Abstract
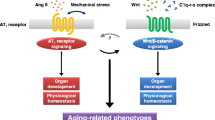
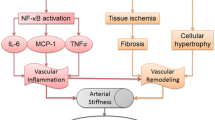
Age is an independent risk factor for develo** various diseases related to the cardiovascular system, kidney, nervous system, diabetes etc. Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) is the main regulator of normal physiology, body fluid homeostasis, normal organ development and cardiovascular functions. Blockage in the RAS system has been shown to induce longevity and to prevent the age-related reduction in the multiple organ functions. RAS has deleterious effects in the acceleration of age-related phenotypes through the over activation of Angiotensin-II receptor type 1 (ATR-1). This promotes excessive cellular growth, inflammation and oxidative damage which leads to ageing. Other pathway is anti-inflammatory and counter-regulatory, which involves Angiotensin-II receptor type 2/Angiotensin converting enzyme/Angiotensin 1-7/Mas receptor or ATR2/ACE2/Ang1-7/MasR axis. This chapter focuses on the mechanisms of involvement of RAS in age-related diseases and the therapeutic strategies from an interdisciplinary clinical perspective.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Morris BJ (2005) A forkhead in the road to longevity: the molecular basis of lifespan becomes clearer. J Hypertens 23(7):1285–1309
Oliverio MI, Kim HS, Ito M, Le T, Audoly L, Best CF et al (1998) Reduced growth, abnormal kidney structure, and type 2 (AT2) angiotensin receptor-mediated blood pressure regulation in mice lacking both AT1A and AT1B receptors for angiotensin II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(26):15496–15501
Gomez RA, Norwood VF (1995) Developmental consequences of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Kidney Dis 26(3):409–431
Conti S, Cassis P, Benigni A (2012) aging and the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 60(4):878–883
Stegbauer J, Coffman TM (2011) New insights into angiotensin receptor actions: from blood pressure to aging. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20(1):84–88
Oliverio MI, Coffman TM (2000) Angiotensin II receptor physiology using gene targeting. News Physiol Sci Int J Physiol Prod Jointly Int Union Physiol Sci Am Physiol Soc 15:171–175
Akazawa H, Yano M, Yabumoto C, Kudo-Sakamoto Y, Komuro I (2013) Angiotensin II Type 1 and Type 2 receptor-induced cell signaling. Curr Pharm Des 19(17):2988–2995
Lambert DW, Clarke NE, Turner AJ (2010) Not just angiotensinases: new roles for the angiotensin-converting enzymes. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 67(1):89–98
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and angiotensin 1–7: novel therapeutic targets | Nature Reviews Cardiology [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrcardio.2014.59
Saravi B, Li Z, Lang CN, Schmid B, Lang FK, Grad S et al (2021) The tissue renin-angiotensin system and its role in the pathogenesis of major human diseases: Quo Vadis? Cells 10(3):650
Ras Induces Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Senescence and Inflammation in Human Atherosclerosis | Circulation [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 9]. Available from: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000093274.82929.22
Min L-J, Mogi M, Iwai M, Horiuchi M (2009) Signaling mechanisms of angiotensin II in regulating vascular senescence. Ageing Res Rev 8(2):113–121
Folkow B (1982) Physiological aspects of primary hypertension. Physiol Rev 62(2):347–504
Julius S, Nesbitt SD, Egan BM, Weber MA, Michelson EL, Kaciroti N et al (2006) Feasibility of treating prehypertension with an angiotensin-receptor blocker. N Engl J Med 354(16):1685–1697
Linz W, Jessen T, Becker RH, Schölkens BA, Wiemer G (1997) Long-term ACE inhibition doubles lifespan of hypertensive rats. Circulation 96(9):3164–3172
Ferrario CM, Strawn WB (2006) Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and proinflammatory mediators in cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 98(1):121–128
Schmieder RE, Hilgers KF, Schlaich MP, Schmidt BMW (2007) Renin-angiotensin system and cardiovascular risk. Lancet Lond Engl. 369(9568):1208–1219
Kim S, Iwao H (2000) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated cardiovascular and renal diseases. Pharmacol Rev 52(1):11–34
Jugdutt BI, Balghith M (2001) Enhanced regional AT(2)-receptor and PKC(epsilon) expression during cardioprotection induced by AT(1)-receptor blockade after reperfused myocardial infarction. J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst JRAAS 2(2):134–40
Xu Y, Menon V, Jugdutt BI (2000) Cardioprotection after angiotensin II type 1 blockade involves angiotensin II type 2 receptor expression and activation of protein kinase C-epsilon in acutely reperfused myocardial infarction in the dog. Effect of UP269-6 and losartan on AT1 and AT2-receptor expression and IP3 receptor and PKCepsilon proteins. J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst JRAAS 1(2):184–95
Liu Y-H, Yang X-P, Shesely EG, Sankey SS, Carretero OA (2004) Role of angiotensin II type 2 receptors and kinins in the cardioprotective effect of angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists in rats with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 43(8):1473–1480
Drexler H (1994) Endothelial dysfunction in heart failure and potential for reversal by ACE inhibition. Br Heart J 72(Suppl 3):S11–S14
Liu YH, Yang XP, Sharov VG, Nass O, Sabbah HN, Peterson E, et al (1997) Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists in rats with heart failure. Role of kinins and angiotensin II type 2 receptors. J Clin Invest 99(8):1926–1935
Mielniczuk L, Stevenson LW (2005) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type I receptor blockers in the management of congestive heart failure patients: what have we learned from recent clinical trials? Curr Opin Cardiol 20(4):250–255
Yang H-C, Rossini M, Ma L-J, Zuo Y, Ma J, Fogo AB (2011) Cells derived from young bone marrow alleviate renal aging. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(11):2028–2036
Lu X, Li N, Shushakova N, Schmitt R, Menne J, Susnik N et al (2011) C57BL/6 and 129/SV mice: genetic difference to renal ischemia-reperfusion. J Nephrol 15(25):738–743
Remuzzi G, Bertani T (1998) Pathophysiology of progressive nephropathies. N Engl J Med 339(20):1448–1456
Remuzzi G, Perico N, Macia M, Ruggenenti P (2005) The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 99:S57-65
Cheng S-Y, Chou Y-H, Liao F-L, Lin C-C, Chang F-C, Liu C-H et al (2016) Losartan reduces ensuing chronic kidney disease and mortality after acute kidney injury. Sci Rep 6(1):34265
Change of telomere length in angiotensin ii-induced human glomerular mesangial cell senescence and the protective role of losartan [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 10]. Available from: https://www.spandidos-publications.com/mmr/4/2/255
Dinh QN, Drummond GR, Kemp-Harper BK, Diep H, Silva TMD, Kim HA et al (2017) Pressor response to angiotensin II is enhanced in aged mice and associated with inflammation, vasoconstriction and oxidative stress. Aging 9(6):1595–1605
Altered Renal Expression of Angiotensin II Receptors, Renin Receptor, and ACE-2 Precede the Development of Renal Fibrosis in Aging Rats—Abstract—American Journal of Nephrology 2010, vol 32, no 3. Karger Publishers [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 10]. Available from: https://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/318607
Gelosa P, Pignieri A, Fändriks L, de Gasparo M, Hallberg A, Banfi C et al (2009) Stimulation of AT2 receptor exerts beneficial effects in stroke-prone rats: focus on renal damage. J Hypertens 27(12):2444–2451
Phillips IM (1987) Functions of angiotensin in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol 49(1):413–433
Labandeira-Garcia JL, Rodríguez-Perez AI, Garrido-Gil P, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Lanciego JL, Guerra MJ (2017) Brain renin-angiotensin system and microglial polarization: implications for aging and neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 10];9. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00129
Min L-J, Mogi M, Shudou M, **g F, Tsukuda K, Ohshima K et al (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation with angiotensin ii type 1 receptor blockade is pivotal for the prevention of blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetic mice. Hypertension 59(5):1079–1088
Wang J, Ho L, Chen L, Zhao Z, Zhao W, Qian X et al (2007) Valsartan lowers brain beta-amyloid protein levels and improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 117(11):3393–3402
Semprun-Prieto LC, Sukhanov S, Yoshida T, Rezk BM, Gonzalez-Villalobos RA, Vaughn C et al (2011) Angiotensin II induced catabolic effect and muscle atrophy are redox dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 409(2):217–221
Larsson L, Degens H, Li M, Salviati L, Lee YI, Thompson W et al (2019) Sarcopenia: aging-related loss of muscle mass and function. Physiol Rev 99(1):427–511
Takeshita H, Yamamoto K, Nozato S, Takeda M, Fukada S, Inagaki T et al (2018) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 deficiency accelerates and angiotensin 1–7 restores age-related muscle weakness in mice. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 9(5):975–986
Gomes-Santos IL, Fernandes T, Couto GK, Ferreira-Filho JCA, Salemi VMC, Fernandes FB et al (2014) Effects of exercise training on circulating and skeletal muscle renin-angiotensin system in chronic heart failure rats. PLoS ONE 9(5):e98012
Carlsson PO, Berne C, Jansson L (1998) Angiotensin II and the endocrine pancreas: effects on islet blood flow and insulin secretion in rats. Diabetologia 41(2):127–133
Simões e Silva AC, Ferreira RN, Miranda AS (2017) The renin angiotensin system and diabetes. In: Kartha CC, Ramachandran S, Pillai RM (eds) Mechanisms of vascular defects in diabetes mellitus [Internet]. Springer International Publishing, Cham [cited 2022 Mar 10]. p 275–91. (Advances in Biochemistry in Health and Disease). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-60324-7_11
Shimizu H, Nakagami H, Osako MK, Hanayama R, Kunugiza Y, Kizawa T et al (2008) Angiotensin II accelerates osteoporosis by activating osteoclasts. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 22(7):2465–2475
Rejnmark L, Vestergaard P, Mosekilde L (2006) Treatment with beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium-channel blockers is associated with a reduced fracture risk: a nationwide case-control study. J Hypertens 24(3):581–589
Fujimoto Y, Sasaki T, Tsuchida A, Chayama K (2001) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in human pancreatic cancer and growth inhibition by angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist. FEBS Lett 495(3):197–200
Egami K, Murohara T, Shimada T, Sasaki K-I, Shintani S, Sugaya T et al (2003) Role of host angiotensin II type 1 receptor in tumor angiogenesis and growth. J Clin Invest 112(1):67–75
Matsuura-Hachiya Y, Arai KY, Ozeki R, Kikuta A, Nishiyama T (2013) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (enalapril maleate) accelerates recovery of mouse skin from UVB-induced wrinkles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 442(1):38–43
Hao S yun, Ren M, Yang C, Lin D zhu, Chen L hong, Zhu P, et al (2011) Activation of skin renin–angiotensin system in diabetic rats. Endocrine 39(3):242–50
A Novel Function of Angiotensin II in Skin Wound Healing—Journal of Biological Chemistry [Internet]. [cited 2022 Mar 11]. Available from: https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(19)74856-X/fulltext
Faghih M, Hosseini SM, Smith B, Mehdi AA, Lay F, Ahmed AK, et al (2015) Knockout of Angiotensin AT2 receptors accelerates healing but impairs quality. Aging 7(12):1185–1197
Garten A, Petzold S, Körner A, Imai S-I, Kiess W (2009) Nampt: linking NAD biology, metabolism and cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab TEM 20(3):130–138
Dali-Youcef N, Lagouge M, Froelich S, Koehl C, Schoonjans K, Auwerx J (2007) Sirtuins: the “magnificent seven”, function, metabolism and longevity. Ann Med 39(5):335–345
Bellizzi D, Rose G, Cavalcante P, Covello G, Dato S, Rango FD et al (2005) A novel VNTR enhancer within the SIRT3 gene, a human homologue of SIR2, is associated with survival at oldest ages. Genomics 85(2):258–263
Jacobs KM, Pennington JD, Bisht KS, Aykin-Burns N, Kim H-S, Mishra M, et al (2008) SIRT3 interacts with the daf-16 homolog FOXO3a in the Mitochondria, as well as increases FOXO3a Dependent Gene expression. Int J Biol Sci 291–299
Sinclair DA (2005) Toward a unified theory of caloric restriction and longevity regulation. Mech Ageing Dev 126(9):987–1002
Sundaresan NR, Samant SA, Pillai VB, Rajamohan SB, Gupta MP (2008) SIRT3 is a stress-responsive deacetylase in cardiomyocytes that protects cells from stress-mediated cell death by deacetylation of Ku70. Mol Cell Biol 28(20):6384–6401
Benigni A, Corna D, Zoja C, Sonzogni A, Latini R, Salio M et al (2009) Disruption of the Ang II type 1 receptor promotes longevity in mice. J Clin Invest 119(3):524–530
Basso N, Cini R, Pietrelli A, Ferder L, Terragno NA, Inserra F (2007) Protective effect of long-term angiotensin II inhibition. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293(3):H1351-1358
Ferder L, Inserra F, Romano L, Ercole L, Pszenny V (1993) Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on mitochondrial number in the aging mouse. Am J Physiol 265(1 Pt 1):C15-18
Sastre J, Pallardó FV, Viña J (2000) Mitochondrial oxidative stress plays a key role in aging and apoptosis. IUBMB Life 49(5):427–435
Herbert KE, Mistry Y, Hastings R, Poolman T, Niklason L, Williams B (2008) Angiotensin II-mediated oxidative DNA damage accelerates cellular senescence in cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells via telomere-dependent and independent pathways. Circ Res 102(2):201–208
Steckelings UM, Artuc M, Wollschläger T, Wiehstutz S, Henz BM (2001) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors as inducers of adverse cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol 81(5):321–325
Liao X, **ao J, Li S-H, **ao L-L, Cheng B, Fu X-B et al (2019) Critical role of the endogenous renin-angiotensin system in maintaining self-renewal and regeneration potential of epidermal stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA—Mol Basis Dis. 1865(10):2647–2656
Takeda H, Katagata Y, Hozumi Y, Kondo S (2004) Effects of angiotensin II receptor signaling during skin wound healing. Am J Pathol 165(5):1653–1662
Koh SL, Ager EI, Christophi C (2010) Liver regeneration and tumour stimulation: implications of the renin–angiotensin system. Liver Int 30(10):1414–1426
Nakano N, Moriguchi A, Morishita R, Kida I, Tomita N, Matsumoto K, et al (1997) Role of angiotensin II in the regulation of a novel vascular modulator, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), in experimental hypertensive rats. Hypertens Dallas Tex 1979 30(6):1448–1454
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R, Nakatani T et al (2001) Angiotensin-II type 1 receptor interaction is a major regulator for liver fibrosis development in rats. Hepatol Baltim Md 34(4 Pt 1):745–750
Ramalho F, Ramalho L, Castro e Silva O, Zucoloto S, Corrêa F (2002) Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on liver regeneration rats. Hepatogastroenterology 49:1347–1351
Cohn RD, van Erp C, Habashi JP, Soleimani AA, Klein EC, Lisi MT et al (2007) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade attenuates TGF-beta-induced failure of muscle regeneration in multiple myopathic states. Nat Med 13(2):204–210
Yoshida T, Galvez S, Tiwari S, Rezk BM, Semprun-Prieto L, Higashi Y et al (2013) Angiotensin II inhibits satellite cell proliferation and prevents skeletal muscle regeneration. J Biol Chem 288(33):23823–23832
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Rawal, N., Mittal, A., Khullar, M. (2023). Renin Angiotensin System in Aging and Regeneration. In: Dhalla, N.S., Bhullar, S.K., Shah, A.K. (eds) The Renin Angiotensin System in Cardiovascular Disease. Advances in Biochemistry in Health and Disease, vol 24. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14952-8_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14952-8_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-14951-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-14952-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)