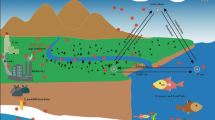
Abstract
Plasticizers, due to their robustness, flexibility, and low production costs, have broad industrial applications. However, they are released into the reservoir environment because of inappropriate disposal discharge and cause adverse health effects. This chapter mainly focuses on the molecular mechanism of the plasticizers, particularly phthalates (PAEs) and bisphenol A (BPA), when they are exposed to or interacted with organisms. Previously, various studies have reported that plasticizers affect growth development by altering the thyroid and estrogen axis, leading to infertility. Furthermore, these chemicals can disturb reproductive capacity and decrease egg production via reducing steroidogenesis, activating peroxisome proliferator receptors (PPAR), and enhancing oxidative stress levels. In a nutshell, plasticizer pollution in the reservoir should be deeply concerned, and more studies on the adverse health effects of plasticizers on aquatic species are critically needed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Yang, C. Chen, Y. Wang, Q. Peng, H. Zhao, D. Guo, Q. Wang, Y. Qian, Mixture toxicity of four commonly used pesticides at different effect levels to the epigeic earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 142, 29–39 (2017)
J. Zhou, Z.-H. Cai, K.-Z. **ng, Potential mechanisms of phthalate ester embryotoxicity in the abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta. Environ. Pollut. 159, 1114–1122 (2011)
Y. Liu, Z. Chen, J. Shen, Occurrence and removal characteristics of phthalate esters from typical water sources in Northeast China. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 419349–419349 (2013)
J. Mathieu-Denoncourt, S.J. Wallace, S.R. de Solla, V.S. Langlois, Plasticizer endocrine disruption: highlighting developmental and reproductive effects in mammals and non-mammalian aquatic species. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 219, 74–88 (2015)
WHO, 3rd ed. Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality (Geneva), (World Health Organization), 1 (2004)
S. Net, S. Rabodonirina, R.B. Sghaier, D. Dumoulin, C. Chbib, I. Tlili, B. Ouddane, Distribution of phthalates, pesticides and drug residues in the dissolved, particulate and sedimentary phases from transboundary rivers (France–Belgium). Sci. Total Environ. 521–522, 152–159 (2015)
A. Ohashi, H. Kotera, H. Hori, M. Hibiya, K. Watanabe, K. Murakami, M. Hasegawa, M. Tomita, Y. Hiki, S. Sugiyama, Evaluation of endocrine disrupting activity of plasticizers in polyvinyl chloride tubes by estrogen receptor alpha binding assay. J. Artif. Organs 8, 252 (2005)
H. Liu, K. Cui, F. Zeng, L. Chen, Y. Cheng, H. Li, S. Li, X. Zhou, F. Zhu, G. Ouyang, T. Luan, Z. Zeng, Occurrence and distribution of phthalate esters in riverine sediments from the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 83, 358–365 (2014)
H.-T. Gao, R. Xu, W.-X. Cao, L.-L. Qian, M. Wang, L. Lu, Q. Xu, S.-Q. Yu, Effects of six priority controlled phthalate esters with long-term low-dose integrated exposure on male reproductive toxicity in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 101, 94–104 (2017)
D.-W. Gao, Z.-D. Wen, Phthalate esters in the environment: a critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 541, 986–1001 (2016)
N. Hamid, M. Junaid, R. Manzoor, P.-P. Jia, D.-S. Pei, Prioritizing phthalate esters (PAEs) using experimental in vitro/vivo toxicity assays and computational in silico approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 398, 122851 (2020)
Y.-B. Ma, P.-P. Jia, M. Junaid, L. Yang, C.-J. Lu, D.-S. Pei, Reproductive effects linked to DNA methylation in male zebrafish chronically exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Environ. Pollut. 237, 1050–1061 (2018)
G. Latini, Monitoring phthalate exposure in humans. Clin. Chim. Acta 361, 20–29 (2005)
M. Junaid, P.-P. Jia, Y.-M. Tang, W.-X. **ong, H.-Y. Huang, P.R. Strauss, W.-G. Li, D.-S. Pei, Mechanistic toxicity of DEHP at environmentally relevant concentrations (ERCs) and ecological risk assessment in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Environ. Pollut. 242, 1939–1949 (2018)
J. Berger, D.E. Moller, The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 53, 409–435 (2002)
C.H. Hurst, D.J. Waxman, Environmental phthalate monoesters activate pregnane X receptor-mediated transcription. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 199, 266–274 (2004)
P. Phrakonkham, S. Viengchareun, C. Belloir, M. Lombès, Y. Artur, M.-C. Canivenc-Lavier, Dietary xenoestrogens differentially impair 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation and persistently affect leptin synthesis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 110, 95–103 (2008)
X. Deng, L. Pan, Y. Cai, Q. **, Transcriptomic changes in the ovaries of scallop Chlamys farreri exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Genes Genom. 38, 509–518 (2016)
G. Latini, E. Scoditti, A. Verrotti, C. De Felice, M. Massaro, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors as mediators of phthalate-induced effects in the male and female reproductive tract: epidemiological and experimental evidence. PPAR Res. 2008, 359267–359267 (2008)
S.Y. Xu, H. Zhang, P.J. He, L.M. Shao, Leaching behaviour of bisphenol A from municipal solid waste under landfill environment. Environ. Technol. 32, 1269–1277 (2011)
S.-K. Tong, H.-J. Hsu, B.-C. Chung, Zebrafish monosex population reveals female dominance in sex determination and earliest events of gonad differentiation. Dev. Biol. 344, 849–856 (2010)
E. Muth-Köhne, K. Westphal-Settele, J. Brückner, S. Konradi, V. Schiller, C. Schäfers, M. Teigeler, M. Fenske, Linking the response of endocrine regulated genes to adverse effects on sex differentiation improves comprehension of aromatase inhibition in a Fish Sexual Development Test. Aquat. Toxicol. 176, 116–127 (2016)
Y.-Q. Liang, G.-Y. Huang, S.-S. Liu, J.-L. Zhao, Y.-Y. Yang, X.-W. Chen, F. Tian, Y.-X. Jiang, G.-G. Ying, Long-term exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of progesterone and norgestrel affects sex differentiation in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 160, 172–179 (2015)
Y.-Q. Liang, G.-Y. Huang, G.-G. Ying, S.-S. Liu, Y.-X. Jiang, S. Liu, F.-J. Peng, The effects of progesterone on transcriptional expression profiles of genes associated with hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axes during the early development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 128, 199–206 (2015)
A. Ishihara, S. Sawatsubashi, K. Yamauchi, Endocrine disrupting chemicals: interference of thyroid hormone binding to transthyretins and to thyroid hormone receptors. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 199, 105–117 (2003)
O. Shen, W. Wu, G. Du, R. Liu, L. Yu, H. Sun, X. Han, Y. Jiang, W. Shi, W. Hu, L. Song, Y. **a, S. Wang, X. Wang, Thyroid disruption by Di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) and mono-n-butyl phthalate (MBP) in Xenopus laevis. PLoS One 6, e19159–e19159 (2011)
N.S. Gayathri, C.R. Dhanya, A.R. Indu, P.A. Kurup, Changes in some hormones by low doses of di (2-ethyl hexyl) phthalate (DEHP), a commonly used plasticizer in PVC blood storage bags & medical tubing. Indian J. Med. Res. 119, 139–144 (2004)
A. Wenzel, C. Franz, E. Breous, U. Loos, Modulation of iodide uptake by dialkyl phthalate plasticisers in FRTL-5 rat thyroid follicular cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 244, 63–71 (2005)
S. Imaoka, T. Mori, T. Kinoshita, Bisphenol A causes malformation of the head region in embryos of Xenopus laevis and decreases the expression of the ESR-1 gene mediated by Notch signaling. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30, 371–374 (2007)
S. Santangeli, F. Maradonna, G. Gioacchini, G. Cobellis, C.C. Piccinetti, L. Dalla Valle, O. Carnevali, BPA-induced deregulation of epigenetic patterns: effects on female zebrafish reproduction. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–11 (2016)
Y. Xu, S. Agrawal, T.J. Cook, G.T. Knipp, Maternal di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate exposure influences essential fatty acid homeostasis in rat placenta. Placenta 29, 962–969 (2008)
C.J. Thompson, S.M. Ross, K.W. Gaido, Di(n-butyl) phthalate impairs cholesterol transport and steroidogenesis in the fetal rat testis through a rapid and reversible mechanism. Endocrinology 145, 1227–1237 (2004)
T.R. Zacharewski, M.D. Meek, J.H. Clemons, Z.F. Wu, M.R. Fielden, J.B. Matthews, Examination of the in vitroandin vivoestrogenic activities of eight commercial phthalate esters. Toxicol. Sci. 46, 282–293 (1998)
Y. Nomura, N. Mitsui, U.K. Bhawal, M. Sawajiri, O. Tooi, T. Takahashi, M. Okazaki, Estrogenic activity of phthalate esters by in vitro VTG assay using primary-cultured Xenopus hepatocytes. Dent. Mater. J. 25, 533–537 (2006)
L.B. Christiansen, K.L. Pedersen, B. Korsgaard, P. Bjerregaard, Estrogenicity of xenobiotics in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) using in vivo synthesis of vitellogenin as a biomarker. Mar. Environ. Res. 46, 137–140 (1998)
O. Carnevali, L. Tosti, C. Speciale, C. Peng, Y. Zhu, F. Maradonna, DEHP impairs zebrafish reproduction by affecting critical factors in oogenesis. PLoS One 5, e10201–e10201 (2010)
G. Levy, I. Lutz, A. Krüger, W. Kloas, Bisphenol A induces feminization in Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Environ. Res. 94, 102–111 (2004)
X. Chen, S. Xu, T. Tan, S.T. Lee, S.H. Cheng, F.W. Lee, S.J. Xu, K.C. Ho, Toxicity and estrogenic endocrine disrupting activity of phthalates and their mixtures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 11, 3156–3168 (2014)
B. Huang, M. Feng, D. Li, Y. Yang, Antagonistic joint toxicity assessment of two current-use phthalates with waterborne copper in liver of Carassius auratus using biochemical biomarkers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 116, 107–112 (2015)
X. Chen, H. An, L. Ao, L. Sun, W. Liu, Z. Zhou, Y. Wang, J. Cao, The combined toxicity of dibutyl phthalate and benzo(a)pyrene on the reproductive system of male Sprague Dawley rats in vivo. J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 835–841 (2011)
A. Pradhan, P.E. Olsson, J. Jass, Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and diethyl phthalate disrupt lipid metabolism, reduce fecundity and shortens lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 190, 375–382 (2018)
N. Xu, P. Chen, L. Liu, Y. Zeng, H. Zhou, S. Li, Effects of combined exposure to 17α-ethynylestradiol and dibutyl phthalate on the growth and reproduction of adult male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 107, 61–70 (2014)
T.V. Madureira, M.J. Rocha, C. Cruzeiro, I. Rodrigues, R.A.F. Monteiro, E. Rocha, The toxicity potential of pharmaceuticals found in the Douro River estuary (Portugal): evaluation of impacts on fish liver, by histopathology, stereology, vitellogenin and CYP1A immunohistochemistry, after sub-acute exposures of the zebrafish model. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 34, 34–45 (2012)
S. Dietrich, F. Ploessl, F. Bracher, C. Laforsch, Single and combined toxicity of pharmaceuticals at environmentally relevant concentrations in Daphnia magna – a multigenerational study. Chemosphere 79, 60–66 (2010)
X. Dong, X. Qiu, S. Meng, H. Xu, X. Wu, M. Yang, Proteomic profile and toxicity pathway analysis in zebrafish embryos exposed to bisphenol A and di-n-butyl phthalate at environmentally relevant levels. Chemosphere 193, 313–320 (2018)
X.-M. Tian, Song Qi-ru, Combined toxic effects of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) and Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate (DEHP) on reproductive ability in male rats, J. Environ. Health (2009)
C. Zhou, L. Gao, J.A. Flaws, Prenatal exposure to an environmentally relevant phthalate mixture disrupts reproduction in F1 female mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 318, 49–57 (2017)
T. Pollock, R.E. Weaver, R. Ghasemi, D. deCatanzaro, A mixture of five endocrine-disrupting chemicals modulates concentrations of bisphenol A and estradiol in mice. Chemosphere 193, 321–328 (2018)
H. Xu, X. Shao, Z. Zhang, Y. Zou, X. Wu, L. Yang, Oxidative stress and immune related gene expression following exposure to di-n-butyl phthalate and diethyl phthalate in zebrafish embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 93, 39–44 (2013)
G. Hu, J. Li, Y. Shan, X. Li, Q. Zhu, H. Li, Y. Wang, X. Chen, Q. Lian, R.-S. Ge, In utero combined di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and diethyl phthalate exposure cumulatively impairs rat fetal Leydig cell development. Toxicology 395, 23–33 (2018)
J. Zhang, L. Yan, M. Tian, Q. Huang, S. Peng, S. Dong, H. Shen, The metabonomics of combined dietary exposure to phthalates and polychlorinated biphenyls in mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 66, 287–297 (2012)
H.-T. Gao, R. Xu, W.-X. Cao, Q.-N. Di, R.-X. Li, L. Lu, Q. Xu, S.-Q. Yu, Combined effects of simultaneous exposure to six phthalates and emulsifier glycerol monosterate on male reproductive system in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 341, 87–97 (2018)
N. Garcia-Reyero, K.J. Kroll, L. Liu, E.F. Orlando, K.H. Watanabe, M.S. Sepulveda, D.L. Villeneuve, E.J. Perkins, G.T. Ankley, N.D. Denslow, Gene expression responses in male fathead minnows exposed to binary mixtures of an estrogen and antiestrogen. BMC Genom. 10, 308 (2009)
B. Huang, D. Li, Y. Yang, Joint toxicity of two phthalates with waterborne copper to Daphnia magna and Photobacterium phosphoreum. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 97, 380–386 (2016)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the funds from the High-level Talents Project of Chongqing Medical University (No. R4014) and Research Program of Chongqing Science and Technology Commission (No. cstc2019jcyj-zdxmX0035 and CSTCCXLJRC201714).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hamid, N., Pei, DS. (2023). Molecular Toxicity Mechanism of Plasticizers in the Reservoir. In: Reservoir Ecotoxicology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26344-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26344-6_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-26343-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-26344-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)