Abstract
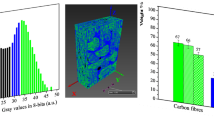
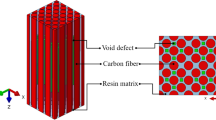
Void morphology affects the mechanical behavior of carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites since void shape results in different stress concentration levels. Concerning of the importance of higher porosity characterization, this study proposes an automated methodology to measure the void content, morphology, and size of CFRP composites using ImageJ software (image processing) without generating toxic residues (sustainable void measurement). The results show that the variations in the threshold level strongly influence void measurement such that inappropriate levels can underestimate or overestimate the void content, highlight incorrect pixels, and prevent the measurement of the hole pore size. The most appropriate threshold level for CFRP composites was selected as 40 to ensure appropriate void content and size measurements. The proposed technique to measure the void content was validated by comparative analysis with a standard method. This study presents a careful analysis of porosity measurement parameters to quantify the void content, morphology, and size, and provides an automated methodology to configure the ImageJ software.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donateo, T., Ficarella, A.: A modeling approach for the effect of battery aging on the performance of a hybrid electric rotorcraft for urban air-mobility. Aerospace (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/AEROSPACE7050056
Clarke, M., Smart, J., Botero, E., Maier, W., Alonso, J.J.: Strategies for posing a well-defined problem for urban air mobility vehicles. In: AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum, pp. 1–14 (2019)
Hamidi, Y.K., Aktas, L., Altan, M.C.: Effect of packing on void morphology in resin transfer molded E-glass/epoxy composites. Polym. Compos. 26, 614–627 (2005)
Monticeli, F.M., Almeida, J.H.S., Neves, R.M., Ornaghi, F.G., Ornaghi, H.L.: On the 3D void formation of hybrid carbon/glass fiber composite laminates: a statistical approach. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 137, 106036 (2020)
Zhu, B., Ma, J., Wang, J., Wu, J., Peng, D.: Thermal, dielectric and compressive properties of hollow glass microsphere filled epoxy-matrix composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 31, 1311–1326 (2012)
Alves, F.C., Monticeli, F.M., Neves, R.M., Voorwald, H.J.C., Cioffi, M.O.H., Ornaghi, H.L.: Influence of void content and morphology on the creep behavior on glass/epoxy composites. Compos. Commun. 25, 100712 (2021)
Hamidi, Y.K., Aktas, L., Altan, M.C.: Three-dimensional features of void morphology in resin transfer molded composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 1306–1320 (2005)
Garschke, C., Weimer, C., Parlevliet, P.P., Fox, B.L.: Out-of-autoclave cure cycle study of a resin film infusion process using in situ process monitoring. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 43, 935–944 (2012)
Meier, R., Kahraman, I., Seyhan, A.T., Zaremba, S., Drechsler, K.: Evaluating vibration assisted vacuum infusion processing of hexagonal boron nitride sheet modified carbon fabric/epoxy composites in terms of interlaminar shear strength and void content. Compos. Sci. Technol. 128, 94–103 (2016)
Giesche, H.: Mercury porosimetry: a general (practical) overview. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 23, 9–19 (2006)
Bodaghi, M., Cristóvão, C., Gomes, R., Correia, N.C.: Experimental characterization of voids in high fibre volume fraction composites processed by high injection pressure RTM. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 82, 88–99 (2016)
Cheon, J.H., Shin, E.S.: Assessment of the ablation characteristics of carbon/phenolic composites using X-ray microtomography. Compos. Sci. Technol. 182, 107740 (2019)
Joffre, T., Segerholm, K., Persson, C., Bardage, S.L., Hendriks, C.L.L., Isaksson, P.: Characterization of interfacial stress transfer ability in acetylation-treated wood fibre composites using X-ray microtomography 95, 43–49 (2017)
Mao, C., Feng, Y., Wang, X., Ren, G.: Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 45, 540–555 (2015)
Seraji, M., Ghafoorian, N., Bahramian, A.: Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of novolac/silica and C/SiO2/SiC aerogels using mercury porosimetry method. J. Non Cryst. Solids 435, 1–7 (2016)
Francesconi, L., Taylor, M., Baldi, A.: An investigation of stress concentration, crack nucleation, and fatigue life of thin low porosity metallic auxetic structures. Conf. Proc. Soc. Exp. Mech. Ser. 6, 65–71 (2019)
Boccaccini, A.R., Ondracek, G., Mombello, E.: Determination of stress concentration factors in porous materials. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 15(6), 534–536 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00275423
Saenz-Castillo, D., Martín, M.I., Calvo, S., Rodriguez-Lence, F., Güemes, A.: Effect of processing parameters and void content on mechanical properties and NDI of thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 121, 308–320 (2019)
He, Q., Wang, H., Fu, K., Ye, L.: 3D printed continuous CF/PA6 composites: effect of microscopic voids on mechanical performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 191, 108077 (2020)
Mehdikhani, M., Steensels, E., Standaert, A., Vallons, K.A.M., Gorbatikh, L., Lomov, S.V.: Multi-scale digital image correlation for detection and quantification of matrix cracks in carbon fiber composite laminates in the absence and presence of voids controlled by the cure cycle. Compos. Part B Eng. 154, 138–147 (2018)
Mehdikhani, M., Gorbatikh, L., Verpoest, I., Lomov, S.V.: Voids in fiber-reinforced polymer composites: a review on their formation, characteristics, and effects on mechanical performance. J. Compos. Mater. 53, 1579–1669 (2019)
Hell, S.W., Dyba, M., Jakobs, S.: Concepts for nanoscale resolution in fluorescence microscopy. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 599–609 (2004)
Di Landro, L., Montalto, A., Bettini, P., Guerra, S., Montagnoli, F., Rigamonti, M.: Detection of voids in carbon/epoxy laminates and their influence on mechanical properties. Polym. Polym. Compos. 25, 371–380 (2017)
Patel, N., Rohatgi, V., Lee, L.J.: Micro scale flow behavior and void formation mechanism during impregnation through a unidirectional stitched fiberglass mat. Polym. Eng. Sci. 35, 837–851 (1995)
Ruiz, E., Achim, V., Soukane, S., Trochu, F., Bréard, J.: Optimization of injection flow rate to minimize micro/macro-voids formation in resin transfer molded composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 475–486 (2006)
Ali, M.A., Umer, R., Khan, K.A., Cantwell, W.J.: In-plane virtual permeability characterization of 3D woven fabrics using a hybrid experimental and numerical approach. Compos. Sci. Technol. 173, 99–109 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the donation of epoxy resin by the Solvay group, Wrexham-UK, and the financial support from FAPESP (process numbers: 2021/05706-5 and 2017/10606-4) and CAPES (financial code 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Monticeli, F., Voorwald, H., Cioffi, M.O. (2023). Porosity Measurement in Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Through Optical Microscopy Using ImageJ Software. In: Altenbach, H., et al. Advances in Mechanical and Power Engineering . CAMPE 2021. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18487-1_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18487-1_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-18486-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-18487-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)