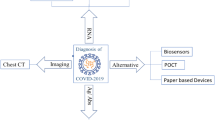
Abstract
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a highly transmissible and pathogenic coronavirus that emerged in late 2019 and has caused a pandemic of acute respiratory illness called ‘Coronavirus Disease 2019’ (COVID19) that threatens human health and public safety. To mitigate the impact of Covid-19, much has been done to ensure that people are able to self-diagnose and determine whether or not they are affected by the virus. While there is a self-assessment tool, it is not on the Nigerian Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) homepage, but on their coronavirus microsite. And this self-assessment tool is so visually unimpressive and small that it stands out among the flood of information on the website. Coupled with the fact that many Nigerians are not smart enough to find their way to the website to take the test, it is highly unlikely that it has been used extensively by the public. Therefore, it is critical to develop a self-assessment tool that not only allows users to assess whether they are at risk and informs them of the steps they need to take to protect their own safety and the safety of others, but that is also easily accessible and understandable to the general public. Therefore, this article presented a standalone wireless application for COVID19 self-assessment that complies with the NCDC guidelines. The software was developed in response to current COVID19 problems around the world, particularly to support self-assessment in rural areas of Nigeria due to a lack of network connection for local people to access the NCDC’s current web-based COVID19 self-assessment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amzat, J., Aminu, K., Kolo, V. I., Akinyele, A. A., Ogundairo, J. A., & Danjibo, M. C. (2020). Coronavirus outbreak in Nigeria: burden and socio-medical response during the first 100 days. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 98, 218–224.
Dong, E., Du, H., & Gardner, L. (2020). An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 20, 533–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1
Fitzgerald, D. A., & Wong, G. W. K. (2020). COVID-19: a tale of two pandemics across the Asia Pacific region. Paediatric Respiratory Reviews, 35, 75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prrv.2020.06.018
Hellou, M. M., Górska, A., Mazzaferri, F., Cremonini, E., Gentilotti, E., De Nardo, P., et al. (2021). Nucleic acid amplification tests on respiratory samples for the diagnosis of coronavirus infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 27(3), 341–351.
Li, Q., Guan, X., Wu, P., Wang, X., Zhou, L., Tong, Y., et al. (2020). Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. The New England Journal of Medicine, 382, 1199–1207.
Li, Q., Wu, J., Nie, J., Zhang, L., Hao, H., Liu, S., et al. (2020). The impact of mutations in SARS-CoV-2 spike on viral infectivity and antigenicity. Cell, 182(5), 1284–1294.
Mardian, Y., Kosasih, H., Karyana, M., Neal, A., & Lau, C. Y. (2021). Review of current COVID-19 diagnostics and opportunities for further development. Frontiers in Medicine, 8, 562.
Ozer, E. A., Simons, L. M., Adewumi, O. M., Fowotade, A. A., Omoruyi, E. C., Adeniji, J. A., et al. (2022). Multiple expansions of globally uncommon SARS-CoV-2 lineages in Nigeria. Nature Communications, 13(1), 1–13.
Peto, J. (2020). Covid-19 mass testing facilities could end the epidemic rapidly. BMJ, 368, m1163. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1163
Roshanravan, N., Ghaffari, S., & Hedayati, M., (2020). Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 as therapeutic target in COVID-19. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 14(4): 637–639.
Salisu, U. O., Akanmu, A. A., Sanni, S. M., Fasina, S. O., Ogunseye, N. O., Ogunsesan, S. A., & Olatunji, M. O. (2021). COVID-19-related socio-economic impacts and palliative care deliveries during lockdown in Nigeria: a case study. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 1–31.
Šehović, A. B., & Govender, K. (2021). Addressing COVID-19 vulnerabilities: how do we achieve global health security in an inequitable world. Global Public Health, 16(8–9), 1198–1208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Haruna, A.A. (2023). COVID-19 Wireless Self-Assessment Software for Rural Areas in Nigeria. In: Tiwari, R., Koundal, D., Upadhyay, S. (eds) Image Based Computing for Food and Health Analytics: Requirements, Challenges, Solutions and Practices. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22959-6_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22959-6_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22958-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22959-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)