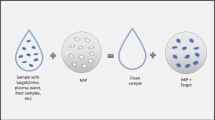
Abstract
The increasing concentration of environmental pollutants is an alarming issue all over the world. These pollutants not only affecting environmental conditions but also show harmful effects on human as well as animal health and therefore monitoring and analysis of the environmental pollutants are essential, for maintaining the quality of the environment and living beings. Fast, errorless, and inexpensive identification and quantification can functionally control the risks raised from environmental contaminants. Pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and heavy metals are some of the major pollutants found in the environment. There are many existing techniques based on chromatographic and spectrometric detection, however, molecular imprinting technology surpasses them and has emerged as an important sensing technique and is nowadays used widely for sensing applications. Molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs) combined with other detection techniques are used for selective detection of various pollutants in different sources. The MIPs possess numerous advantages over the classical natural biorecognition element/bioreceptor-based techniques as they are more physically and chemically stable, cheaper, highly selective, and sensitive. MIPs are often modified with nanomaterial for enhancing their performance, various nanomaterial modified MIPs have been reported for sensing application. The presented chapter will provide an insight into molecular imprinted polymers-based nanosensors and their application for the detection of various environmental pollutants.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghoutane Y, Diouf A, Österlund L, Bouchikhi B, El Bari N (2020) Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer electrochemical sensor and its application for sensitive detection and determination of malathion in olive fruits and oils. Bioelectrochemistry 132:107404
Çakır O, Baysal Z (2019) Pesticide analysis with molecularly imprinted nanofilms using surface plasmon resonance sensor and LC-MS/MS: comparative study for environmental water samples. Sens Actuators B Chem 297:126764
Chapman PM (2007) Determining when contamination is pollution—weight of evidence determinations for sediments and effluents. Environ Int 33:492–501
He S, Zhang L, Bai S, Yang H, Cui Z, Zhang X, Li Y (2020) Advances of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) and the application in drug delivery. Eur Polym J 110179
Li H, Wei X, Xu Y, Lu K, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Li C (2017) A thin shell and “sunny shape” molecular imprinted fluorescence sensor in selective detection of trace level pesticides in river. J Alloy Compd 705:524–532
Li S, Li J, Ma X, Pang C, Yin G, Luo J (2019) Molecularly imprinted electroluminescence switch sensor with a dual recognition effect for determination of ultra-trace levels of cobalt (II). Biosens Bioelectron 139:111321
Li H, Jia X, Jiang W, Zhou T, He J, Luan Y, Shang Y, Liu C, Che G (2020) Magnetically assisted imprinted sensor for selective detection antibiotics in river based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Opt Mater 108:110200
Lin XH, Aik SXL, Angkasa J, Le Q, Chooi KS, Li SFY (2018) Selective and sensitive sensors based on molecularly imprinted poly (vinylidene fluoride) for determination of pesticides and chemical threat agent simulants. Sens Actuators B Chem 258:228–237
Liu L, Long C, Wei S, Sun Y (2021) Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted film for high sensitivity detection of clenbuterol prepared using sol-gel method. Int J Electrochem Sci 16(4)
Ma Z, Wang Q, Gao N, Li H (2020) Electrochemical detection of clenbuterol with gold-nanoparticles-modified porous boron-doped diamond electrode. Microchem J 157:104911
Madkour LH (2020) Reactive oxygen species (ROS), nanoparticles, and endoplasmic reticulum (er) stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Academic Press, London, pp 131–157
Miao J, Liu A, Wu L, Yu M, Wei W, Liu S (2020) Magnetic ferroferric oxide and polydopamine molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposites based electrochemical impedance sensor for the selective separation and sensitive determination of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). Anal Chim Acta 1095:82–92
Munawar A, Tahir MA, Shaheen A, Lieberzeit PA, Khan WS, Bajwa SZ (2018) Investigating nanohybrid material based on 3D CNTs@ Cu nanoparticle composite and imprinted polymer for highly selective detection of chloramphenicol. J Hazard Mater 342:96–106
Parween T, Jan S (2019) Ecophysiology of pesticides: interface between pesticide chemistry and plant physiology. Academic Press, pp 223–263
Prasad BB, Fatma S (2016) Electrochemical sensing of ultra trace copper (II) by alga-OMNiIIP modified pencil graphite electrode. Sens Actuators B Chem 229:655–663
Prasad BB, Singh K (2016) An electroconducting copper (II) imprinted sensor using algae as cheap substitute of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim Acta 187:193–203
Prüss-Üstün A, Wolf J, Corvalán C, Bos R, Neira M (2016) Preventing disease through healthy environments: a global assessment of the burden of disease from environmental risks. World Health Organization
Qi P, Wang J, Wang X, Wang Z, Xu H, Di S, Wang Q, Wang X (2018) Sensitive and selective detection of the highly toxic pesticide carbofuran in vegetable samples by a molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor with signal enhancement by AuNPs. RSC Adv 8:25334–25341
Shahtaheri SJ, Faridbod F, Khadem M (2017) Highly selective voltammetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and carbon nanotubes to determine the dicloran pesticide in biological and environmental samples. Proc Technol 27:96–97
Shi X, Zuo Y, Jia X, Wu X, **g N, Wen B, Mi X (2020) A novel molecularly imprinted sensor based on gold nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide/single-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite for the detection of pefloxacin. Int J Electrochem Sci 15:9683–9697
Shirzadmehr A, Rezaei M, Bagheri H, Khoshsafar H (2016) Novel potentiometric sensor for the trace-level determination of Zn2+ based on a new nanographene/ion imprinted polymer composite. Int J Environ Anal Chem 96:929–944
Singhal A, Parihar A, Kumar N, Khan R (2022a) High throughput molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical nanosensors for point-of-care diagnostics of COVID-19. Mater Lett 306:130898
Singhal A, Sadique Mohd.A, Kumar N, Yadav S, Ranjan P, Parihar A, Khan R, Kaushik AK (2022b) Multifunctional carbon nanomaterials decorated molecularly imprinted hybrid polymers for efficient electrochemical antibiotics sensing. J Environ Chem Eng 107703
Sroysee W, Chunta S, Amatatongchai M, Lieberzeit PA (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymers to detect profenofos and carbofuran selectively with QCM sensors. Phys Med 7:100016
Tarannum N, Hendrickson OD, Khatoon S, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB (2020a) Molecularly imprinted polymers as receptors for assays of antibiotics. Crit Rev Anal Chem 50:291–310
Tarannum N, Khatoon S, Dzantiev BB (2020b) Perspective and application of molecular imprinting approach for antibiotic detection in food and environmental samples: a critical review. Food Control 107381
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In: Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology, pp 133–164
Tornero V, d’Alcalà MR (2014) Contamination by hazardous substances in the Gulf of Naples and nearby coastal areas: a review of sources, environmental levels and potential impacts in the MSFD perspective. Sci Total Environ 466:820–840
Turiel E, Esteban AM (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymers. In: Solid-phase extraction, Elsevier, pp 215–233
Wang H, Yao S, Liu Y, Wei S, Su J, Hu G (2017) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on Au nanoparticles in carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes for sensitive determination of olaquindox in food and feedstuffs. Biosens Bioelectron 87:417–421
Wang J, Hu J, Hu S, Gao G, Song Y (2020) A novel electrochemical sensor based on electropolymerized ion imprinted PoPD/ERGO composite for trace Cd (II) determination in water. Sensors 20:1004
Whitcombe MJ, Chianella I, Larcombe L, Piletsky SA, Noble J, Porter R, Horgan A (2011) The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem Soc Rev 40:1547–1571
Xu W, Vebrosky EN, Armbrust KL (2018) Potential risk to human skin cells from exposure to dicloran photodegradation products in water. Environ Int 121:861–870
Yang JC, Lee J, Hong SW, Park J (2020) Molecularly imprinted quartz crystal microbalance sensors with lithographically patterned frisbee-like pillar arrays for sensitive and selective detection of iprodione. Sens Actuators B Chem 320:128366
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to Dr. Avanish Kumar Srivastava, Director, CSIR-AMPRI for his support and encouragement in this work. Pushpesh Ranjan is thankful to CSIR, India for SRF. Mohd. Abubakar Sadique is thankful to DST-SERB for JRF. Neeraj Kumar is thankful to the UGC, India for the award of SRF. Raju Khan would like to acknowledge SERB for providing funds in the form of the IPA/2020/000130 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Singhal, A. et al. (2022). Molecularly Imprinted Polymers-Based Nanobiosensors for Environmental Monitoring and Analysis. In: Singh, R.P., Ukhurebor, K.E., Singh, J., Adetunji, C.O., Singh, K.R. (eds) Nanobiosensors for Environmental Monitoring. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16106-3_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16106-3_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16105-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16106-3
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)