Abstract
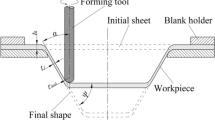
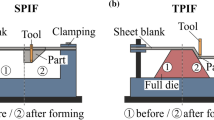
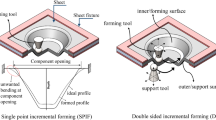
Forming-induced residual stresses can be used to increase the fatigue strength of formed components. By adjusting the process parameters of the incremental sheet metal forming process (ISF), the forming mechanisms can be adjusted and thus the resulting residual stress can be targetedly set, to meet specific component requirements. Within the scope of this work, experimental results show that superposed compressive stresses using a flexible polymer die during ISF, near-to-surface compressive residual stresses can be induced on both sides of aluminum alloy 5083 truncated cones. The resulting residual stress state is measured by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD). In addition, the amount of near-to-surface residual stress can be adjusted by varying the degree of hardness of the elastomeric die material. These findings can be used to set tailored properties of formed components by forming-induced residual stresses, to extend the operating time of the component until failure.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martins, P.A.F., Bay, N., Skjoedt, M., Silva, M.B.: Theory of single point incremental forming. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 57, 247–252 (2009)
Jeswiet, J., Hagan, E.: Rapid proto-ty** of a headlight with sheet metal. In: Proceedings of Shemet, pp. 165–170 (2001)
Emmens, W.C., van den Boogaard, A.H.: An overview of stabilizing deformation mechanisms in incremental sheet forming. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 3688–3695 (2009)
Leszak, E.: Apparatus and process for incremental dieless forming. U.S. Patent 3342051A1 (1967)
Powell, N.N., Andrew, C.: Incremental forming of flanged sheet metal components without dedicated dies. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 206, 41–47 (1992)
Lu, H., Kearney, M., Wang, C., Liu, S., Meehan, P.A.: Part accuracy improvement in two point incremental forming with a partial die using a model predictive control algorithm. Precis. Eng. J. 49, 179–188 (2017)
Maaß, F., Hahn, M., Tekkaya, A.E.: Adjusting residual stresses by flexible stress superposition in incremental sheet metal forming. Arch. Appl. Mech. 91(8), 3489–3499 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-01929-x
Maaß, F., Hahn, M., Tekkaya, A.E.: Interaction of process parameters, forming mechanisms and residual stresses in single point incremental forming. Metals 10(5), 656 (2020)
Macherauch, E., Müller, P.: Das sin2-ψ Verfahren von röntgenographischen Eigenspannungen. Zeitschrift für angewandte Physik 13, 305–312 (1961)
Emmens, W.C., van den Boogaard, A.H.: An overview of stabilizing deformation mechanisms in incremental sheet forming. J. Mater. Process 209(8), 3688–3695 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the German Research Foundation (DFG, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) for funding the research project 372803376 (TE 508/67-3) as part of the priority program SPP 2013 “The utilization of residual stresses induced by metal forming”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Maaß, F., Hahn, M., Tekkaya, A.E. (2024). Controlling Product Properties by Compressive Stress-Superposed Incremental Forming. In: Mocellin, K., Bouchard, PO., Bigot, R., Balan, T. (eds) Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity - Current Trends in the Technology of Plasticity. ICTP 2023. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41023-9_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41023-9_73
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-41022-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-41023-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)