Abstract
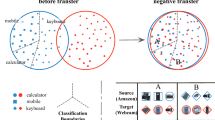
Unsupervised partial domain adaptation (PDA) is a unsupervised domain adaptation problem which assumes that the source label space subsumes the target label space. A critical challenge of PDA is the negative transfer problem, which is triggered by learning to match the whole source and target domains. To mitigate negative transfer, we note a fact that, it is impossible for a source sample of outlier classes to find a target sample of the same category due to the absence of outlier classes in the target domain, while it is possible for a source sample of shared classes. Inspired by this fact, we exploit the cycle inconsistency, i.e., category discrepancy between the original features and features after cycle transformations, to distinguish outlier classes apart from shared classes in the source domain. Accordingly, we propose to filter out source samples of outlier classes by weight suppression and align the distributions of shared classes between the source and target domains by adversarial learning. To learn accurate weight assignment for filtering out outlier classes, we design cycle transformations based on domain prototypes and soft nearest neighbor, where center losses are introduced in individual domains to reduce the intra-class variation. Experiment results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
K. Lin and J. Zhou—Equal contributions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousmalis, K., Silberman, N., Dohan, D., Erhan, D., Krishnan, D.: Unsupervised pixel-level domain adaptation with generative adversarial networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 95–104 (2017)
Bucci, S., D’Innocente, A., Tommasi, T.: Tackling partial domain adaptation with self-supervision. In: International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, vol. 11752, pp. 70–81 (2019)
Busto, P.P., Gall, J.: Open set domain adaptation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 754–763 (2017)
Cao, Z., Long, M., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Partial transfer learning with selective adversarial networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2724–2732 (2018)
Cao, Z., Ma, L., Long, M., Wang, J.: Partial adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 139–155 (2018)
Cao, Z., You, K., Long, M., Wang, J., Yang, Q.: Learning to transfer examples for partial domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2985–2994 (2019)
Chen, C., Li, J., Zheng, Z., Huang, Y., Ding, X., Yu, Y.: Dual bipartite graph learning: a general approach for domain adaptive object detection. In: IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2683–2692 (2021)
Chen, Z., Chen, C., Cheng, Z., Jiang, B., Fang, K., **, X.: Selective transfer with reinforced transfer network for partial domain adaptation. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12703–12711 (2020)
Cui, S., Wang, S., Zhuo, J., Su, C., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Gradually vanishing bridge for adversarial domain adaptation. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12452–12461 (2020)
Damodaran, B.B., Kellenberger, B., Flamary, R., Tuia, D., Courty, N.: DeepJDOT: deep joint distribution optimal transport for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 467–483 (2018)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255 (2009)
Dwibedi, D., Aytar, Y., Tompson, J., Sermanet, P., Zisserman, A.: Temporal cycle-consistency learning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1801–1810 (2019)
French, G., Mackiewicz, M., Fisher, M.H.: Self-ensembling for visual domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2018)
Fu, B., Cao, Z., Long, M., Wang, J.: Learning to detect open classes for universal domain adaptation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12360, pp. 567–583. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58555-6_34
Ganin, Y., et al.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17, 59:1–59:35 (2016)
Goldberger, J., Roweis, S.T., Hinton, G.E., Salakhutdinov, R.: Neighbourhood components analysis. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 513–520 (2004)
Goodfellow, I.J., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680 (2014)
Grandvalet, Y., Bengio, Y.: Semi-supervised learning by entropy minimization. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 529–536 (2004)
Griffin, G., Holub, A., Perona, P.: Caltech-256 object category dataset (2007)
Gu, X., Yu, X., Yang, Y., Sun, J., Xu, Z.: Adversarial reweighting for partial domain adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2021)
Häusser, P., Frerix, T., Mordvintsev, A., Cremers, D.: Associative domain adaptation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2784–2792 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hoffman, J., et al.: CyCADA: cycle-consistent adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 80, pp. 1994–2003 (2018)
Hsu, T.H., Chen, W., Hou, C., Tsai, Y.H., Yeh, Y., Wang, Y.F.: Unsupervised domain adaptation with imbalanced cross-domain data. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4121–4129 (2015)
Hu, J., Tuo, H., Wang, C., Qiao, L., Zhong, H., **g, Z.: Multi-weight partial domain adaptation. In: 30th British Machine Vision Conference, p. 5 (2019)
Hu, J., et al.: Discriminative partial domain adversarial network. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12372, pp. 632–648. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58583-9_38
Hu, L., Kan, M., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Duplex generative adversarial network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1498–1507 (2018)
**, Y., Wang, X., Long, M., Wang, J.: Minimum class confusion for versatile domain adaptation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12366, pp. 464–480. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58589-1_28
**g, T., **a, H., Ding, Z.: Adaptively-accumulated knowledge transfer for partial domain adaptation. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1606–1614 (2020)
Kang, G., Wei, Y., Yang, Y., Zhuang, Y., Hauptmann, A.G.: Pixel-level cycle association: a new perspective for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. In: Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M., Lin, H. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2020)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1106–1114 (2012)
Kundu, J.N., Venkat, N., Revanur, A., V., R.M., Babu, R.V.: Towards inheritable models for open-set domain adaptation. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12373–12382 (2020)
Kundu, J.N., Venkat, N., V., R.M., Babu, R.V.: Universal source-free domain adaptation. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4543–4552 (2020)
Li, G., Kang, G., Zhu, Y., Wei, Y., Yang, Y.: Domain consensus clustering for universal domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9757–9766 (2021)
Li, S., Liu, C.H., Lin, Q., Wen, Q., Su, L., Huang, G., Ding, Z.: Deep residual correction network for partial domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(7), 2329–2344 (2021)
Liang, J., Hu, D., Feng, J.: Do we really need to access the source data? Source hypothesis transfer for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 119, pp. 6028–6039 (2020)
Liang, J., Hu, D., Feng, J.: Domain adaptation with auxiliary target domain-oriented classifier. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16632–16642 (2021)
Liang, J., Hu, D., Wang, Y., He, R., Feng, J.: Source data-absent unsupervised domain adaptation through hypothesis transfer and labeling transfer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2021)
Liang, J., Wang, Y., Hu, D., He, R., Feng, J.: A balanced and uncertainty-aware approach for partial domain adaptation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12356, pp. 123–140. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58621-8_8
Liu, H., Cao, Z., Long, M., Wang, J., Yang, Q.: Separate to adapt: open set domain adaptation via progressive separation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2927–2936 (2019)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 37, pp. 97–105 (2015)
Long, M., Cao, Z., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Conditional adversarial domain adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1647–1657 (2018)
Long, M., Zhu, H., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Unsupervised domain adaptation with residual transfer networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 136–144 (2016)
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11) (2008)
Matsuura, T., Saito, K., Harada, T.: TWINs: two weighted inconsistency-reduced networks for partial domain adaptation. CoRR abs/1812.07405 (2018)
Murez, Z., Kolouri, S., Kriegman, D.J., Ramamoorthi, R., Kim, K.: Image to image translation for domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4500–4509 (2018)
Pan, S.J., Yang, Q.: A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 22(10), 1345–1359 (2010)
Peng, X., Usman, B., Kaushik, N., Hoffman, J., Wang, D., Saenko, K.: VisDA: the visual domain adaptation challenge. CoRR abs/1710.06924 (2017)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R.B., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 91–99 (2015)
Saenko, K., Kulis, B., Fritz, M., Darrell, T.: Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6314, pp. 213–226. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15561-1_16
Saito, K., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T.: Asymmetric tri-training for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 70, pp. 2988–2997 (2017)
Saito, K., Watanabe, K., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T.: Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3723–3732 (2018)
Saito, K., Yamamoto, S., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T.: Open set domain adaptation by backpropagation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11209, pp. 156–171. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01228-1_10
Sankaranarayanan, S., Balaji, Y., Castillo, C.D., Chellappa, R.: Generate to Adapt: aligning domains using generative adversarial networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8503–8512 (2018)
Shu, R., Bui, H.H., Narui, H., Ermon, S.: A DIRT-T approach to unsupervised domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2018)
Snell, J., Swersky, K., Zemel, R.S.: Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 4077–4087 (2017)
Sun, B., Saenko, K.: Deep CORAL: correlation alignment for deep domain adaptation. In: Hua, G., Jégou, H. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9915, pp. 443–450. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49409-8_35
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2962–2971 (2017)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Zhang, N., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Deep domain confusion: maximizing for domain invariance. CoRR abs/1412.3474 (2014)
Venkateswara, H., Eusebio, J., Chakraborty, S., Panchanathan, S.: Deep hashing network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5385–5394 (2017)
Wen, Y., Zhang, K., Li, Z., Qiao, Yu.: A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9911, pp. 499–515. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46478-7_31
**ao, W., Ding, Z., Liu, H.: Implicit semantic response alignment for partial domain adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2021)
**e, S., Zheng, Z., Chen, L., Chen, C.: Learning semantic representations for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 5419–5428 (2018)
Xu, R., Li, G., Yang, J., Lin, L.: Larger norm more transferable: an adaptive feature norm approach for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1426–1435 (2019)
Yang, J., Zou, H., Zhou, Y., Zeng, Z., **e, L.: Mind the Discriminability: Asymmetric adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 589–606 (2020)
Yang, S., Wang, Y., van de Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S.: Exploiting the intrinsic neighborhood structure for source-free domain adaptation. CoRR abs/2110.04202 (2021)
Yang, S., Wang, Y., van de Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S.: Generalized source-free domain adaptation. In: IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8978–8987 (2021)
Yosinski, J., Clune, J., Bengio, Y., Lipson, H.: How transferable are features in deep neural networks? In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3320–3328 (2014)
You, K., Long, M., Cao, Z., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Universal domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2720–2729 (2019)
Zellinger, W., Grubinger, T., Lughofer, E., Natschläger, T., Saminger-Platz, S.: Central moment discrepancy (CMD) for domain-invariant representation learning. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2017)
Zhang, J., Ding, Z., Li, W., Ogunbona, P.: Importance weighted adversarial nets for partial domain adaptation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8156–8164 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Deng, B., Li, S., Jia, K., Zhang, L.: Semi-supervised models are strong unsupervised domain adaptation learners. CoRR abs/2106.00417 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Liu, T., Long, M., Jordan, M.I.: Bridging theory and algorithm for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 97, pp. 7404–7413 (2019)
Zhu, J., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2242–2251 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partially by the NSFC (U21A2-0471, U1911401, U1811461), Guangdong NSF Project (No. 2020B1515120085, 2018B030312002), Guangzhou Research Project (201902010037), and the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangzhou (202007030004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lin, KY., Zhou, J., Qiu, Y., Zheng, WS. (2022). Adversarial Partial Domain Adaptation by Cycle Inconsistency. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13693. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19827-4_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19827-4_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19826-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19827-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)