Abstract
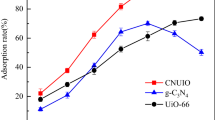
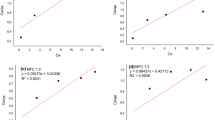
The adsorption process is consistent with Langmuir and the pseudo-first order kinetics, indicating that the adsorption is a monolayer adsorption process. The pH effect study shows that at pH = 3, the adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) is 356.8 mg/g as the highest, and electrostatic interaction is the main mechanism of action. The carbonized magnetic UiO-66 adsorbent showed good adsorption capacity as well as the advantage of the easy recovery, showing great potential for application in the field of wastewater chromium ion treatment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altundogan HS (2005) Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution by iron (III) hydroxide-loaded sugar beet pulp[J]. Process Biochem 40(3/4):1443–1452
Arabkhani P, Asfaram A (2019) Development of a novel three-dimensional magnetic polymer aerogel as an efficient adsorbent for malachite green removal[J]. J Hazard Mater 384:121394
Dhal B, Thatoi HN, Das NN et al (2013) Chemical and microbial remediation of hexavalent chromium from contaminated soil and mining/metallurgical solid waste: a review[J]. J Hazard Mater 250–251(30):272–291
Fan S, Yi W, Yang L et al (2017) Facile synthesis of tea waste/Fe3O4nanoparticle composite for hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution[J]. RSC Adv 7(13):7576–7590
Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q et al (2014) Metal–organic framework derived magnetic nanoporous carbon: novel adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction[J]. Anal Chem 86(24)
Hao W, Shuai W, Swa B et al (2021) Adenosine-functionalized UiO-66-NH2 to efficiently remove Pb(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution: thermodynamics, kinetics and isothermal adsorption—ScienceDirect[J]
Hao J, Guo C, Gao X, Li M, Long H (2022) Synergistic mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by thiourea/sodium alginate adsorption and photocatalytic reduction[J/OL]. J Composites 1–12[2022–03–06].20210622.001
Li B, Zhu X, Hu K et al (2016) Defect creation in metal-organic frameworks for rapid and controllable decontamination of roxarsone from aqueous solution[J]. J Hazardous Mater 302(JAN.25):57–64
Li P, Fu T, Gao X et al (2019) Adsorption and reduction transformation behaviors of Cr(VI) on mesoporous polydopamine/titanium dioxide composite nanospheres[J]. J Chem Eng Data
Liu Y, Li G, Guo Y et al (2017) Flexible and binder-free hierarchical porous carbon film for supercapacitor electrodes derived from MOFs/CNT[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces
Lu YQ, Deng ZH (1989) Analysis of IR spectra. Bei**g, Publishing House of Electronics Industry 21
Maleki A, Hayati B, Naghizadeh M et al (2015) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by metal organic frameworks from aqueous solution[J]. J Ind Eng Chem 28:211–216
Owlad M, Aroua MK, Daud WAW et al (2009) Removal of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water and wastewater: a review[J]. Water Air Soil Pollut 200(1–4):59–77
Pan C, Troyer LD, Catalano JG et al (2016) Dynamics of chromium(VI) removal from drinking water by iron electrocoagulation[J]. Environ Sci Technol 50(24):13502
Plummer S, Gorman C, Henrie T et al (2018) Optimization of strong-base anion exchange O&M costs for hexavalent chromium treatment[J]. Water Res 139(AUG.1):420–433
Rowsell J, Yaghi OM (2004) Metal–organic frameworks: a new class of porous materials[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 73(1–2):3–14
Shiyang C, Zhou S, Xuerui L, Lin D, Yong S (2012) Study on the removal of Cr(VI) from drinking water by ion exchange membrane chemical reactor[J]. J Safety Environ 12(04):72–75
Song JY, Jhung SH (2017) Adsorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products over metal-organic frameworks functionalized with hydroxyl groups: quantitative analyses of H-bonding in adsorption. Chem Eng J 322:366–374
Wang TT, Cui QL, Wang LL et al (2018) Adsorption characteristics of Al-modified lemon biochar on P and its mechanism[J]. China Environ Sci 38(6):13
Wang, Yuan XZ et al (2015) Synthesis and applications of novel graphitic carbon nitride/metal-organic frameworks mesoporous photocatalyst for dyes removal[J]. APPL CATAL B-ENVIRON 174:445–454
Wen C, **ao M et al (2017) MOFs-derived carbon covered alumina (CCA) supported Pt nanoparticles as catalyst for enantioselective hydrogenation[J]. Curr Appl Phys: Official J Korean Phys Soc 17(10):1347–1352
Wu S, Ge Y, Wang Y et al (2017) Adsorption of Cr(VI) on nano Uio-66-NH2 MOFs in water[J]. Environ Technol 39(15):1–40
Ye Y, Zhao et al (2017) Efficient removal of Cr(III)-organic complexes from water using UV/Fe(III) system: negligible Cr(VI) accumulation and mechanism.[J]. Water Res
Yuan F, Zhang Y, Xu H, Gong G (2022) Exploration and prospect of the mechanism of Cr(VI) removal from the environment by humic acid[J/OL]. Environ Chem 1–10[2022–03–06].20220214.1402.006
Yu Z, **aodan et al (2013) Magnetic chitosan–iron(III) hydrogel as a fast and reusable adsorbent for chromium(VI) removal[J]. Indus Eng Chem Res
Zhang J, Zhao Z, **a Z et al (2015) A metal-free bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions[J]. Nat Nanotechnol 10(5):444–452
Zhou W, Lu J, Zhou K et al (2016) CoSe2 nanoparticles embedded defective carbon nanotubes derived from MOFs as efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Nano Energy 28:143–150
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Research Project of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (LJ2019QL009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, X., Wang, S., Che, W. (2023). Study on the Adsorption of Cr(VI) by Carbonated Fe3O4@UiO-66. In: Zhang, J., Ruan, R., Bashir, M.J.K. (eds) Environmental Pollution Governance and Ecological Remediation Technology. ICEPG 2022. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25284-6_57
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25284-6_57
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25283-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25284-6
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)