Abstract
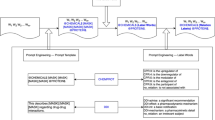
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are a rich source of information that can be leveraged for various medical applications, such as disease inference, treatment recommendation, and outcome analysis. However, the complexity and heterogeneity of EHR data, along with the limited availability of well-labeled samples, present significant challenges to the development of efficient and adaptable models for EHR tasks (such as rare or novel disease prediction or inference). In this paper, we propose Soft prompt transfer for Electronic Health Records (SptEHR), a novel pipeline designed to address these challenges. Specifically, SptEHR consists of three main stages: (1) self-supervised pre-training on raw EHR data for an EHR-centric transformer-based foundation model, (2) supervised multi-task continual learning from existing well-labeled tasks to further refine the foundation model and learn transferable task-specific soft prompts, and (3) further improve zero-shot and few-shot ability via prompt transfer. Specifically, the transformer-based foundation model learned from stage one captures domain-specific knowledge. Then the multi-task continual training in stage two improves model adaptability and performance on EHR tasks. Finally, stage three leverages soft prompt transfer which is based on the similarity between the new and the existing tasks, to effectively address new tasks without requiring additional/extensive training. The effectiveness of the SptEHR has been validated on the benchmark dataset - MIMIC-III.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aribandi, V., et al.: Ext5: towards extreme multi-task scaling for transfer learning. ar**v preprint ar**v:2111.10952 (2021)
Beltagy, I., Lo, K., Cohan, A.: SciBERT: a pretrained language model for scientific text. ar**v preprint ar**v:1903.10676 (2019)
Brown, T., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 1877–1901 (2020)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Swersky, K., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.E.: Big self-supervised models are strong semi-supervised learners. NeurIPS 33, 22243–22255 (2020)
Choi, E., Xu, Z., Li, Y., Dusenberry, M., Flores, G., Xue, E., Dai, A.: Learning the graphical structure of electronic health records with graph convolutional transformer. In: Proceedings of the AAAI. vol. 34, pp. 606–613 (2020)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. ar**v preprint ar**v:1810.04805 (2018)
Devlin, J., Chang, M., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 4171–4186. ACL (2019)
Gu, Y., Han, X., Liu, Z., Huang, M.: Ppt: Pre-trained prompt tuning for few-shot learning. ar**v preprint ar**v:2109.04332 (2021)
Gururangan, S., et al.: Don’t stop pretraining: adapt language models to domains and tasks. ar**v preprint ar**v:2004.10964 (2020)
Han, X., et al.: Pre-trained models: past, present and future. AI Open 2, 225–250 (2021)
Jiang, Z., Xu, F.F., Araki, J., Neubig, G.: How can we know what language models know? Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 8, 423–438 (2020)
Johnson, A.E., et al.: Mimic-iii, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 3, 160035 (2016)
Lan, Z., Chen, M., Goodman, S., Gimpel, K., Sharma, P., Soricut, R.: Albert: a lite BERT for self-supervised learning of language representations. ar**v preprint ar**v:1909.11942 (2019)
Lester, B., Al-Rfou, R., Constant, N.: The power of scale for parameter-efficient prompt tuning. ar**v preprint ar**v:2104.08691 (2021)
Li, X.L., Liang, P.: Prefix-tuning: Optimizing continuous prompts for generation. ar**v preprint ar**v:2101.00190 (2021)
Li, X.L., Liang, P.: Prefix-tuning: Optimizing continuous prompts for generation. In: Proceedings of ACL/IJCNLP 2021, (Volume 1: Long Papers), Virtual Event, August 1–6, 2021. pp. 4582–4597. ACL (2021)
Li, Y., et al.: BEHRT: transformer for electronic health records. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–12 (2020)
Liu, P., Yuan, W., Fu, J., Jiang, Z., Hayashi, H., Neubig, G.: Pre-train, prompt, and predict: a systematic survey of prompting methods in natural language processing. ACM Comput. Surv. 55(9), 1–35 (2023)
Liu, X., Ji, K., Fu, Y., Du, Z., Yang, Z., Tang, J.: P-tuning v2: prompt tuning can be comparable to fine-tuning universally across scales and tasks. CoRR abs/2110.07602 (2021)
Liu, X., et al.: P-tuning v2: prompt tuning can be comparable to fine-tuning universally across scales and tasks. ar**v preprint ar**v:2110.07602 (2021)
OpenAI: Gpt-4 technical report (2023)
Pan, S.J., Yang, Q.: A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 22(10), 1345–1359 (2010)
Peng, X., Long, G., Shen, T., Wang, S., Jiang, J.: Sequential diagnosis prediction with transformer and ontological representation. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 489–498. IEEE (2021)
Peng, X., Long, G., Shen, T., Wang, S., Jiang, J., Zhang, C.: Bitenet: bidirectional temporal encoder network to predict medical outcomes. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 412–421. IEEE (2020)
Peng, X., et al.: MIPO: mutual integration of patient journey and medical ontology for healthcare representation learning. ar**v preprint ar**v:2107.09288 (2021)
Qin, G., Eisner, J.: Learning how to ask: querying LMS with mixtures of soft prompts. ar**v preprint ar**v:2104.06599 (2021)
Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., Sutskever, I., et al.: Improving language understanding by generative pre-training (2018)
Ren, H., Wang, J., Zhao, W.X., Wu, N.: Rapt: Pre-training of time-aware transformer for learning robust healthcare representation. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD, pp. 3503–3511 (2021)
Schick, T., Schütze, H.: It’s not just size that matters: Small language models are also few-shot learners. In: Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the NAACL: Human Language Technologies, pp. 2339–2352 (2021)
Shin, T., Razeghi, Y., Logan IV, R.L., Wallace, E., Singh, S.: AutoPrompt: eliciting knowledge from language models with automatically generated prompts. ar** with limited data. J. Biomed. Inform. 116, 103726 (2021)
Steinberg, E., Jung, K., Fries, J.A., Corbin, C.K., Pfohl, S.R., Shah, N.H.: Language models are an effective representation learning technique for electronic health record data. J. Biomed. Inform. 113, 103637 (2021)
Taylor, N., Zhang, Y., Joyce, D., Nevado-Holgado, A., Kormilitzin, A.: Clinical prompt learning with frozen language models. ar**v preprint ar**v:2205.05535 (2022)
Thrun, S., Pratt, L.: Learning to learn: Introduction and overview. learning to learn, pp. 3–17 (1998)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: NeurIPS 2017, December 4–9, 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Vu, T., Lester, B., Constant, N., Al-Rfou, R., Cer, D.: Spot: better frozen model adaptation through soft prompt transfer. ar**v preprint ar**v:2110.07904 (2021)
Vu, T., Lester, B., Constant, N., Al-Rfou’, R., Cer, D.: Spot: better frozen model adaptation through soft prompt transfer. In: Proceedings of ACL, pp. 5039–5059. Association for Computational Linguistics (2022)
Wang, W., et al.: Structbert: Incorporating language structures into pre-training for deep language understanding. ar**v preprint ar**v:1908.04577 (2019)
Xu, H., Chen, Y., Du, Y., Shao, N., Wang, Y., Li, H., Yang, Z.: ZeroPrompt: scaling prompt-based pretraining to 1, 000 tasks improves zero-shot generalization. In: Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP, pp. 4235–4252 (2022)
Zhao, Z., Wallace, E., Feng, S., Klein, D., Singh, S.: Calibrate before use: improving few-shot performance of language models. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 12697–12706. PMLR (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Y. et al. (2023). Soft Prompt Transfer for Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Learning in EHR Understanding. In: Yang, X., et al. Advanced Data Mining and Applications. ADMA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14178. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46671-7_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46671-7_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-46670-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-46671-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)