilar, E.R. (2024). Analysis of Mechanical Behavior of Biomaterials of HA/Ti for Bone Tissue Regeneration Using Finite Element Method. In: Flores Cuautle, J.d.J.A., et al. XLVI Mexican Conference on Biomedical Engineering. CNIB 2023. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 97. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46936-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46936-7_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-46935-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-46936-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)