Abstract
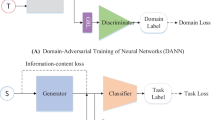
EEG-based affective computing aims to provide an objective method to evaluate people’s emotional states in human-computer interactions, but it suffers the dilemma of individual differences in EEG signals. The existing approaches usually extract domain-specific features, which ignore the commonness of subjects or treat all subjects as one source for transfer. This paper proposes a novel multi-source information-shared domain adaptation framework for cross-subject EEG emotion recognition. In the proposed framework, we assume that all EEG data share the same low-level features, the shared representations and private components are captured by the shared extractor and private extractors, respectively. Besides the maximum mean discrepancy and diff losses, we also propose the was-loss to align the private domains for the purpose of extracting tight shared domain and thus enhancing the domain adaptation ability of the network. Finally, we build the domain-specific classifiers and shared classifier in parallel and dynamically integrate their predictions by the similarity of marginal distributions among domains. The experimental results on the SEED and SEED-IV datasets demonstrate that our framework outperforms the state-of-the-art domain adaptation methods with accuracies of 88.1% and 73.8% on average.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, H., Rong, P., Sun, G.: Subject-independent emotion recognition based on entropy of EEG signals. In: the 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference, pp. 1513–1518. IEEE (2021)
Zheng, W.L., Zhu, J.Y.: Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from eeg. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 10, 417–429 (2017)
Zheng, W.L., Lu, B.L.: Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 7(3), 162–175 (2015)
Pfurtscheller, G., Müller-Putz, G.R., Scherer, R., Neuper, C.: Rehabilitation with brain-computer interface systems. Computer 41(10), 58–65 (2008)
Putnam, K.M., McSweeney, L.B.: Depressive symptoms and baseline prefrontal EEG alpha activity: a study utilizing ecological momentary assessment. Biol. Psychol. 77(2), 237–240 (2008)
Samek, W., Meinecke, F.C., Müller, K.R.: Transferring subspaces between subjects in brain-computer interfacing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(8), 2289–2298 (2013)
Sugiyama, M., Krauledat, M., Müller, K.R.: Covariate shift adaptation by importance weighted cross validation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 8(5) (2007)
Sanei, S., Chambers, J.A.: EEG Signal Processing. Wiley (2013)
Wang, J., Chen, Y.: Introduction to transfer learning. Publishing House of Electronics Industry (2021)
Blanchard, G., Lee, G., Scott, C.: Generalizing from several related classification tasks to a new unlabeled sample. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. vol. 24. Curran Associates, Inc. (2011)
Zhou, K., Liu, Z., Qiao, Y.: Domain generalization: a survey. CoRR (2021)
Wang, J., Lan, C., Liu, C., Ouyang, Y., Qin, T.: Generalizing to unseen domains: a survey on domain generalization. CoRR (2021)
Ghifary, M., Balduzzi, D., Kleijn, W.B., Zhang, M.: Scatter component analysis: a unified framework for domain adaptation and domain generalization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(7), 1414–1430 (2016)
Ma, B.-Q., Li, H., Zheng, W.-L., Lu, B.-L.: Reducing the subject variability of EEG signals with adversarial domain generalization. In: Gedeon, T., Wong, K.W., Lee, M. (eds.) ICONIP 2019. LNCS, vol. 11953, pp. 30–42. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36708-4_3
Zheng, W.L., Lu, B.L.: Personalizing EEG-based affective models with transfer learning. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 2732–2738 (2016)
Li, H., **, Y.-M., Zheng, W.-L., Lu, B.-L.: Cross-subject emotion recognition using deep adaptation networks. In: Cheng, L., Leung, A.C.S., Ozawa, S. (eds.) ICONIP 2018. LNCS, vol. 11305, pp. 403–413. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04221-9_36
Luo, Y., Zhang, S.-Y., Zheng, W.-L., Lu, B.-L.: WGAN domain adaptation for EEG-based emotion recognition. In: Cheng, L., Leung, A.C.S., Ozawa, S. (eds.) ICONIP 2018. LNCS, vol. 11305, pp. 275–286. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04221-9_25
Zhao, L.M., Yan, X., Lu, B.L.: Plug-and-play domain adaptation for cross-subject EEG-based emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 863–870 (2021)
Chen, H., Li, Z., **, M., Li, J.: MEERNet: multi-source EEG-based emotion recognition network for generalization across subjects and sessions. In: Annual International Conference of IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society. pp. 6094–6097 (2021)
Chen, H., **, M., Li, Z., Fan, C., Li, J., He, H.: MS-MDA: multisource marginal distribution adaptation for cross-subject and cross-session EEG emotion recognition. Frontiers in Neuroscience 15 (2021)
Borgwardt, K.M., Gretton, A., Rasch, M.J.: Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics 22(14), e49–e57 (2006)
Pan, S.J., Tsang, I.W., Kwok, J.T., Yang, Q.: Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 22(2), 199–210 (2011)
Arjovsky, M., Chintala, S., Bottou, L.: Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 214–223 (2017)
Liu, W., Qiu, J.L., Zheng, W.L., Lu, B.L.: Comparing recognition performance and robustness of multimodal deep learning models for multimodal emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Cognitive Dev. Syst. (2021)
Zheng, W.L., Liu, W., Lu, Y., Lu, B.L., Cichocki, A.: Emotionmeter: a multimodal framework for recognizing human emotions. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(3), 1110–1122 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gong, M., Zhong, W., Hu, J., Ye, L., Zhang, Q. (2022). Multi-source Information-Shared Domain Adaptation for EEG Emotion Recognition. In: Yu, S., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13535. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18910-4_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18910-4_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-18909-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-18910-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)