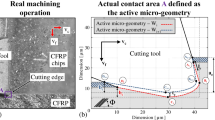
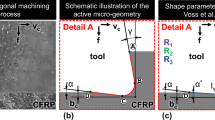
Abstract
A theoretical study of tool wear assessment during machining of reinforced polymer composite materials is presented. Based on the known experimental data on turning, drilling and milling of polymer composites, published in the open press, a theoretical model for assessing tool wear was proposed. This model is based on an analytical description in tool geometry change over time. One of the most effective, simple and accurate methods for determining tool wear is to weigh it before and after machining. The resulting absolute weight loss of the tool falls on the cutting edges, which in the process of contact interaction change their shape due to the material removal under conditions of force loading and thermal heating. When machining reinforced composites, the wear along the flank surface is taken as the main criterion for tool wear. This is due to the specifics of the composite material structure and the nature of the destruction in contact with the tool. Thus, having a reliable analytical apparatus that predicts the shape and nature in the shape of the tool cutting edges change and the value of the weight loss of these cutting edges, one can try to determine the distribution of the lost weight along the geometric tool shape and, most importantly, along the tool flank surface. In other words, the task is to link the tool weight loss during cutting with a change in the amount of wear along the tool flank surface. To implement this approach, a geometric model is proposed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lokesh, K.S., Pinto, T., Ramachandra, C.G.: Effect of tool wear and machinability studies on polymer composites; a review. Int. J. Eng. Inf. Syst. 1(5), 99–110 (2017). Hal-01571294f
Siddhpura, A., Paurobally, R.: A review of flank wear prediction methods for tool condition monitoring in a turning process. Int. J Adv. Manuf. Technol. 65, 371–393 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4177-1
Hrechuk, A., Bushlya, V., Saoubi, M.R., et al.: Experimental investigations into tool wear of drilling CFRP. Procedia Manuf. 25, 294–301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.06.086
Faraz, A., Biermann, D., Weinert, K.: Cutting edge rounding: an innovative tool wear criterion in drilling CFRP composite laminates. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf 49, 1185–1196 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2009.08.002
Seeholzer, L., Voss, R., Grossenbacher, F., et al.: Fundamental analysis of the cutting edge micro-geometry in orthogonal machining of the unidirectional Carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastics (CFRP). Procedia CIRP 7, 379–382 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.09.040
Seeholzer, L., Kneubühler, F., Grossenbacher, F., Wegener, K.: Tool wear and spring back analysis in orthogonal machining unidirectional CFRP with respect to tool geometry and fibre orientation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 115(9–10), 2905–2928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07222-z
Denkena, B., Lucas, A., Bassett, E.: Effects of the cutting edge microgeometry on tool wear and its thermomechanical load. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 60, 73–76 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.098
Ramireza, C., Poulachona, G., Rossia, F., et al.: Tool wear monitoring and hole surface quality during CFRP drilling. Procedia CIRP 13, 163–168 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.04.028
Xu, W., Zhang, L.: Tool wear and its effect on the surface integrity in the machining of fibre reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Struct. 188, 257–265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.01.018
Biermann, D., Baschin, A.: Influence of cutting edge geometry and cutting edge radius on the stability of micromilling processes. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 3, 375–380 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-009-0188-7
Rawat, S., Attia, H.: Wear mechanisms and tool life management of WC–Co drills during dry high speed drilling of woven carbon fibre composites. Wear 267, 1022–1030 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.01.031
Azmi, A.I., Lind, R.J.T., Bhattacharyya, D.: Fuzzy logic predictive model of tool wear in end milling glass fibre reinforced polymer composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 214, 329–333 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.214.329
Feito, N., Muñoz-Sánchez, A., Díaz-Álvarez, A., et al.: Analysis of the machinability of carbon fiber composite materials in function of tool wear and cutting parameters using the artificial neural network approach. Materials 12, 27–47 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172747
Voss, R., Henerichs, M., Capricano, G., et al.: Post-coating treatment of cutting edge for drilling carbon fibre reinforced plastics. Procedia CIRP 46, 161–164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.03.173
Nor Khairusshimaa, M.K., Sharifahb, I.S.S.: Study on tool wear during milling CFRP under dry and chilled air machining. Procedia Eng. 184, 506–517 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.04.121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Khavin, G., Zhiwen, H. (2023). Geometrical Model for Tool Wear Assessment in the Processing of Reinforced Composite. In: Cioboată, D.D. (eds) International Conference on Reliable Systems Engineering (ICoRSE) - 2022. ICoRSE 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 534. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15944-2_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15944-2_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-15943-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-15944-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)