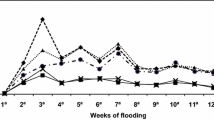
Abstract
The reuse of treated leachate in irrigation or green spaces watering can be considered as an alternative solution for facing water deficit. However, it represents a risk of environmental contamination by the accumulation of hazardous elements in the soil layers and plant tissues, which reduce the crop yields and its performance. This article will assess the irrigation suitability of different types of leachates by measuring their impacts on soil quality. The experimental test has been done using Meknes municipal landfill leachate. We have irrigated ten plots of corn with clean water (witness plot) and three types of effluent: (1) raw leachate (RL), (2) leachate treated by membrane bioreactor (MBRL), and (3) leachate treated by membrane bioreactor and reverse osmosis (MBRROL). In this investigation, soil parameters have been analyzed before and after irrigation to follow up the quality degradation of this one. The initial values of the studied soil were: pH = 8.31, the salinity = 0.36 mS/cm, the permeability = 0.53 cm/h. The results obtained show that MBRL can be used in irrigation with continuous control to avoid soil salinity (EC) after irrigation had increased up to 2.89 mS/cm). As for the MBRROL, it is respecting the recommended standards and can be judged suitable for irrigation. Contrary to RL which is strictly banned for irrigation because of the high pollution loads that had increased the soil pH (8.65) and salinity (6.22 mS/cm) and had reduced the permeability rate (0.13 cm/h).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Mansouri, H. M., & Alhendawi, A. M. R. (2014). Effect of increasing concentration of bicarbonate on plant growth and nutrient uptake by Maize plants. American-Eurasian Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 14(1), 01–06.
Alghobar, A., & Suresha, S. (2017). Evaluation of metal accumulation in soil and in tomatoes irrigated with sewage water from Mysore city, Karnataka, India. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 16, 49–59.
American Publishing Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), & Water Environment Federation (WEF). (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21 edition. Washington DC, USA.
Bedbabis, S., Ben Rouina, B., Boukhris, M., & Ferrara, G. (2014). Effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on soil chemical properties and infiltration rate. Journal of Environmental Management, 133, 45–50.
Besri, M. (1981). Influence de la salinité du sol et des eaux d'irrigation sur la population de Fusarium oxysporum (Schl.) f.sp. lycopersici (Sacc.) Snyd. et Hans. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 20(2, 3), 101–106.
Bouma, J., Ziebell, W. A., Olcott, P. G., Mc Coyle, E., & Hole, F. D. (1972). Soil absorption of septic tank effluent. University of Wisconsin, Extention-Geological and Natural History Survey, 20, 2–55.
Cheng, C. Y., & Chu, L. M. (2011). Fate and distribution of nitrogen in soil and plants irrigated with landfill leachate. Waste Management, 31, 1239–1249 (2011).
Douaoui, A., & Hartani, T. (2007). Impact de l’irrigation par les eaux souterraines sur la dégradation des sols de la plaine du Bas-Chéliff. In 3rd Regional workshop of Sirma project atelier, pp. 1–5. Nabeul, Tunisie.
Falizi, N. J., Hacıfazlıoğlua, M. C., Parlara, I., Kabaya, N., Ö. Pekc, T., & Yüksela, M. (2018). Evaluation of MBR treated industrial wastewater quality before and after desalination by NF and RO processes for agricultural reuse. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 22, 103–108.
Hamoda, M. F. (2004). Water strategies and potential of water reuse in the south Mediterranean countries. Desalination, 165, 31–41.
Heidarpour, M., Mostafazadeh-Fard, B., Abedi Koupai, J., & Malekian, R. (2007). The effects of treated wastewater on soil chemical properties using subsurface and surface irrigation methods. Agricultural Water Management, 90, 87–94.
Justin, M. Z., & Zupančič, M. (2009). Combined purification and reuse of landfill leachate by constructed wetland and irrigation of grass and willows. Desalination, 24, 157–168.
Lucena, J. J. (2000). Effects of bicarbonate, nitrate and other environmental factors on iron deficiency chlorosis: A review. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 23, 1591–1606.
Qadir, M., Ghaffoor, A., & Murtaza, G. (2000). Amelioration strategies for saline soils: A review. Land Degrad, 11, 501–521.
Recommended Limits for Constituents in Reclaimed Water for Irrigation, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Tables 2–7 (2004).
Rhouat, S., El Youbi, M. S., & Dimane, F. (2019). Physico-chemical characterization of Meknes municipal landfill leachate and assessment of the seasonal effects using PCA. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 18(11).
Romero, C., Ramos, P., Costa, C., & Márquez, M. C. (2013). Raw and digested municipal waste compost leachate as potential fertilizer: Comparison with a commercial fertilizer. Journal of Cleaner Production, 59, 73–78.
SEEE (2007). Water quality guidelines for irrigation in Morocco. State Secretariat at the Ministry of Energy, Mines, Water and Environment, in charge of Water and Environment.
Singh, S., Janardhana Raju, N., & RamaKrishna, Ch. (2017). Assessment of the effect of landfill leachate irrigation of different doses on wheat plant growth and harvest index: A laboratory simulation study. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 8, 150–156.
Singh, R. P., & Agrawal, M. (2010). Variations in heavy metal accumulation, growth and yield of rice plants grown at different sewage sludge amendment rates. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73(4), 632–664.
Solis, C., Andrade, E., Mireles, A., Reyes-Solis, I. E., Garcia-Calderon, N., Lagunas-Solar, M. C., Pina, C. U., & Flocchini, R. G. (2005). Distribution of heavy metals in plants cultivated with wastewater irrigated soils during different periods of time. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, 241, 351–355.
Sparks, D. L., Page, A. L., Helmek, P. A., Loeppert, R. H., Soltanpour, P. N., Tabatabai, M. A., Johnston, C. T., & Sumner, M. E. (1996). Methods of soil analysis, Part 3, chemical methods. ASA, CSSA, SSSA.
SSSA. (1997). Glossary of soil science terms. Soil Science Society of America.
Tarchouna, L. G., Merdy, P., Raynaud, M., Pfeifer, H., & Lucas, Y. (2010). Effects of long-term irrigation with treated wastewater. Part I: Evolution of soil physico-chemical properties. Applied Geochemistry, 25, 1703–1710.
Zupanc, V., & Justin, M. Z. (2010). Changes in soil characteristics during landfill leachate irrigation of Populus deltoids. Waste Management, 30, 2130–2136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rhouat, S., El Youbi, M.S., Dimane, F. (2023). The Effects of Landfill Leachate Irrigation on Soil Properties. In: Kallel, A., et al. Selected Studies in Environmental Geosciences and Hydrogeosciences. CAJG 2020. Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43803-5_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43803-5_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43802-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43803-5
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)